Vaclav Cvicek
SPIRe: Boosting LLM Inference Throughput with Speculative Decoding
Apr 08, 2025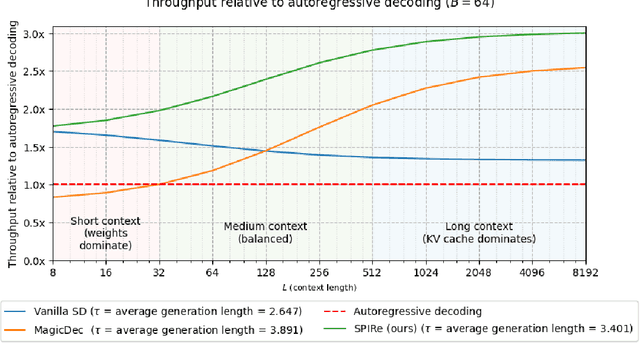
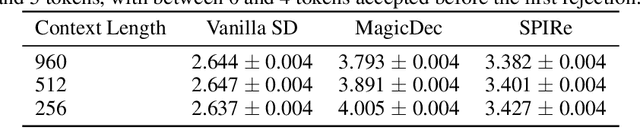
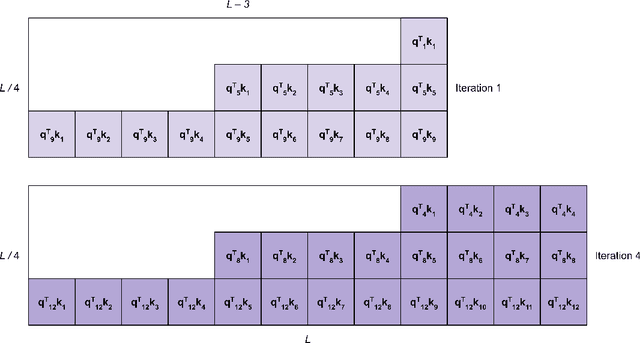
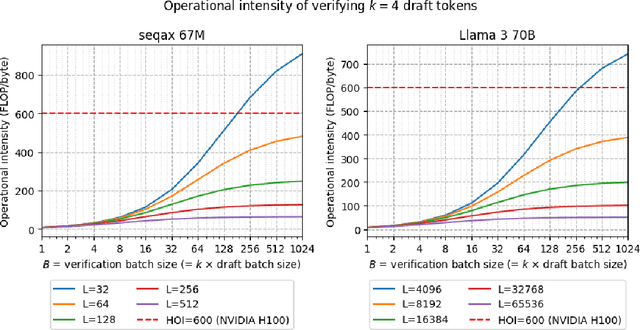
Abstract:Speculative decoding (SD) has been shown to reduce the latency of autoregressive decoding (AD) by 2-3x for small batch sizes. However, increasing throughput and therefore reducing the cost per token requires decoding with large batch sizes. Recent work shows that SD can accelerate decoding with large batch sizes too if the context is sufficiently long and the draft model's KV cache is sparse. We introduce SPIRe, a draft model that combines static sparse attention, pruned initialization, and feedback memory to increase the modeled throughput of speculative decoding by over 100% compared to speculation with a much smaller draft model and by over 35% compared to the strong baseline of sparse self-speculation. Our approach is particularly effective when context lengths vary significantly across requests.
LogicInference: A New Dataset for Teaching Logical Inference to seq2seq Models
Apr 11, 2022
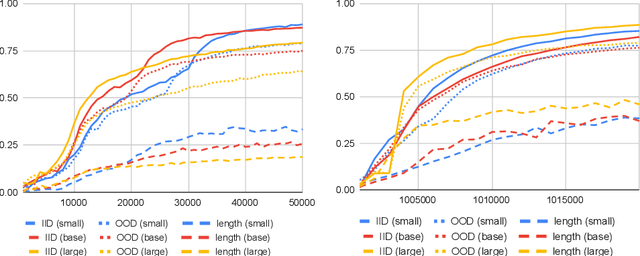
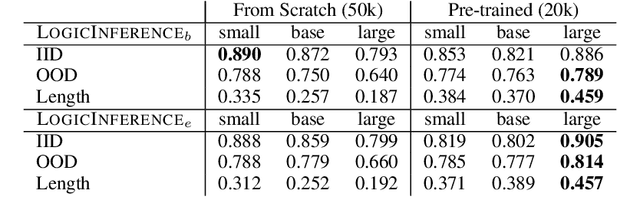
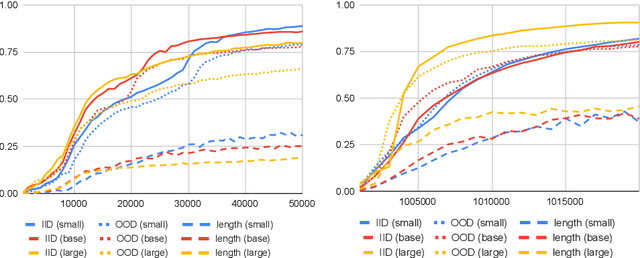
Abstract:Machine learning models such as Transformers or LSTMs struggle with tasks that are compositional in nature such as those involving reasoning/inference. Although many datasets exist to evaluate compositional generalization, when it comes to evaluating inference abilities, options are more limited. This paper presents LogicInference, a new dataset to evaluate the ability of models to perform logical inference. The dataset focuses on inference using propositional logic and a small subset of first-order logic, represented both in semi-formal logical notation, as well as in natural language. We also report initial results using a collection of machine learning models to establish an initial baseline in this dataset.
Making Transformers Solve Compositional Tasks
Aug 09, 2021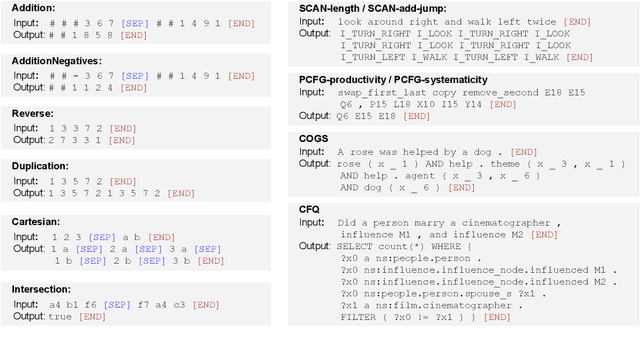
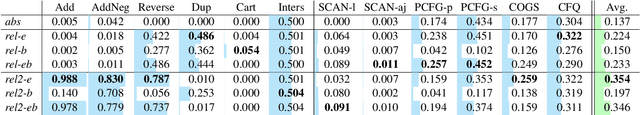
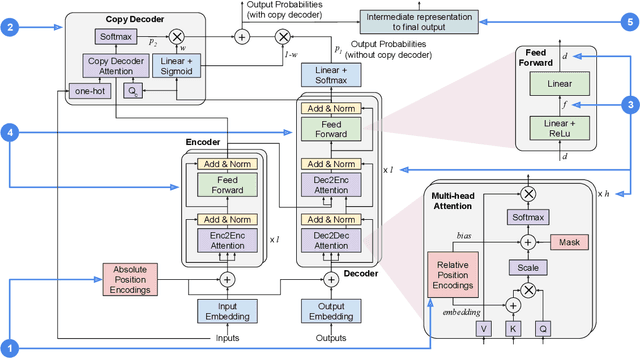
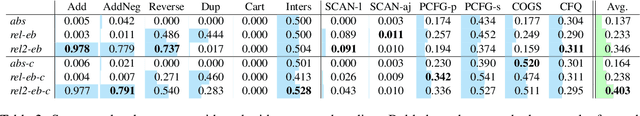
Abstract:Several studies have reported the inability of Transformer models to generalize compositionally, a key type of generalization in many NLP tasks such as semantic parsing. In this paper we explore the design space of Transformer models showing that the inductive biases given to the model by several design decisions significantly impact compositional generalization. Through this exploration, we identified Transformer configurations that generalize compositionally significantly better than previously reported in the literature in a diverse set of compositional tasks, and that achieve state-of-the-art results in a semantic parsing compositional generalization benchmark (COGS), and a string edit operation composition benchmark (PCFG).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge