Tobias Thommes
Kirchhoff-Institute for Physics, Heidelberg, Germany
Demonstrating BrainScaleS-2 Inter-Chip Pulse-Communication using EXTOLL
Mar 03, 2022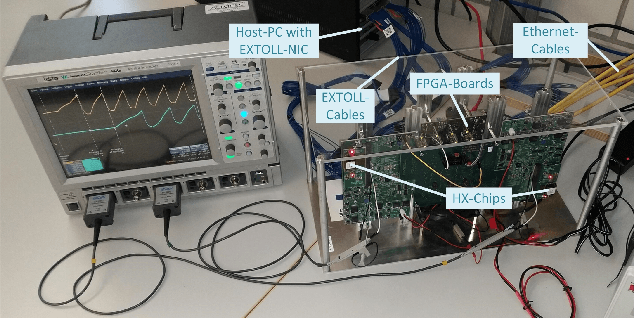
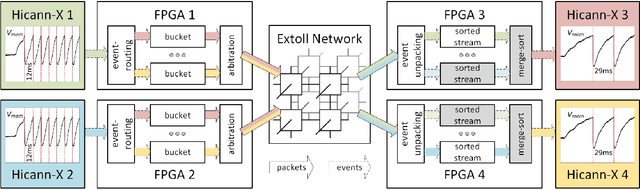
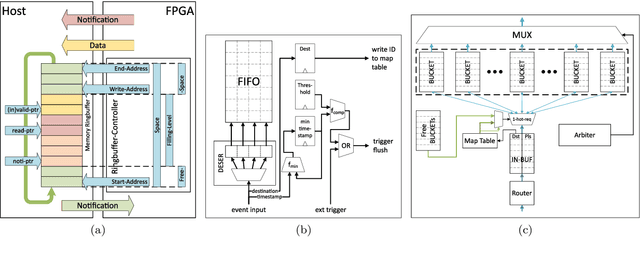
Abstract:The BrainScaleS-2 (BSS-2) Neuromorphic Computing System currently consists of multiple single-chip setups, which are connected to a compute cluster via Gigabit-Ethernet network technology. This is convenient for small experiments, where the neural networks fit into a single chip. When modeling networks of larger size, neurons have to be connected across chip boundaries. We implement these connections for BSS-2 using the EXTOLL networking technology. This provides high bandwidths and low latencies, as well as high message rates. Here, we describe the targeted pulse-routing implementation and required extensions to the BSS-2 software stack. We as well demonstrate feed-forward pulse-routing on BSS-2 using a scaled-down version without temporal merging.
BrainScaleS Large Scale Spike Communication using Extoll
Dec 14, 2021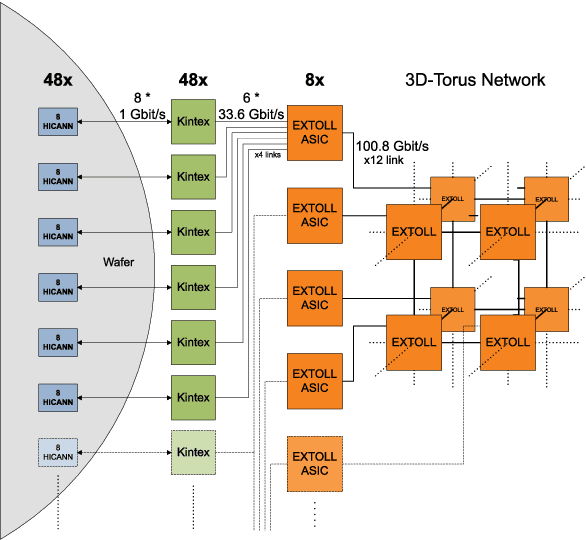
Abstract:The BrainScaleS Neuromorphic Computing System is currently connected to a compute cluster via Gigabit-Ethernet network technology. This is convenient for the currently used experiment mode, where neuronal networks cover at most one wafer module. When modelling networks of larger size, as for example a full sized cortical microcircuit model, one has to think about connecting neurons across wafer modules to larger networks. This can be done, using the Extoll networking technology, which provides high bandwidth and low latencies, as well as a low overhead packet protocol format.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge