Tobias Scheck
Human Pose Estimation in Monocular Omnidirectional Top-View Images
Apr 17, 2023Abstract:Human pose estimation (HPE) with convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for indoor monitoring is one of the major challenges in computer vision. In contrast to HPE in perspective views, an indoor monitoring system can consist of an omnidirectional camera with a field of view of 180{\deg} to detect the pose of a person with only one sensor per room. To recognize human pose, the detection of keypoints is an essential upstream step. In our work we propose a new dataset for training and evaluation of CNNs for the task of keypoint detection in omnidirectional images. The training dataset, THEODORE+, consists of 50,000 images and is created by a 3D rendering engine, where humans are randomly walking through an indoor environment. In a dynamically created 3D scene, persons move randomly with simultaneously moving omnidirectional camera to generate synthetic RGB images and 2D and 3D ground truth. For evaluation purposes, the real-world PoseFES dataset with two scenarios and 701 frames with up to eight persons per scene was captured and annotated. We propose four training paradigms to finetune or re-train two top-down models in MMPose and two bottom-up models in CenterNet on THEODORE+. Beside a qualitative evaluation we report quantitative results. Compared to a COCO pretrained baseline, we achieve significant improvements especially for top-view scenes on the PoseFES dataset. Our datasets can be found at https://www.tu-chemnitz.de/etit/dst/forschung/comp_vision/datasets/index.php.en.
Unsupervised Domain Adaptation from Synthetic to Real Images for Anchorless Object Detection
Dec 15, 2020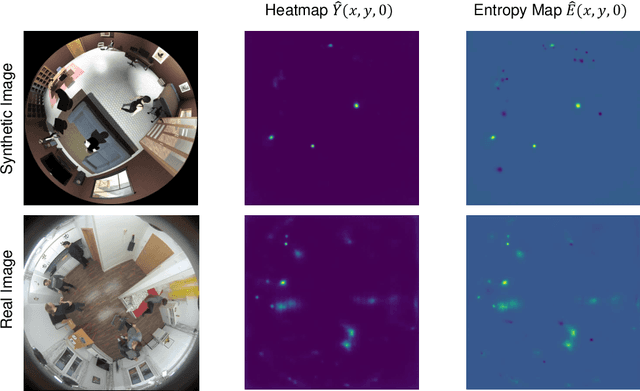

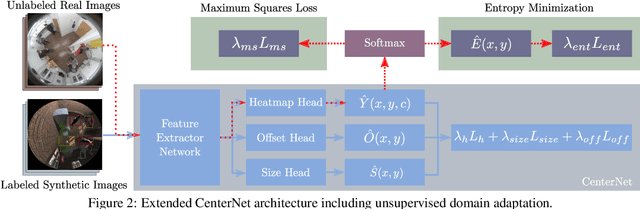

Abstract:Synthetic images are one of the most promising solutions to avoid high costs associated with generating annotated datasets to train supervised convolutional neural networks (CNN). However, to allow networks to generalize knowledge from synthetic to real images, domain adaptation methods are necessary. This paper implements unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) methods on an anchorless object detector. Given their good performance, anchorless detectors are increasingly attracting attention in the field of object detection. While their results are comparable to the well-established anchor-based methods, anchorless detectors are considerably faster. In our work, we use CenterNet, one of the most recent anchorless architectures, for a domain adaptation problem involving synthetic images. Taking advantage of the architecture of anchorless detectors, we propose to adjust two UDA methods, viz., entropy minimization and maximum squares loss, originally developed for segmentation, to object detection. Our results show that the proposed UDA methods can increase the mAPfrom61 %to69 %with respect to direct transfer on the considered anchorless detector. The code is available: https://github.com/scheckmedia/centernet-uda.
Where to drive: free space detection with one fisheye camera
Nov 11, 2020Abstract:The development in the field of autonomous driving goes hand in hand with ever new developments in the field of image processing and machine learning methods. In order to fully exploit the advantages of deep learning, it is necessary to have sufficient labeled training data available. This is especially not the case for omnidirectional fisheye cameras. As a solution, we propose in this paper to use synthetic training data based on Unity3D. A five-pass algorithm is used to create a virtual fisheye camera. This synthetic training data is evaluated for the application of free space detection for different deep learning network architectures. The results indicate that synthetic fisheye images can be used in deep learning context.
* Accepted at International Conference on Machine Vision 2019 (ICMV 2019)
A CNN-based Feature Space for Semi-supervised Incremental Learning in Assisted Living Applications
Nov 11, 2020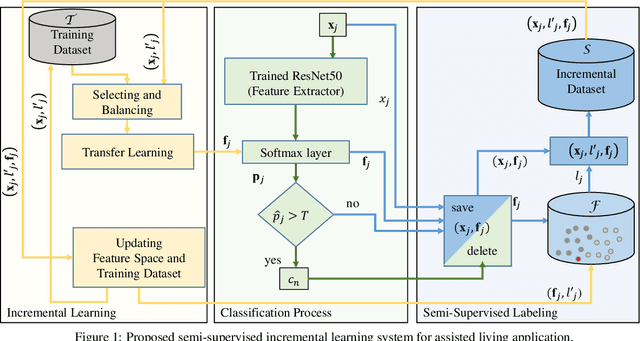
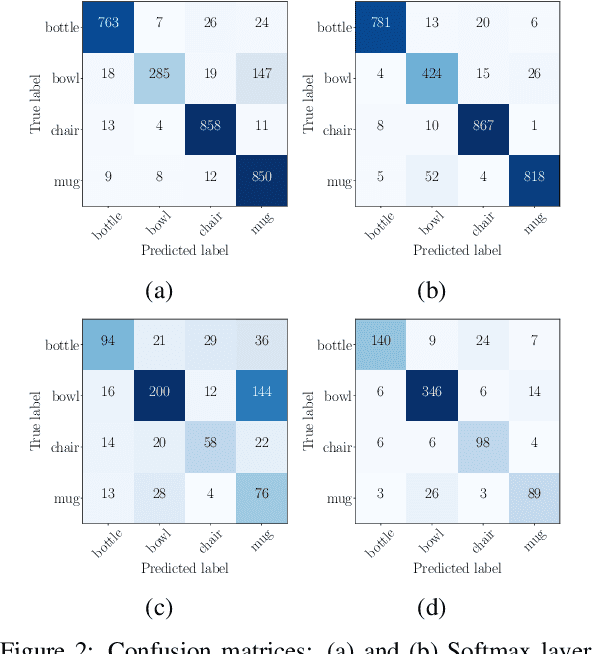

Abstract:A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is sometimes confronted with objects of changing appearance ( new instances) that exceed its generalization capability. This requires the CNN to incorporate new knowledge, i.e., to learn incrementally. In this paper, we are concerned with this problem in the context of assisted living. We propose using the feature space that results from the training dataset to automatically label problematic images that could not be properly recognized by the CNN. The idea is to exploit the extra information in the feature space for a semi-supervised labeling and to employ problematic images to improve the CNN's classification model. Among other benefits, the resulting semi-supervised incremental learning process allows improving the classification accuracy of new instances by 40% as illustrated by extensive experiments.
Learning from THEODORE: A Synthetic Omnidirectional Top-View Indoor Dataset for Deep Transfer Learning
Nov 11, 2020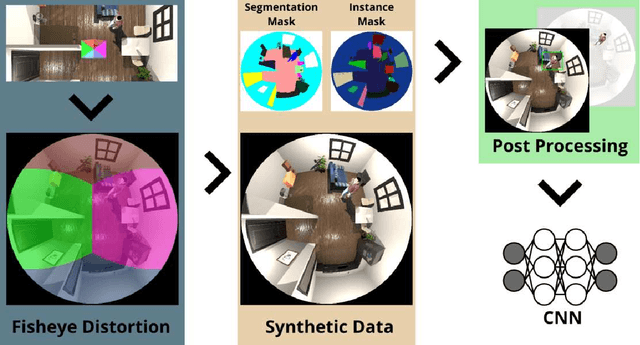
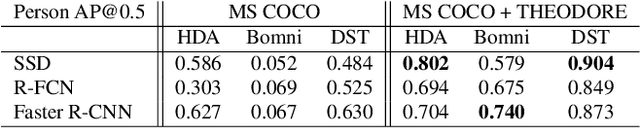
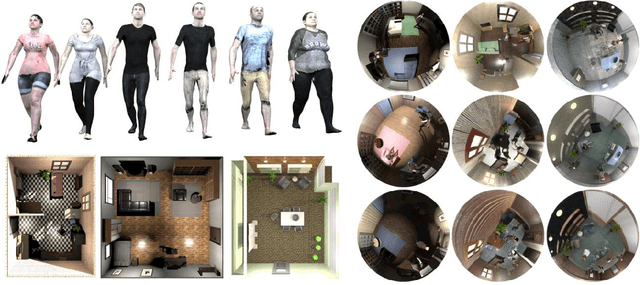
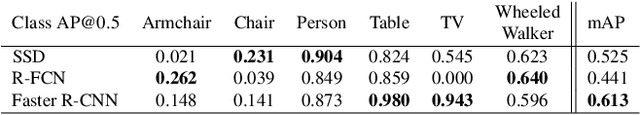
Abstract:Recent work about synthetic indoor datasets from perspective views has shown significant improvements of object detection results with Convolutional Neural Networks(CNNs). In this paper, we introduce THEODORE: a novel, large-scale indoor dataset containing 100,000 high-resolution diversified fisheye images with 14 classes. To this end, we create 3D virtual environments of living rooms, different human characters and interior textures. Beside capturing fisheye images from virtual environments we create annotations for semantic segmentation, instance masks and bounding boxes for object detection tasks. We compare our synthetic dataset to state of the art real-world datasets for omnidirectional images. Based on MS COCO weights, we show that our dataset is well suited for fine-tuning CNNs for object detection. Through a high generalization of our models by means of image synthesis and domain randomization, we reach an AP up to 0.84 for class person on High-Definition Analytics dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge