Tsung-Ting Kuo
A Collaborative Filtering-Based Two Stage Model with Item Dependency for Course Recommendation
Nov 01, 2023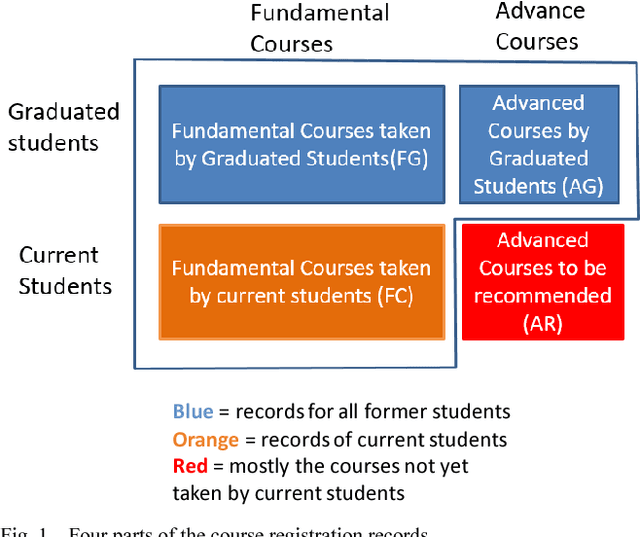
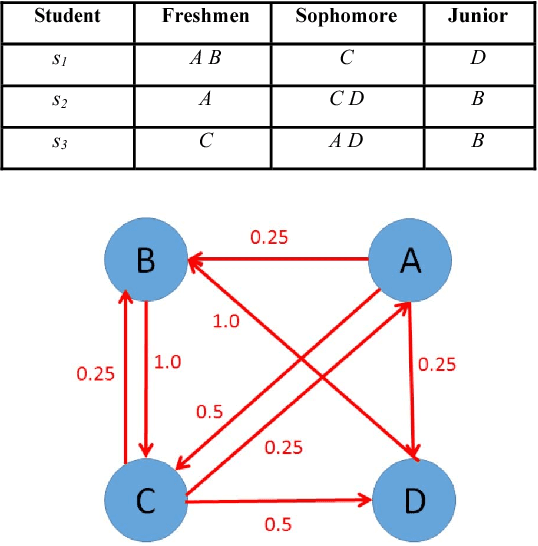
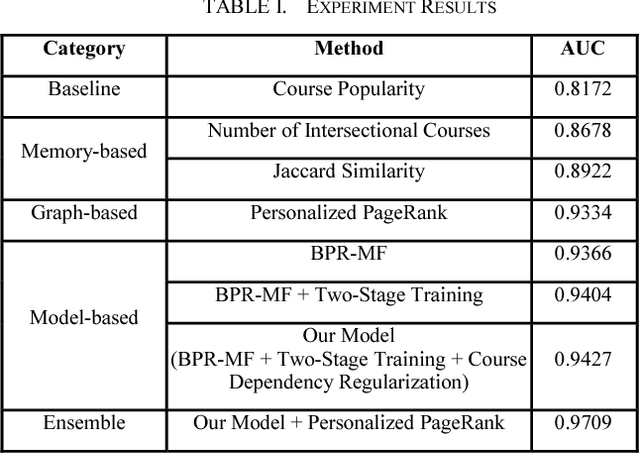
Abstract:Recommender systems have been studied for decades with numerous promising models been proposed. Among them, Collaborative Filtering (CF) models are arguably the most successful one due to its high accuracy in recommendation and elimination of privacy-concerned personal meta-data from training. This paper extends the usage of CF-based model to the task of course recommendation. We point out several challenges in applying the existing CF-models to build a course recommendation engine, including the lack of rating and meta-data, the imbalance of course registration distribution, and the demand of course dependency modeling. We then propose several ideas to address these challenges. Eventually, we combine a two-stage CF model regularized by course dependency with a graph-based recommender based on course-transition network, to achieve AUC as high as 0.97 with a real-world dataset.
* 8 pages, 2 figures, 2017 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA)
The Impact of Automatic Pre-annotation in Clinical Note Data Element Extraction - the CLEAN Tool
Aug 11, 2018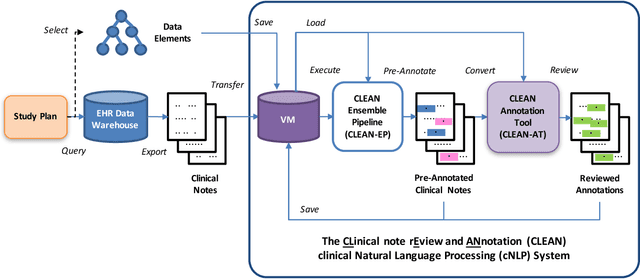
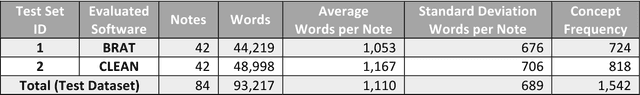
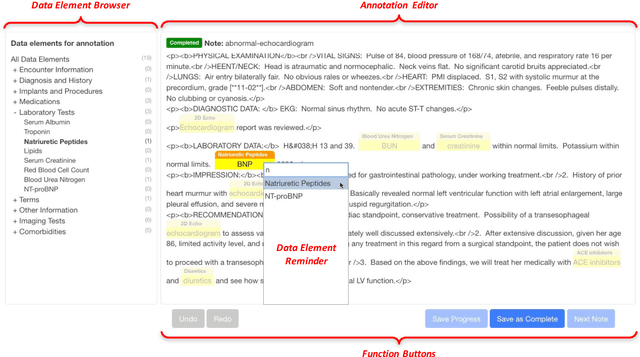
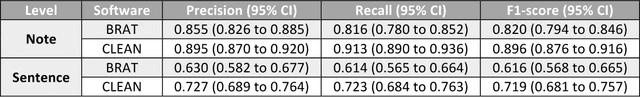
Abstract:Objective. Annotation is expensive but essential for clinical note review and clinical natural language processing (cNLP). However, the extent to which computer-generated pre-annotation is beneficial to human annotation is still an open question. Our study introduces CLEAN (CLinical note rEview and ANnotation), a pre-annotation-based cNLP annotation system to improve clinical note annotation of data elements, and comprehensively compares CLEAN with the widely-used annotation system Brat Rapid Annotation Tool (BRAT). Materials and Methods. CLEAN includes an ensemble pipeline (CLEAN-EP) with a newly developed annotation tool (CLEAN-AT). A domain expert and a novice user/annotator participated in a comparative usability test by tagging 87 data elements related to Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) and Kawasaki Disease (KD) cohorts in 84 public notes. Results. CLEAN achieved higher note-level F1-score (0.896) over BRAT (0.820), with significant difference in correctness (P-value < 0.001), and the mostly related factor being system/software (P-value < 0.001). No significant difference (P-value 0.188) in annotation time was observed between CLEAN (7.262 minutes/note) and BRAT (8.286 minutes/note). The difference was mostly associated with note length (P-value < 0.001) and system/software (P-value 0.013). The expert reported CLEAN to be useful/satisfactory, while the novice reported slight improvements. Discussion. CLEAN improves the correctness of annotation and increases usefulness/satisfaction with the same level of efficiency. Limitations include untested impact of pre-annotation correctness rate, small sample size, small user size, and restrictedly validated gold standard. Conclusion. CLEAN with pre-annotation can be beneficial for an expert to deal with complex annotation tasks involving numerous and diverse target data elements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge