Terrence Szymanski
Diachronic word embeddings and semantic shifts: a survey
Jun 13, 2018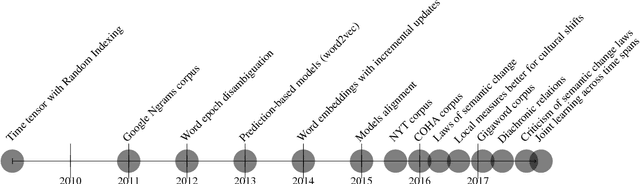
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed a surge of publications aimed at tracing temporal changes in lexical semantics using distributional methods, particularly prediction-based word embedding models. However, this vein of research lacks the cohesion, common terminology and shared practices of more established areas of natural language processing. In this paper, we survey the current state of academic research related to diachronic word embeddings and semantic shifts detection. We start with discussing the notion of semantic shifts, and then continue with an overview of the existing methods for tracing such time-related shifts with word embedding models. We propose several axes along which these methods can be compared, and outline the main challenges before this emerging subfield of NLP, as well as prospects and possible applications.
Helping News Editors Write Better Headlines: A Recommender to Improve the Keyword Contents & Shareability of News Headlines
May 26, 2017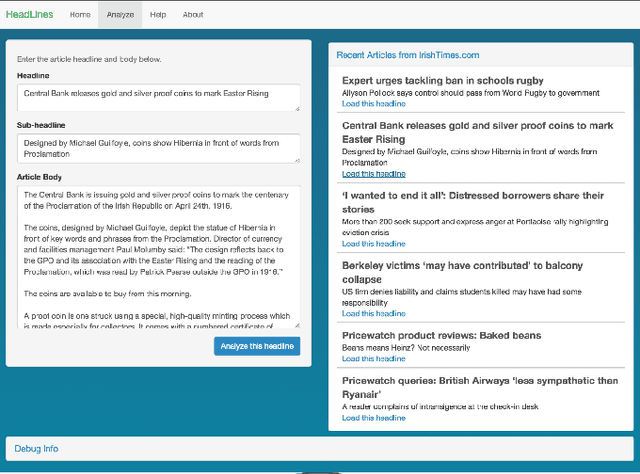

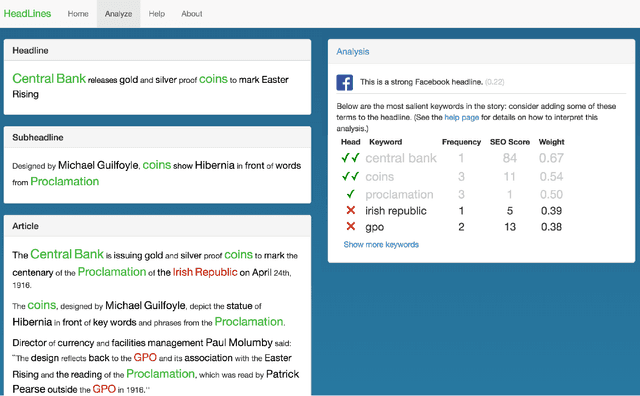
Abstract:We present a software tool that employs state-of-the-art natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning techniques to help newspaper editors compose effective headlines for online publication. The system identifies the most salient keywords in a news article and ranks them based on both their overall popularity and their direct relevance to the article. The system also uses a supervised regression model to identify headlines that are likely to be widely shared on social media. The user interface is designed to simplify and speed the editor's decision process on the composition of the headline. As such, the tool provides an efficient way to combine the benefits of automated predictors of engagement and search-engine optimization (SEO) with human judgments of overall headline quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge