Thomas Helten
Building Statistical Shape Spaces for 3D Human Modeling
Mar 03, 2017
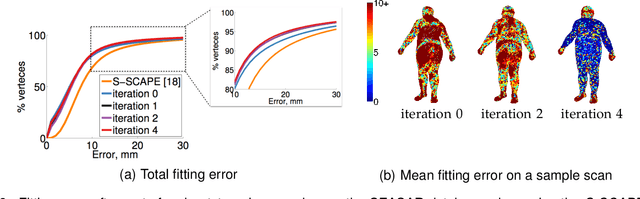
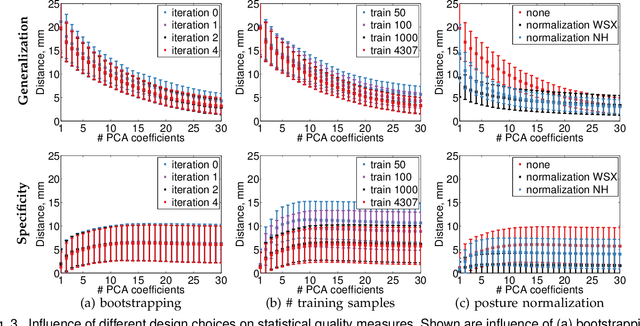
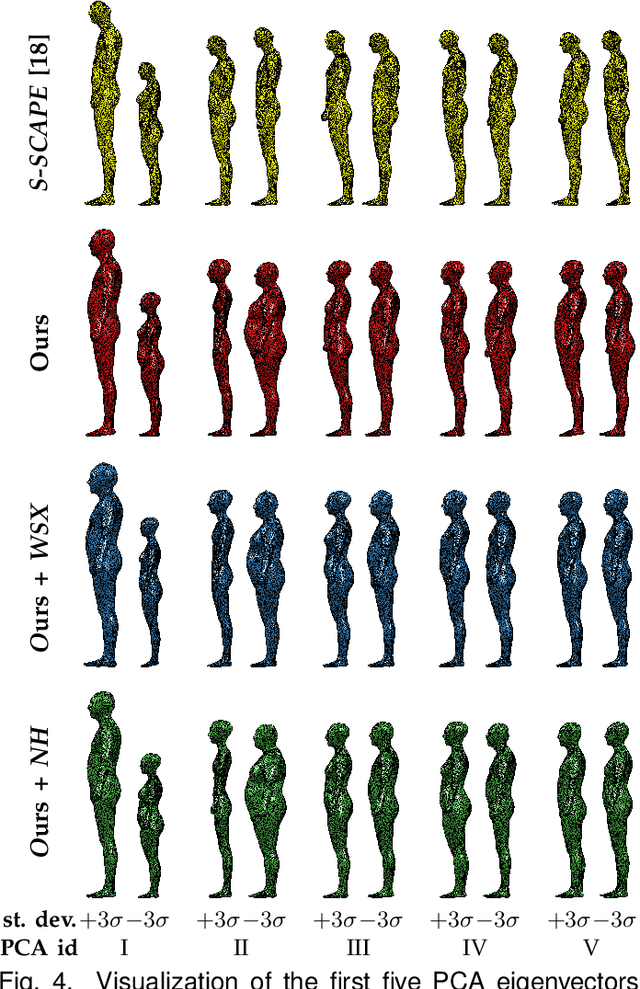
Abstract:Statistical models of 3D human shape and pose learned from scan databases have developed into valuable tools to solve a variety of vision and graphics problems. Unfortunately, most publicly available models are of limited expressiveness as they were learned on very small databases that hardly reflect the true variety in human body shapes. In this paper, we contribute by rebuilding a widely used statistical body representation from the largest commercially available scan database, and making the resulting model available to the community (visit http://humanshape.mpi-inf.mpg.de). As preprocessing several thousand scans for learning the model is a challenge in itself, we contribute by developing robust best practice solutions for scan alignment that quantitatively lead to the best learned models. We make implementations of these preprocessing steps also publicly available. We extensively evaluate the improved accuracy and generality of our new model, and show its improved performance for human body reconstruction from sparse input data.
Efficient Multi-view Performance Capture of Fine-Scale Surface Detail
Feb 05, 2016
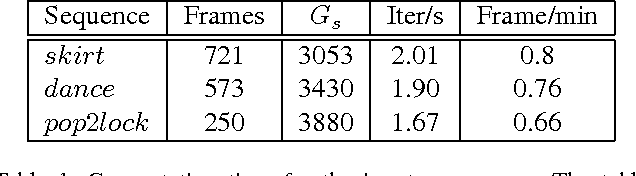


Abstract:We present a new effective way for performance capture of deforming meshes with fine-scale time-varying surface detail from multi-view video. Our method builds up on coarse 4D surface reconstructions, as obtained with commonly used template-based methods. As they only capture models of coarse-to-medium scale detail, fine scale deformation detail is often done in a second pass by using stereo constraints, features, or shading-based refinement. In this paper, we propose a new effective and stable solution to this second step. Our framework creates an implicit representation of the deformable mesh using a dense collection of 3D Gaussian functions on the surface, and a set of 2D Gaussians for the images. The fine scale deformation of all mesh vertices that maximizes photo-consistency can be efficiently found by densely optimizing a new model-to-image consistency energy on all vertex positions. A principal advantage is that our problem formulation yields a smooth closed form energy with implicit occlusion handling and analytic derivatives. Error-prone correspondence finding, or discrete sampling of surface displacement values are also not needed. We show several reconstructions of human subjects wearing loose clothing, and we qualitatively and quantitatively show that we robustly capture more detail than related methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge