Thomas Geert de Jong
Harnessing omnipresent oscillator networks as computational resource
Feb 07, 2025


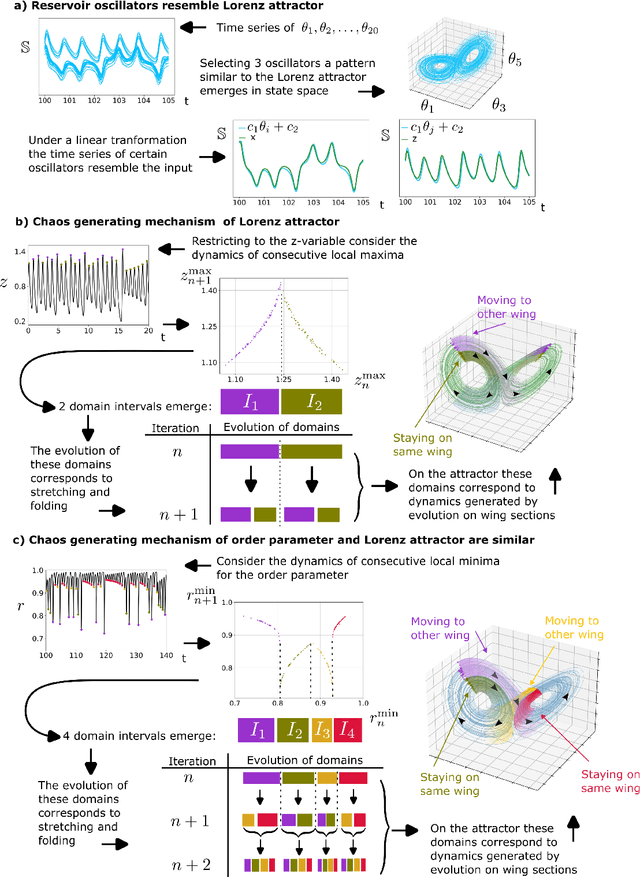
Abstract:Nature is pervaded with oscillatory behavior. In networks of coupled oscillators patterns can arise when the system synchronizes to an external input. Hence, these networks provide processing and memory of input. We present a universal framework for harnessing oscillator networks as computational resource. This reservoir computing framework is introduced by the ubiquitous model for phase-locking, the Kuramoto model. We force the Kuramoto model by a nonlinear target-system, then after substituting the target-system with a trained feedback-loop it emulates the target-system. Our results are two-fold. Firstly, the trained network inherits performance properties of the Kuramoto model, where all-to-all coupling is performed in linear time with respect to the number of nodes and parameters for synchronization are abundant. Secondly, the learning capabilities of the oscillator network can be explained using Kuramoto model's order parameter. This work provides the foundation for utilizing nature's oscillator networks as a new class of information processing systems.
Virtual reservoir acceleration for CPU and GPU: Case study for coupled spin-torque oscillator reservoir
Dec 02, 2023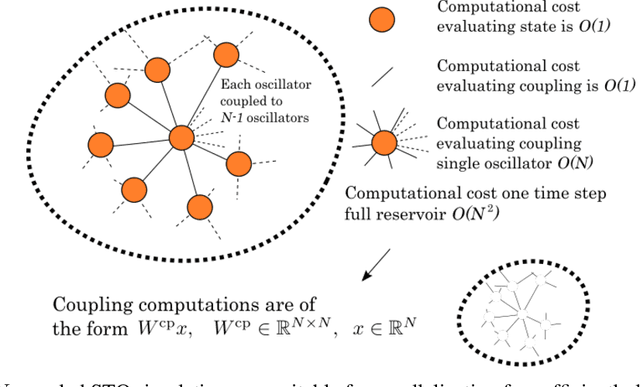
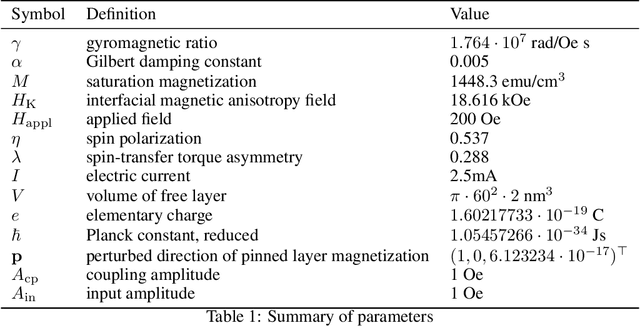
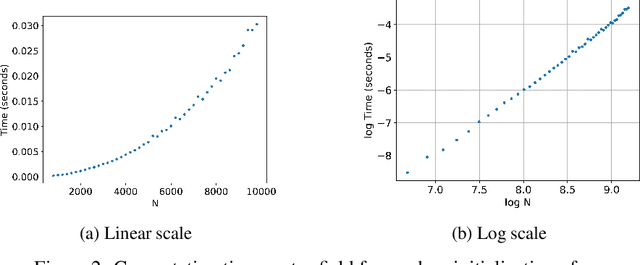
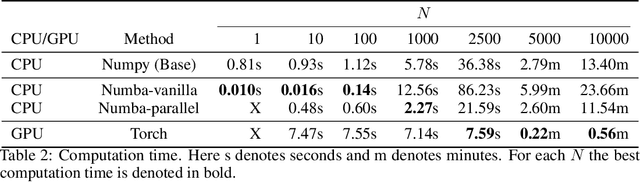
Abstract:We provide high-speed implementations for simulating reservoirs described by $N$-coupled spin-torque oscillators. Here $N$ also corresponds to the number of reservoir nodes. We benchmark a variety of implementations based on CPU and GPU. Our new methods are at least 2.6 times quicker than the baseline for $N$ in range $1$ to $10^4$. More specifically, over all implementations the best factor is 78.9 for $N=1$ which decreases to 2.6 for $N=10^3$ and finally increases to 23.8 for $N=10^4$. GPU outperforms CPU significantly at $N=2500$. Our results show that GPU implementations should be tested for reservoir simulations. The implementations considered here can be used for any reservoir with evolution that can be approximated using an explicit method.
How neural networks learn to classify chaotic time series
Jun 04, 2023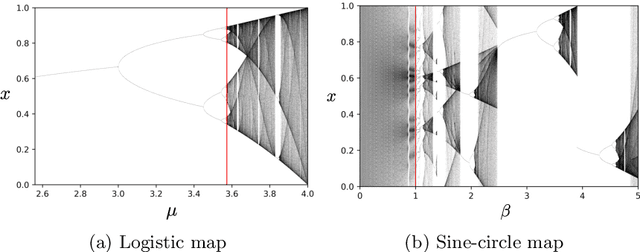

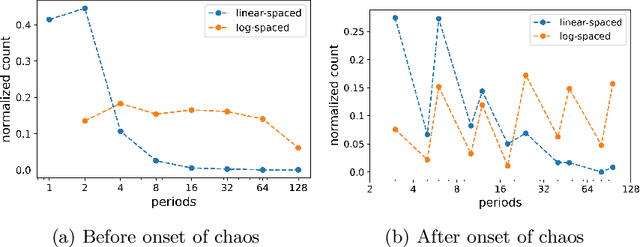
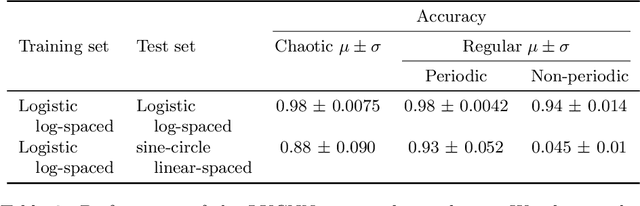
Abstract:Neural networks are increasingly employed to model, analyze and control non-linear dynamical systems ranging from physics to biology. Owing to their universal approximation capabilities, they regularly outperform state-of-the-art model-driven methods in terms of accuracy, computational speed, and/or control capabilities. On the other hand, neural networks are very often they are taken as black boxes whose explainability is challenged, among others, by huge amounts of trainable parameters. In this paper, we tackle the outstanding issue of analyzing the inner workings of neural networks trained to classify regular-versus-chaotic time series. This setting, well-studied in dynamical systems, enables thorough formal analyses. We focus specifically on a family of networks dubbed Large Kernel Convolutional Neural Networks (LKCNN), recently introduced by Boull\'{e} et al. (2021). These non-recursive networks have been shown to outperform other established architectures (e.g. residual networks, shallow neural networks and fully convolutional networks) at this classification task. Furthermore, they outperform ``manual'' classification approaches based on direct reconstruction of the Lyapunov exponent. We find that LKCNNs use qualitative properties of the input sequence. In particular, we show that the relation between input periodicity and activation periodicity is key for the performance of LKCNN models. Low performing models show, in fact, analogous periodic activations to random untrained models. This could give very general criteria for identifying, a priori, trained models that have poor accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge