Tianxin Shi
Dense Semantic 3D Map Based Long-Term Visual Localization with Hybrid Features
May 21, 2020
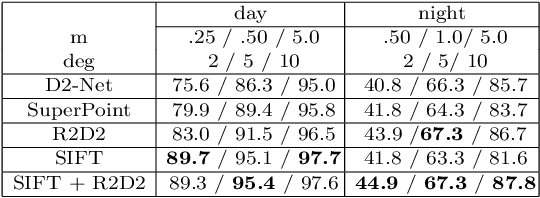

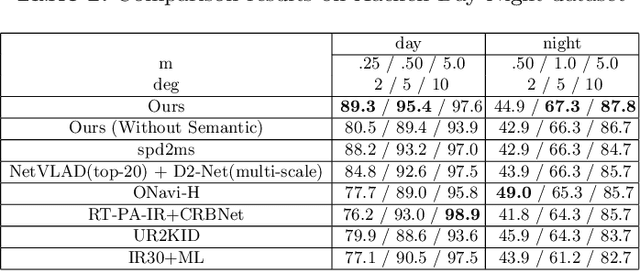
Abstract:Visual localization plays an important role in many applications. However, due to the large appearance variations such as season and illumination changes, as well as weather and day-night variations, it's still a big challenge for robust long-term visual localization algorithms. In this paper, we present a novel visual localization method using hybrid handcrafted and learned features with dense semantic 3D map. Hybrid features help us to make full use of their strengths in different imaging conditions, and the dense semantic map provide us reliable and complete geometric and semantic information for constructing sufficient 2D-3D matching pairs with semantic consistency scores. In our pipeline, we retrieve and score each candidate database image through the semantic consistency between the dense model and the query image. Then the semantic consistency score is used as a soft constraint in the weighted RANSAC-based PnP pose solver. Experimental results on long-term visual localization benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method compared with state-of-the-arts.
Complete Scene Reconstruction by Merging Images and Laser Scans
May 17, 2019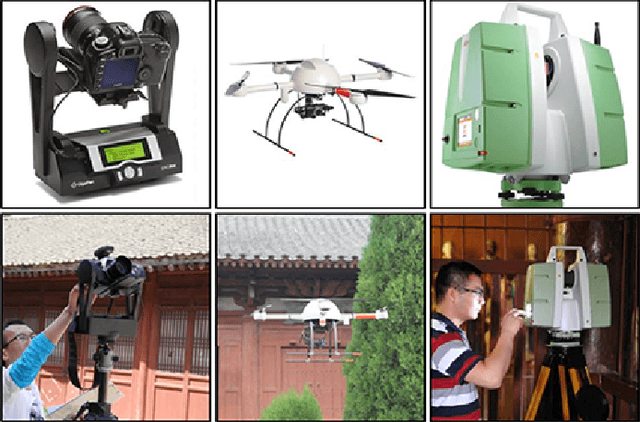
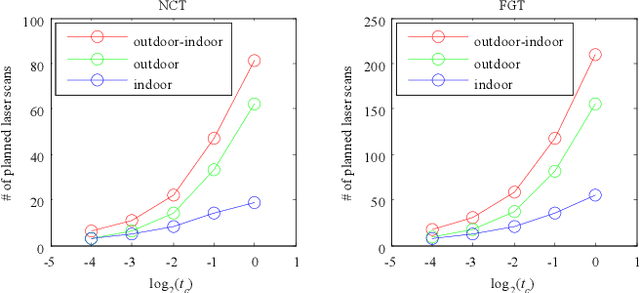
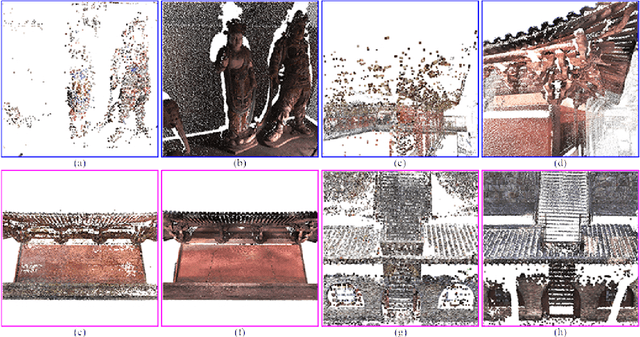
Abstract:Image based modeling and laser scanning are two commonly used approaches in large-scale architectural scene reconstruction nowadays. In order to generate a complete scene reconstruction, an effective way is to completely cover the scene using ground and aerial images, supplemented by laser scanning on certain regions with low texture and complicated structure. Thus, the key issue is to accurately calibrate cameras and register laser scans in a unified framework. To this end, we proposed a three-step pipeline for complete scene reconstruction by merging images and laser scans. First, images are captured around the architecture in a multi-view and multi-scale way and are feed into a structure-from-motion (SfM) pipeline to generate SfM points. Then, based on the SfM result, the laser scanning locations are automatically planned by considering textural richness, structural complexity of the scene and spatial layout of the laser scans. Finally, the images and laser scans are accurately merged in a coarse-to-fine manner. Experimental evaluations on two ancient Chinese architecture datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed complete scene reconstruction pipeline.
Visual Localization Using Sparse Semantic 3D Map
May 17, 2019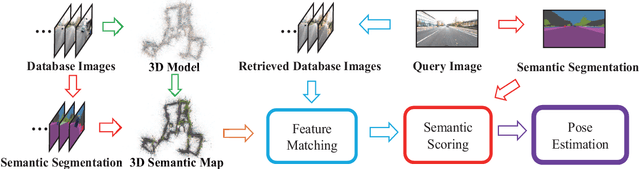
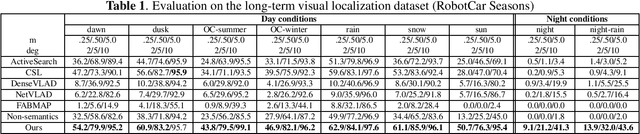
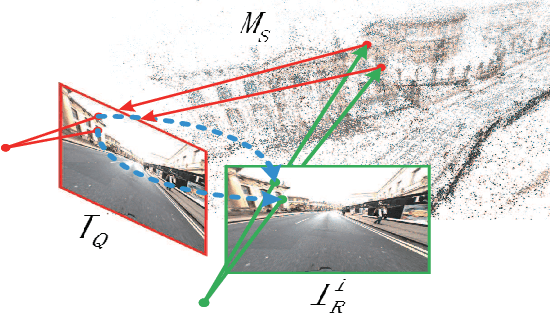
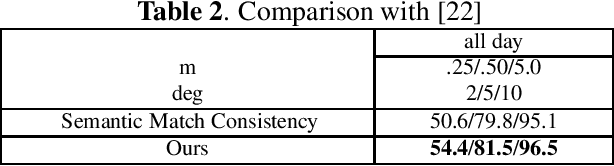
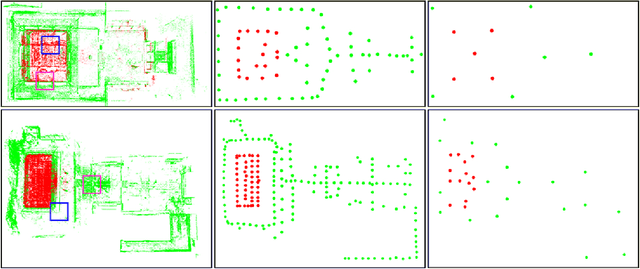
Abstract:Accurate and robust visual localization under a wide range of viewing condition variations including season and illumination changes, as well as weather and day-night variations, is the key component for many computer vision and robotics applications. Under these conditions, most traditional methods would fail to locate the camera. In this paper we present a visual localization algorithm that combines structure-based method and image-based method with semantic information. Given semantic information about the query and database images, the retrieved images are scored according to the semantic consistency of the 3D model and the query image. Then the semantic matching score is used as weight for RANSAC's sampling and the pose is solved by a standard PnP solver. Experiments on the challenging long-term visual localization benchmark dataset demonstrate that our method has significant improvement compared with the state-of-the-arts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge