Theodor Westny
A Preprocessing and Evaluation Toolbox for Trajectory Prediction Research on the Drone Datasets
May 01, 2024



Abstract:The availability of high-quality datasets is crucial for the development of behavior prediction algorithms in autonomous vehicles. This paper highlights the need for standardizing the use of certain datasets for motion forecasting research to simplify comparative analysis and proposes a set of tools and practices to achieve this. Drawing on extensive experience and a comprehensive review of current literature, we summarize our proposals for preprocessing, visualizing, and evaluation in the form of an open-sourced toolbox designed for researchers working on trajectory prediction problems. The clear specification of necessary preprocessing steps and evaluation metrics is intended to alleviate development efforts and facilitate the comparison of results across different studies. The toolbox is available at: https://github.com/westny/dronalize.
Diffusion-Based Environment-Aware Trajectory Prediction
Mar 18, 2024



Abstract:The ability to predict the future trajectories of traffic participants is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of autonomous vehicles. In this paper, a diffusion-based generative model for multi-agent trajectory prediction is proposed. The model is capable of capturing the complex interactions between traffic participants and the environment, accurately learning the multimodal nature of the data. The effectiveness of the approach is assessed on large-scale datasets of real-world traffic scenarios, showing that our model outperforms several well-established methods in terms of prediction accuracy. By the incorporation of differential motion constraints on the model output, we illustrate that our model is capable of generating a diverse set of realistic future trajectories. Through the use of an interaction-aware guidance signal, we further demonstrate that the model can be adapted to predict the behavior of less cooperative agents, emphasizing its practical applicability under uncertain traffic conditions.
Stability-Informed Initialization of Neural Ordinary Differential Equations
Dec 01, 2023Abstract:This paper addresses the training of Neural Ordinary Differential Equations (neural ODEs), and in particular explores the interplay between numerical integration techniques, stability regions, step size, and initialization techniques. It is shown how the choice of integration technique implicitly regularizes the learned model, and how the solver's corresponding stability region affects training and prediction performance. From this analysis, a stability-informed parameter initialization technique is introduced. The effectiveness of the initialization method is displayed across several learning benchmarks and industrial applications.
Analysis of Numerical Integration in RNN-Based Residuals for Fault Diagnosis of Dynamic Systems
May 08, 2023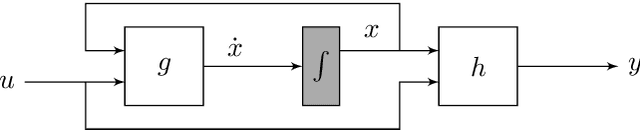

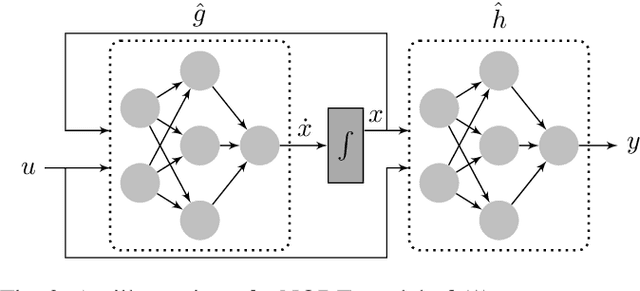
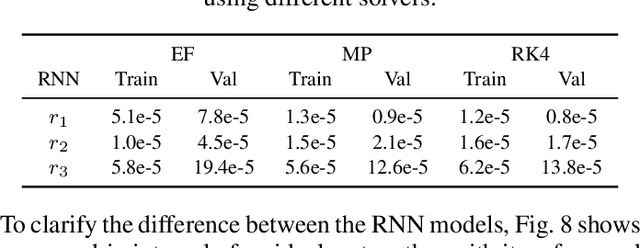
Abstract:Data-driven modeling and machine learning are widely used to model the behavior of dynamic systems. One application is the residual evaluation of technical systems where model predictions are compared with measurement data to create residuals for fault diagnosis applications. While recurrent neural network models have been shown capable of modeling complex non-linear dynamic systems, they are limited to fixed steps discrete-time simulation. Modeling using neural ordinary differential equations, however, make it possible to evaluate the state variables at specific times, compute gradients when training the model and use standard numerical solvers to explicitly model the underlying dynamic of the time-series data. Here, the effect of solver selection on the performance of neural ordinary differential equation residuals during training and evaluation is investigated. The paper includes a case study of a heavy-duty truck's after-treatment system to highlight the potential of these techniques for improving fault diagnosis performance.
Evaluation of Differentially Constrained Motion Models for Graph-Based Trajectory Prediction
Apr 24, 2023



Abstract:Given their flexibility and encouraging performance, deep-learning models are becoming standard for motion prediction in autonomous driving. However, with great flexibility comes a lack of interpretability and possible violations of physical constraints. Accompanying these data-driven methods with differentially-constrained motion models to provide physically feasible trajectories is a promising future direction. The foundation for this work is a previously introduced graph-neural-network-based model, MTP-GO. The neural network learns to compute the inputs to an underlying motion model to provide physically feasible trajectories. This research investigates the performance of various motion models in combination with numerical solvers for the prediction task. The study shows that simpler models, such as low-order integrator models, are preferred over more complex, e.g., kinematic models, to achieve accurate predictions. Further, the numerical solver can have a substantial impact on performance, advising against commonly used first-order methods like Euler forward. Instead, a second-order method like Heun's can greatly improve predictions.
MTP-GO: Graph-Based Probabilistic Multi-Agent Trajectory Prediction with Neural ODEs
Feb 09, 2023



Abstract:Enabling resilient autonomous motion planning requires robust predictions of surrounding road users' future behavior. In response to this need and the associated challenges, we introduce our model, titled MTP-GO. The model encodes the scene using temporal graph neural networks to produce the inputs to an underlying motion model. The motion model is implemented using neural ordinary differential equations where the state-transition functions are learned with the rest of the model. Multi-modal probabilistic predictions are provided by combining the concept of mixture density networks and Kalman filtering. The results illustrate the predictive capabilities of the proposed model across various data sets, outperforming several state-of-the-art methods on a number of metrics.
Vehicle Behavior Prediction and Generalization Using Imbalanced Learning Techniques
Sep 22, 2021

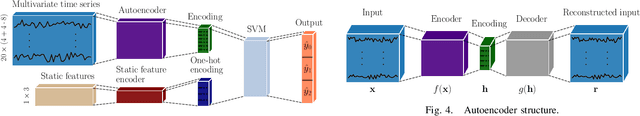

Abstract:The use of learning-based methods for vehicle behavior prediction is a promising research topic. However, many publicly available data sets suffer from class distribution skews which limits learning performance if not addressed. This paper proposes an interaction-aware prediction model consisting of an LSTM autoencoder and SVM classifier. Additionally, an imbalanced learning technique, the multiclass balancing ensemble is proposed. Evaluations show that the method enhances model performance, resulting in improved classification accuracy. Good generalization properties of learned models are important and therefore a generalization study is done where models are evaluated on unseen traffic data with dissimilar traffic behavior stemming from different road configurations. This is realized by using two distinct highway traffic recordings, the publicly available NGSIM US-101 and I80 data sets. Moreover, methods for encoding structural and static features into the learning process for improved generalization are evaluated. The resulting methods show substantial improvements in classification as well as generalization performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge