Valerio Paolicelli
Learning Semantics for Visual Place Recognition through Multi-Scale Attention
Jan 25, 2022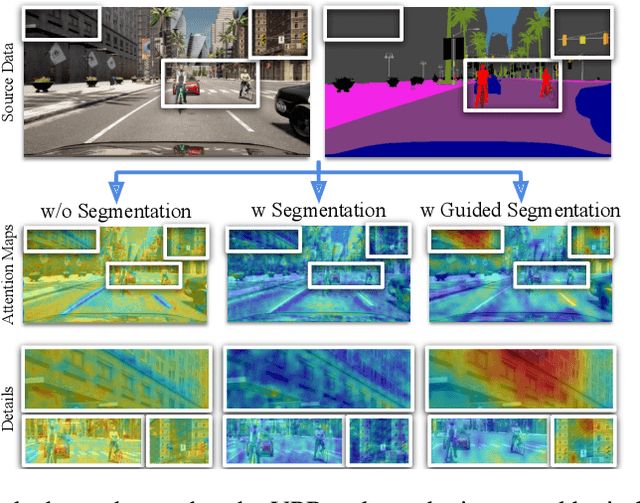
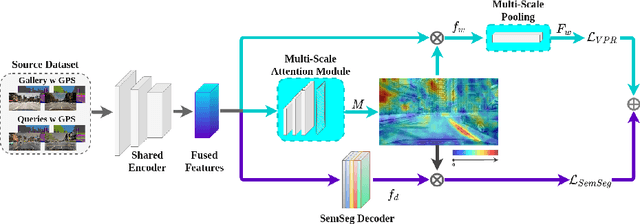
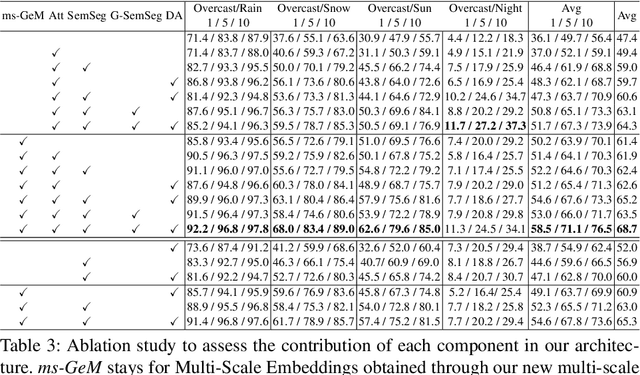
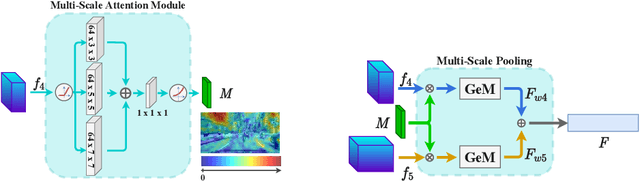
Abstract:In this paper we address the task of visual place recognition (VPR), where the goal is to retrieve the correct GPS coordinates of a given query image against a huge geotagged gallery. While recent works have shown that building descriptors incorporating semantic and appearance information is beneficial, current state-of-the-art methods opt for a top down definition of the significant semantic content. Here we present the first VPR algorithm that learns robust global embeddings from both visual appearance and semantic content of the data, with the segmentation process being dynamically guided by the recognition of places through a multi-scale attention module. Experiments on various scenarios validate this new approach and demonstrate its performance against state-of-the-art methods. Finally, we propose the first synthetic-world dataset suited for both place recognition and segmentation tasks.
Viewpoint Invariant Dense Matching for Visual Geolocalization
Sep 20, 2021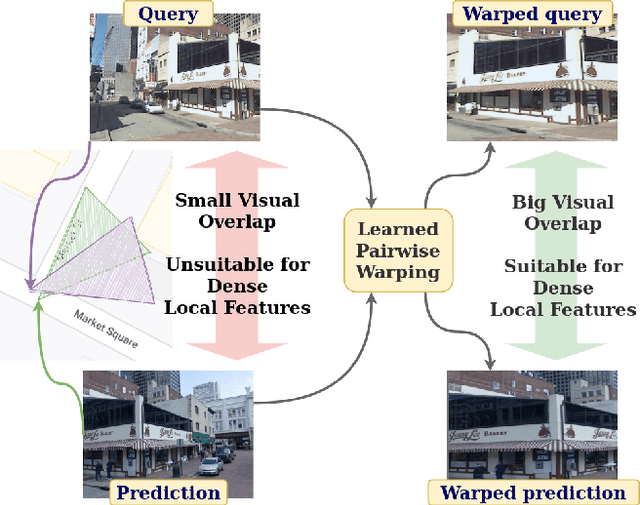
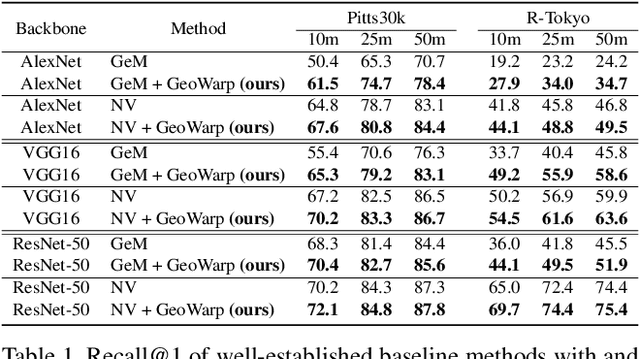
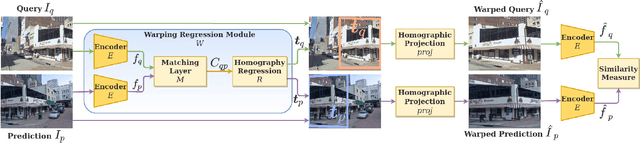
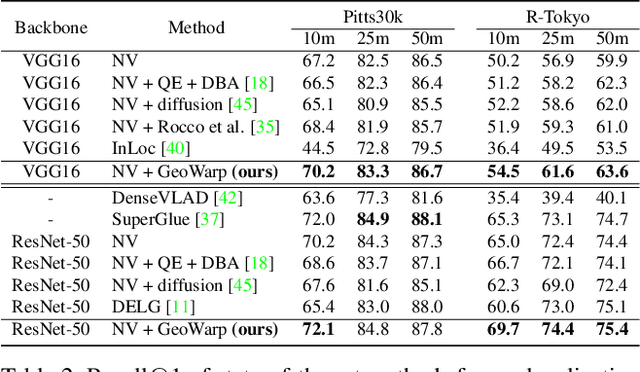
Abstract:In this paper we propose a novel method for image matching based on dense local features and tailored for visual geolocalization. Dense local features matching is robust against changes in illumination and occlusions, but not against viewpoint shifts which are a fundamental aspect of geolocalization. Our method, called GeoWarp, directly embeds invariance to viewpoint shifts in the process of extracting dense features. This is achieved via a trainable module which learns from the data an invariance that is meaningful for the task of recognizing places. We also devise a new self-supervised loss and two new weakly supervised losses to train this module using only unlabeled data and weak labels. GeoWarp is implemented efficiently as a re-ranking method that can be easily embedded into pre-existing visual geolocalization pipelines. Experimental validation on standard geolocalization benchmarks demonstrates that GeoWarp boosts the accuracy of state-of-the-art retrieval architectures. The code and trained models are available at https://github.com/gmberton/geo_warp
Adaptive-Attentive Geolocalization from few queries: a hybrid approach
Oct 14, 2020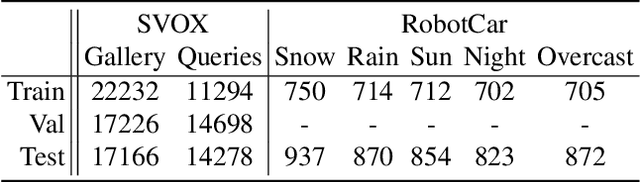
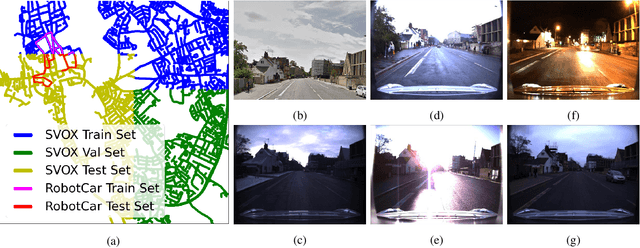
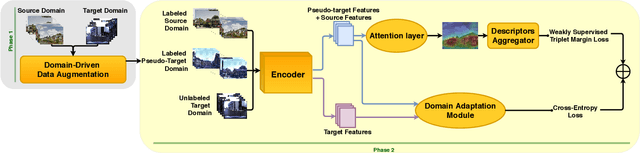
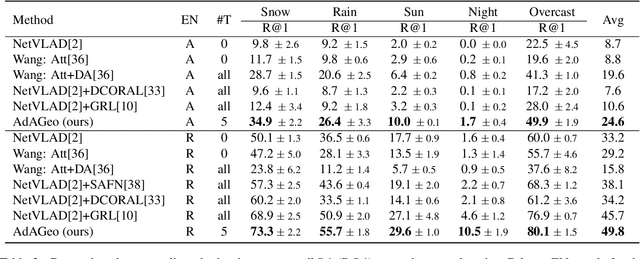
Abstract:We address the task of cross-domain visual place recognition, where the goal is to geolocalize a given query image against a labeled gallery, in the case where the query and the gallery belong to different visual domains. To achieve this, we focus on building a domain robust deep network by leveraging over an attention mechanism combined with few-shot unsupervised domain adaptation techniques, where we use a small number of unlabeled target domain images to learn about the target distribution. With our method, we are able to outperform the current state of the art while using two orders of magnitude less target domain images. Finally we propose a new large-scale dataset for cross-domain visual place recognition, called SVOX. Upon acceptance of the paper, code and dataset will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge