Tobias Klosek
Energy-based Potential Games for Joint Motion Forecasting and Control
Dec 04, 2023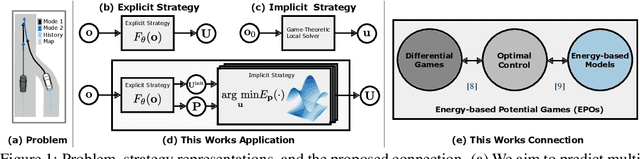
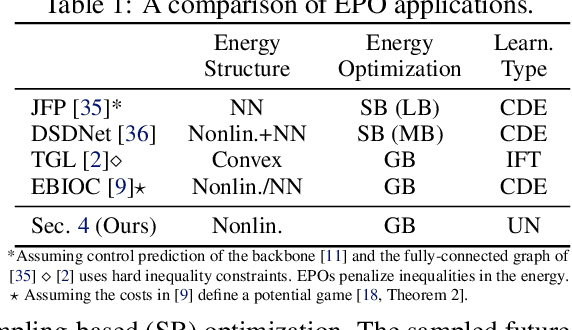
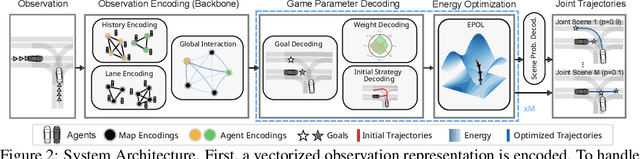
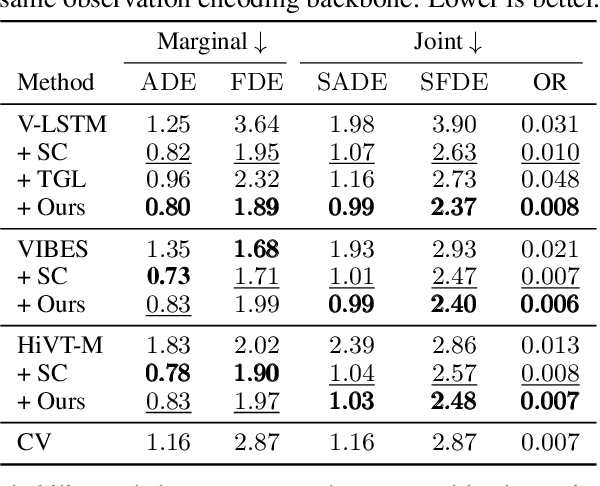
Abstract:This work uses game theory as a mathematical framework to address interaction modeling in multi-agent motion forecasting and control. Despite its interpretability, applying game theory to real-world robotics, like automated driving, faces challenges such as unknown game parameters. To tackle these, we establish a connection between differential games, optimal control, and energy-based models, demonstrating how existing approaches can be unified under our proposed Energy-based Potential Game formulation. Building upon this, we introduce a new end-to-end learning application that combines neural networks for game-parameter inference with a differentiable game-theoretic optimization layer, acting as an inductive bias. The analysis provides empirical evidence that the game-theoretic layer adds interpretability and improves the predictive performance of various neural network backbones using two simulations and two real-world driving datasets.
On a Connection between Differential Games, Optimal Control, and Energy-based Models for Multi-Agent Interactions
Aug 31, 2023Abstract:Game theory offers an interpretable mathematical framework for modeling multi-agent interactions. However, its applicability in real-world robotics applications is hindered by several challenges, such as unknown agents' preferences and goals. To address these challenges, we show a connection between differential games, optimal control, and energy-based models and demonstrate how existing approaches can be unified under our proposed Energy-based Potential Game formulation. Building upon this formulation, this work introduces a new end-to-end learning application that combines neural networks for game-parameter inference with a differentiable game-theoretic optimization layer, acting as an inductive bias. The experiments using simulated mobile robot pedestrian interactions and real-world automated driving data provide empirical evidence that the game-theoretic layer improves the predictive performance of various neural network backbones.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge