Ursin Brunner
ZHAW Zurich University of Applied Sciences, Switzerland
INODE: Building an End-to-End Data Exploration System in Practice
Apr 09, 2021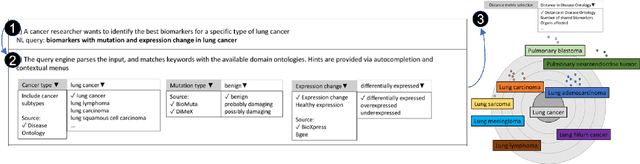
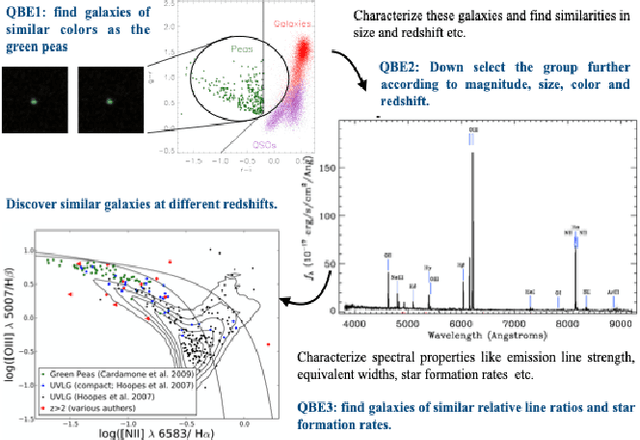
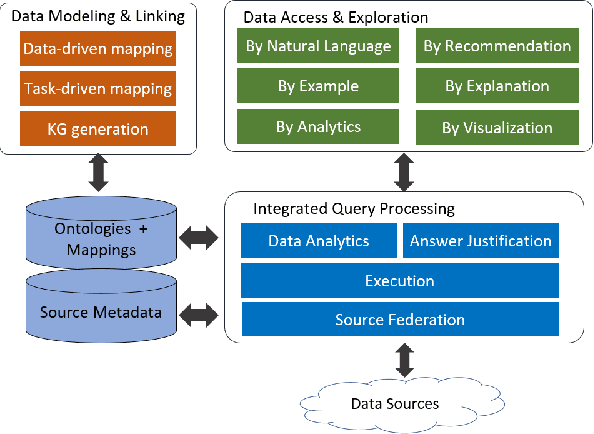
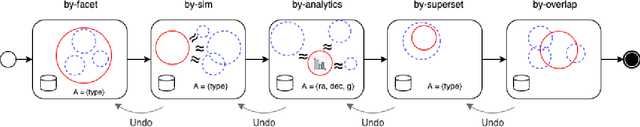
Abstract:A full-fledged data exploration system must combine different access modalities with a powerful concept of guiding the user in the exploration process, by being reactive and anticipative both for data discovery and for data linking. Such systems are a real opportunity for our community to cater to users with different domain and data science expertise. We introduce INODE -- an end-to-end data exploration system -- that leverages, on the one hand, Machine Learning and, on the other hand, semantics for the purpose of Data Management (DM). Our vision is to develop a classic unified, comprehensive platform that provides extensive access to open datasets, and we demonstrate it in three significant use cases in the fields of Cancer Biomarker Reearch, Research and Innovation Policy Making, and Astrophysics. INODE offers sustainable services in (a) data modeling and linking, (b) integrated query processing using natural language, (c) guidance, and (d) data exploration through visualization, thus facilitating the user in discovering new insights. We demonstrate that our system is uniquely accessible to a wide range of users from larger scientific communities to the public. Finally, we briefly illustrate how this work paves the way for new research opportunities in DM.
ValueNet: A Neural Text-to-SQL Architecture Incorporating Values
May 29, 2020



Abstract:Building natural language interfaces for databases has been a long-standing challenge for several decades. The major advantage of these so-called text-to-SQL systems is that end-users can query complex databases without the need to know SQL or the underlying database schema. Due to significant advancements in machine learning, the recent focus of research has been on neural networks to tackle this challenge on complex datasets like Spider. Several recent text-to-SQL systems achieve promising results on this dataset. However, none of them extracts and incorporates values from the user questions for generating SQL statements. Thus, the practical use of these systems in a real-world scenario has not been sufficiently demonstrated yet. In this paper we propose ValueNet light and ValueNet -- the first end-to-end text-to-SQL system incorporating values on the challenging Spider dataset. The main idea of our approach is to use not only metadata information about the underlying database but also information on the base data as input for our neural network architecture. In particular, we propose a novel architecture sketch to extract values from a user question and come up with possible value candidates which are not explicitly mentioned in the question. We then use a neural model based on an encoder-decoder architecture to synthesize the SQL query. Finally, we evaluate our model on the Spider challenge using the Execution Accuracy metric, a more difficult metric than used by most participants of the challenge. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates that ValueNet light and ValueNet reach state-of-the-art results of 64% and 60% accuracy, respectively, for translating from text to SQL, even when applying this more difficult metric than used by previous work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge