Tony Mak
LLMs cannot find reasoning errors, but can correct them!
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:While self-correction has shown promise in improving LLM outputs in terms of style and quality (e.g. Chen et al., 2023; Madaan et al., 2023), recent attempts to self-correct logical or reasoning errors often cause correct answers to become incorrect, resulting in worse performances overall (Huang et al., 2023). In this paper, we break down the self-correction process into two core components: mistake finding and output correction. For mistake finding, we release BIG-Bench Mistake, a dataset of logical mistakes in Chain-of-Thought reasoning traces. We provide benchmark numbers for several state-of-the-art LLMs, and demonstrate that LLMs generally struggle with finding logical mistakes. For output correction, we propose a backtracking method which provides large improvements when given information on mistake location. We construe backtracking as a lightweight alternative to reinforcement learning methods, and show that it remains effective with a reward model at 60-70% accuracy.
Predicting Text Readability from Scrolling Interactions
May 13, 2021
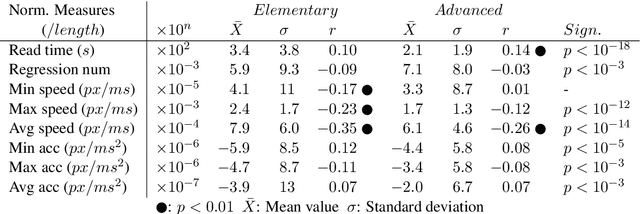


Abstract:Judging the readability of text has many important applications, for instance when performing text simplification or when sourcing reading material for language learners. In this paper, we present a 518 participant study which investigates how scrolling behaviour relates to the readability of a text. We make our dataset publicly available and show that (1) there are statistically significant differences in the way readers interact with text depending on the text level, (2) such measures can be used to predict the readability of text, and (3) the background of a reader impacts their reading interactions and the factors contributing to text difficulty.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge