Tina Jiang
Improved Content Understanding With Effective Use of Multi-task Contrastive Learning
May 21, 2024



Abstract:In enhancing LinkedIn core content recommendation models, a significant challenge lies in improving their semantic understanding capabilities. This paper addresses the problem by leveraging multi-task learning, a method that has shown promise in various domains. We fine-tune a pre-trained, transformer-based LLM using multi-task contrastive learning with data from a diverse set of semantic labeling tasks. We observe positive transfer, leading to superior performance across all tasks when compared to training independently on each. Our model outperforms the baseline on zero shot learning and offers improved multilingual support, highlighting its potential for broader application. The specialized content embeddings produced by our model outperform generalized embeddings offered by OpenAI on Linkedin dataset and tasks. This work provides a robust foundation for vertical teams across LinkedIn to customize and fine-tune the LLM to their specific applications. Our work offers insights and best practices for the field to build on.
Joint Policy Search for Multi-agent Collaboration with Imperfect Information
Aug 24, 2020
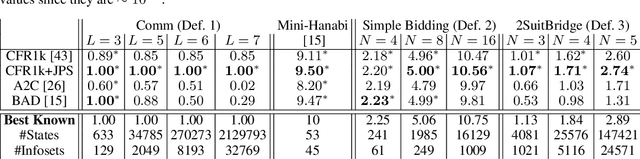
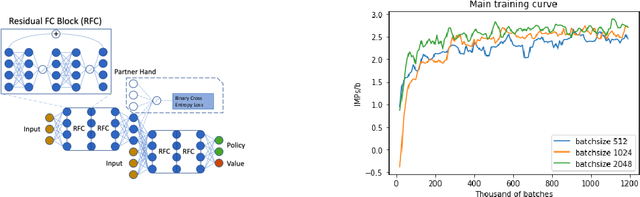

Abstract:To learn good joint policies for multi-agent collaboration with imperfect information remains a fundamental challenge. While for two-player zero-sum games, coordinate-ascent approaches (optimizing one agent's policy at a time, e.g., self-play) work with guarantees, in multi-agent cooperative setting they often converge to sub-optimal Nash equilibrium. On the other hand, directly modeling joint policy changes in imperfect information game is nontrivial due to complicated interplay of policies (e.g., upstream updates affect downstream state reachability). In this paper, we show global changes of game values can be decomposed to policy changes localized at each information set, with a novel term named policy-change density. Based on this, we propose Joint Policy Search(JPS) that iteratively improves joint policies of collaborative agents in imperfect information games, without re-evaluating the entire game. On multi-agent collaborative tabular games, JPS is proven to never worsen performance and can improve solutions provided by unilateral approaches (e.g, CFR), outperforming algorithms designed for collaborative policy learning (e.g. BAD). Furthermore, for real-world games, JPS has an online form that naturally links with gradient updates. We test it to Contract Bridge, a 4-player imperfect-information game where a team of $2$ collaborates to compete against the other. In its bidding phase, players bid in turn to find a good contract through a limited information channel. Based on a strong baseline agent that bids competitive bridge purely through domain-agnostic self-play, JPS improves collaboration of team players and outperforms WBridge5, a championship-winning software, by $+0.63$ IMPs (International Matching Points) per board over 1k games, substantially better than previous SoTA ($+0.41$ IMPs/b) under Double-Dummy evaluation.
Luck Matters: Understanding Training Dynamics of Deep ReLU Networks
Jun 10, 2019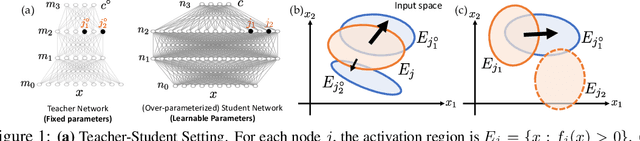
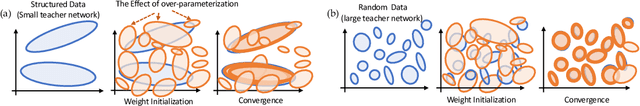
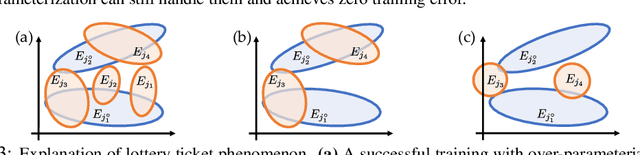
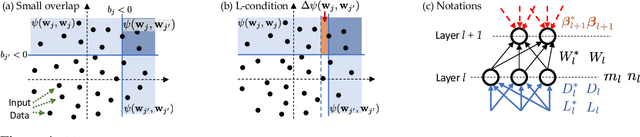
Abstract:We analyze the dynamics of training deep ReLU networks and their implications on generalization capability. Using a teacher-student setting, we discovered a novel relationship between the gradient received by hidden student nodes and the activations of teacher nodes for deep ReLU networks. With this relationship and the assumption of small overlapping teacher node activations, we prove that (1) student nodes whose weights are initialized to be close to teacher nodes converge to them at a faster rate, and (2) in over-parameterized regimes and 2-layer case, while a small set of lucky nodes do converge to the teacher nodes, the fan-out weights of other nodes converge to zero. This framework provides insight into multiple puzzling phenomena in deep learning like over-parameterization, implicit regularization, lottery tickets, etc. We verify our assumption by showing that the majority of BatchNorm biases of pre-trained VGG11/16 models are negative. Experiments on (1) random deep teacher networks with Gaussian inputs, (2) teacher network pre-trained on CIFAR-10 and (3) extensive ablation studies validate our multiple theoretical predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge