Valentina Tomassini
Rotation-Equivariant Deep Learning for Diffusion MRI
Feb 13, 2021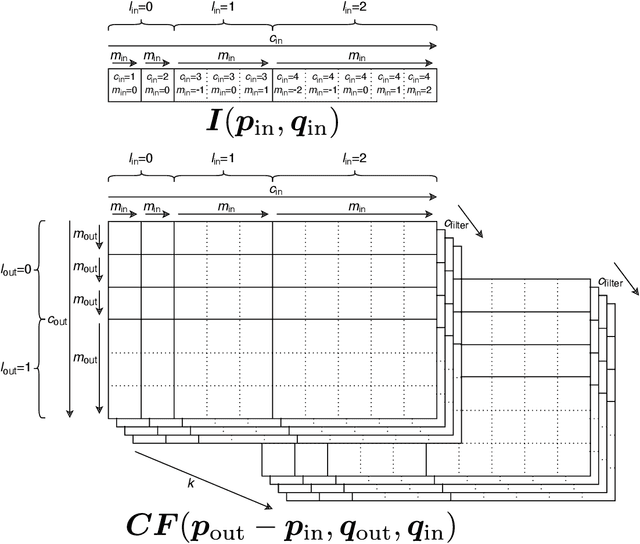
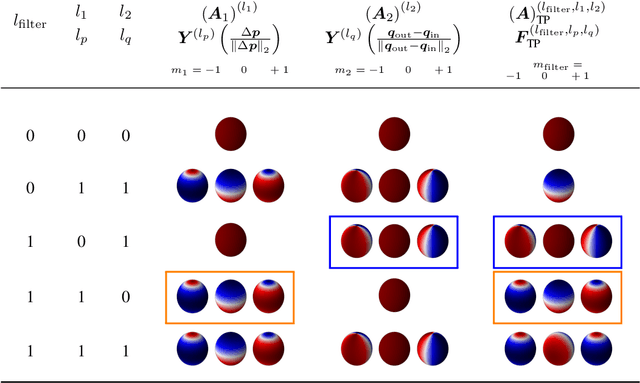
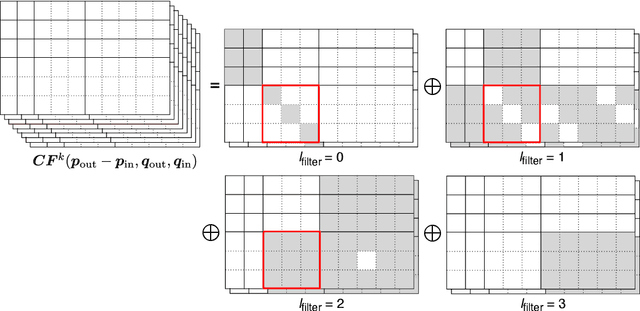
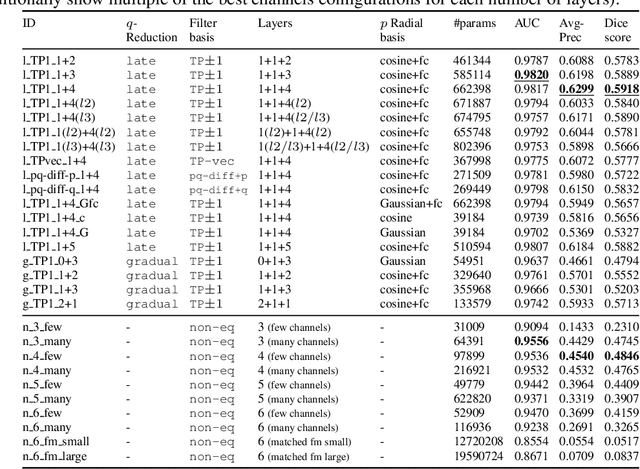
Abstract:Convolutional networks are successful, but they have recently been outperformed by new neural networks that are equivariant under rotations and translations. These new networks work better because they do not struggle with learning each possible orientation of each image feature separately. So far, they have been proposed for 2D and 3D data. Here we generalize them to 6D diffusion MRI data, ensuring joint equivariance under 3D roto-translations in image space and the matching 3D rotations in $q$-space, as dictated by the image formation. Such equivariant deep learning is appropriate for diffusion MRI, because microstructural and macrostructural features such as neural fibers can appear at many different orientations, and because even non-rotation-equivariant deep learning has so far been the best method for many diffusion MRI tasks. We validate our equivariant method on multiple-sclerosis lesion segmentation. Our proposed neural networks yield better results and require fewer scans for training compared to non-rotation-equivariant deep learning. They also inherit all the advantages of deep learning over classical diffusion MRI methods. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/philip-mueller/equivariant-deep-dmri and can be used off the shelf without understanding the mathematical background.
q-Space Novelty Detection with Variational Autoencoders
Oct 25, 2018


Abstract:In machine learning, novelty detection is the task of identifying novel unseen data. During training, only samples from the normal class are available. Test samples are classified as normal or abnormal by assignment of a novelty score. Here we propose novelty detection methods based on training variational autoencoders (VAEs) on normal data. Since abnormal samples are not used during training, we define novelty metrics based on the (partially complementary) assumptions that the VAE is less capable of reconstructing abnormal samples well; that abnormal samples more strongly violate the VAE regularizer; and that abnormal samples differ from normal samples not only in input-feature space, but also in the VAE latent space and VAE output. These approaches, combined with various possibilities of using (e.g. sampling) the probabilistic VAE to obtain scalar novelty scores, yield a large family of methods. We apply these methods to magnetic resonance imaging, namely to the detection of diffusion-space (q-space) abnormalities in diffusion MRI scans of multiple sclerosis patients, i.e. to detect multiple sclerosis lesions without using any lesion labels for training. Many of our methods outperform previously proposed q-space novelty detection methods. We also evaluate the proposed methods on the MNIST handwritten digits dataset and show that many of them are able to outperform the state of the art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge