Toshiaki Nakazawa
ChatGPT as a Translation Engine: A Case Study on Japanese-English
Oct 09, 2025



Abstract:This study investigates ChatGPT for Japanese-English translation, exploring simple and enhanced prompts and comparing against commercially available translation engines. Performing both automatic and MQM-based human evaluations, we found that document-level translation outperforms sentence-level translation for ChatGPT. On the other hand, we were not able to determine if enhanced prompts performed better than simple prompts in our experiments. We also discovered that ChatGPT-3.5 was preferred by automatic evaluation, but a tradeoff exists between accuracy (ChatGPT-3.5) and fluency (ChatGPT-4). Lastly, ChatGPT yields competitive results against two widely-known translation systems.
Revisiting Context Choices for Context-aware Machine Translation
Sep 07, 2021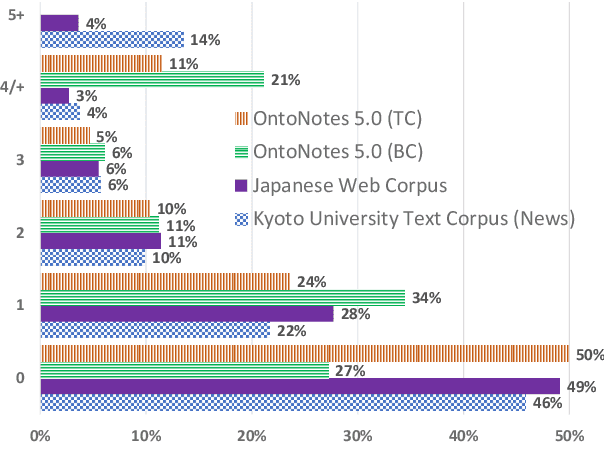
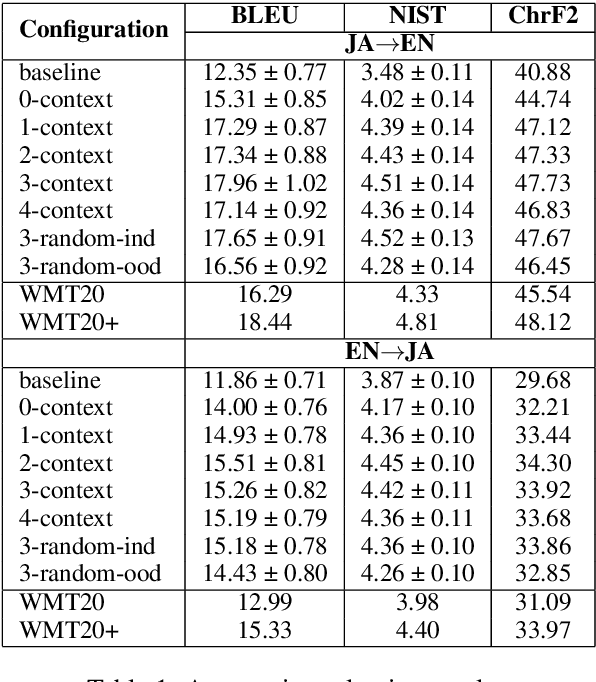

Abstract:One of the most popular methods for context-aware machine translation (MT) is to use separate encoders for the source sentence and context as multiple sources for one target sentence. Recent work has cast doubt on whether these models actually learn useful signals from the context or are improvements in automatic evaluation metrics just a side-effect. We show that multi-source transformer models improve MT over standard transformer-base models even with empty lines provided as context, but the translation quality improves significantly (1.51 - 2.65 BLEU) when a sufficient amount of correct context is provided. We also show that even though randomly shuffling in-domain context can also improve over baselines, the correct context further improves translation quality and random out-of-domain context further degrades it.
Modeling Target-side Inflection in Placeholder Translation
Jul 01, 2021
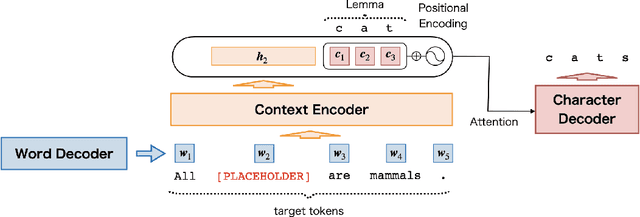

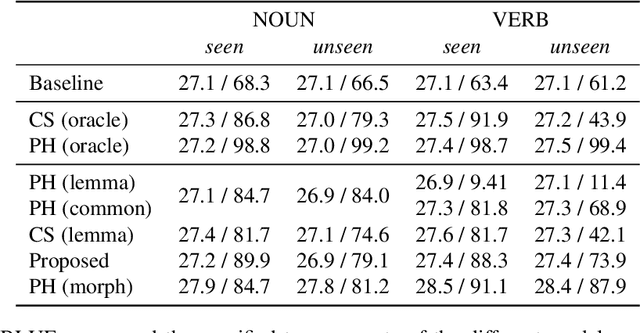
Abstract:Placeholder translation systems enable the users to specify how a specific phrase is translated in the output sentence. The system is trained to output special placeholder tokens, and the user-specified term is injected into the output through the context-free replacement of the placeholder token. However, this approach could result in ungrammatical sentences because it is often the case that the specified term needs to be inflected according to the context of the output, which is unknown before the translation. To address this problem, we propose a novel method of placeholder translation that can inflect specified terms according to the grammatical construction of the output sentence. We extend the sequence-to-sequence architecture with a character-level decoder that takes the lemma of a user-specified term and the words generated from the word-level decoder to output the correct inflected form of the lemma. We evaluate our approach with a Japanese-to-English translation task in the scientific writing domain, and show that our model can incorporate specified terms in the correct form more successfully than other comparable models.
Zero-pronoun Data Augmentation for Japanese-to-English Translation
Jul 01, 2021



Abstract:For Japanese-to-English translation, zero pronouns in Japanese pose a challenge, since the model needs to infer and produce the corresponding pronoun in the target side of the English sentence. However, although fully resolving zero pronouns often needs discourse context, in some cases, the local context within a sentence gives clues to the inference of the zero pronoun. In this study, we propose a data augmentation method that provides additional training signals for the translation model to learn correlations between local context and zero pronouns. We show that the proposed method significantly improves the accuracy of zero pronoun translation with machine translation experiments in the conversational domain.
Document-aligned Japanese-English Conversation Parallel Corpus
Dec 11, 2020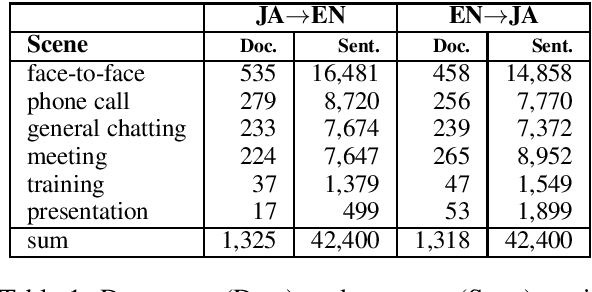
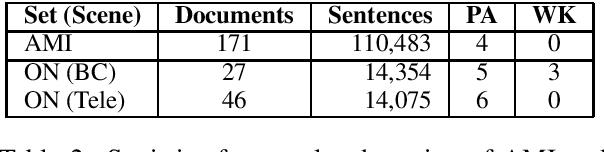

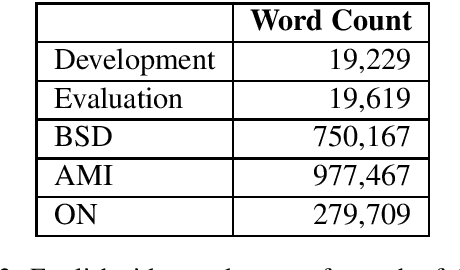
Abstract:Sentence-level (SL) machine translation (MT) has reached acceptable quality for many high-resourced languages, but not document-level (DL) MT, which is difficult to 1) train with little amount of DL data; and 2) evaluate, as the main methods and data sets focus on SL evaluation. To address the first issue, we present a document-aligned Japanese-English conversation corpus, including balanced, high-quality business conversation data for tuning and testing. As for the second issue, we manually identify the main areas where SL MT fails to produce adequate translations in lack of context. We then create an evaluation set where these phenomena are annotated to alleviate automatic evaluation of DL systems. We train MT models using our corpus to demonstrate how using context leads to improvements.
* Published in proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation, 2020
Designing the Business Conversation Corpus
Aug 05, 2020
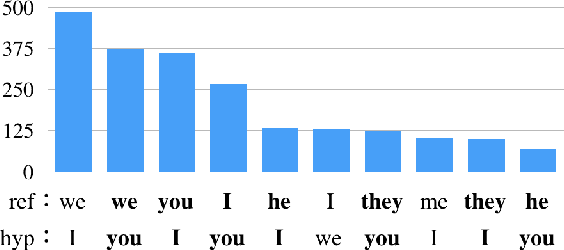
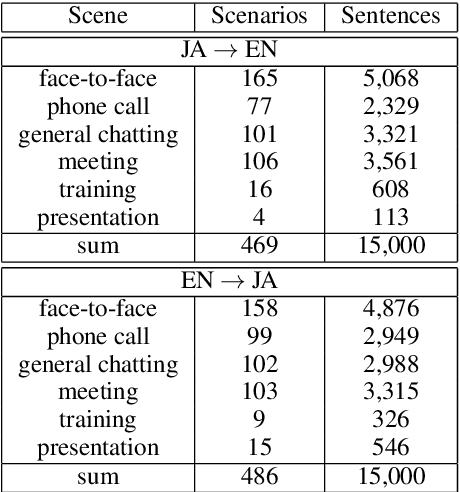
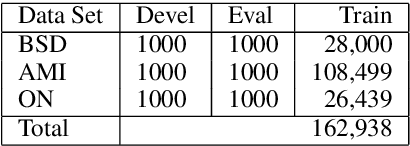
Abstract:While the progress of machine translation of written text has come far in the past several years thanks to the increasing availability of parallel corpora and corpora-based training technologies, automatic translation of spoken text and dialogues remains challenging even for modern systems. In this paper, we aim to boost the machine translation quality of conversational texts by introducing a newly constructed Japanese-English business conversation parallel corpus. A detailed analysis of the corpus is provided along with challenging examples for automatic translation. We also experiment with adding the corpus in a machine translation training scenario and show how the resulting system benefits from its use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge