Tayyebeh Saeedi
Multidimensional Data Analysis Based on Block Convolutional Tensor Decomposition
Aug 11, 2023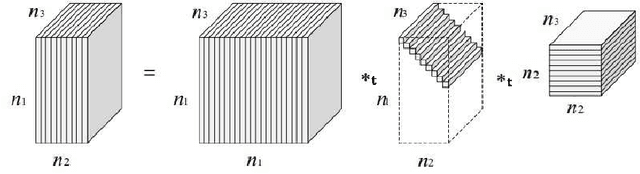
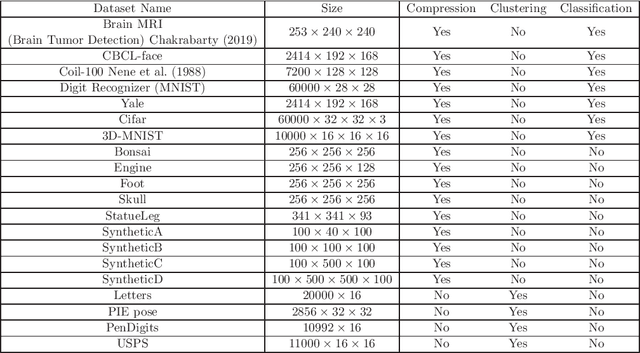
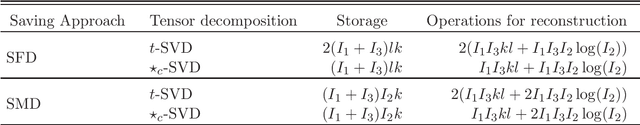
Abstract:Tensor decompositions are powerful tools for analyzing multi-dimensional data in their original format. Besides tensor decompositions like Tucker and CP, Tensor SVD (t-SVD) which is based on the t-product of tensors is another extension of SVD to tensors that recently developed and has found numerous applications in analyzing high dimensional data. This paper offers a new insight into the t-Product and shows that this product is a block convolution of two tensors with periodic boundary conditions. Based on this viewpoint, we propose a new tensor-tensor product called the $\star_c{}\text{-Product}$ based on Block convolution with reflective boundary conditions. Using a tensor framework, this product can be easily extended to tensors of arbitrary order. Additionally, we introduce a tensor decomposition based on our $\star_c{}\text{-Product}$ for arbitrary order tensors. Compared to t-SVD, our new decomposition has lower complexity, and experiments show that it yields higher-quality results in applications such as classification and compression.
A Persian Benchmark for Joint Intent Detection and Slot Filling
Mar 01, 2023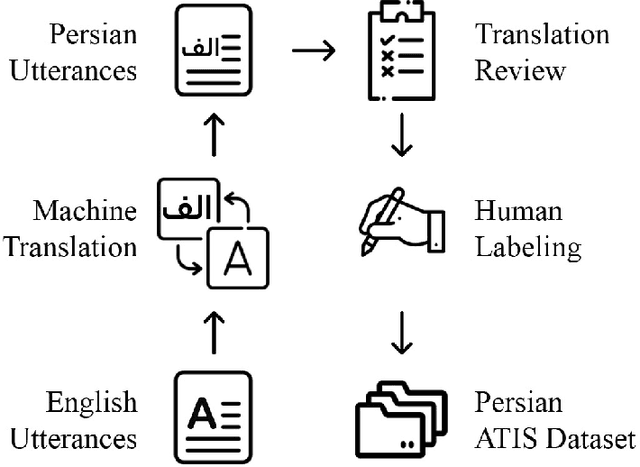
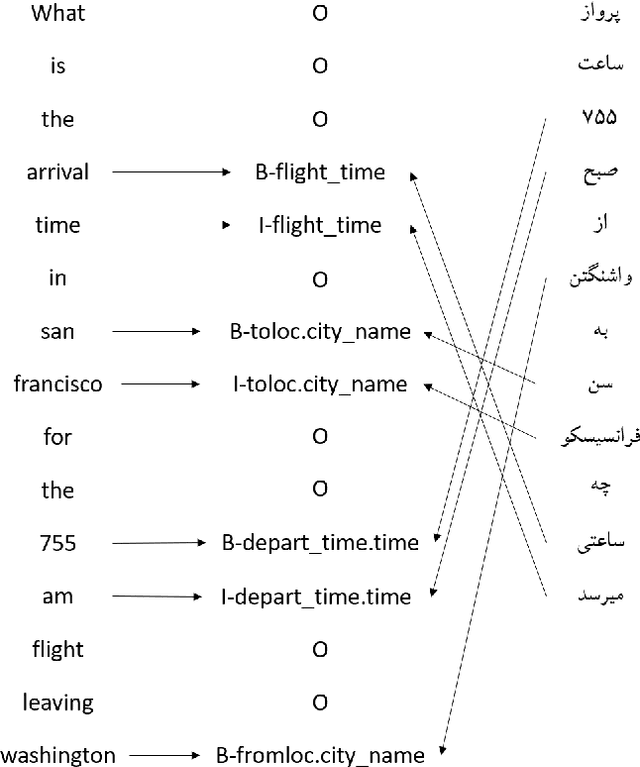
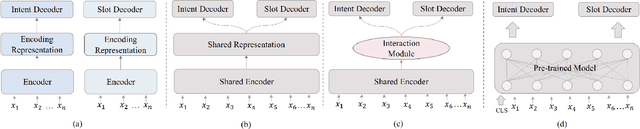
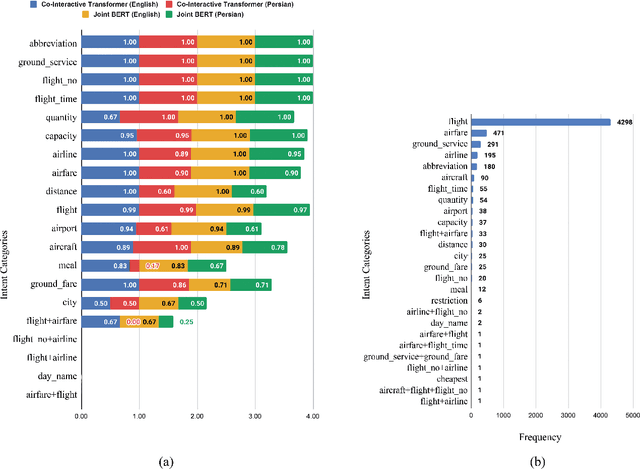
Abstract:Natural Language Understanding (NLU) is important in today's technology as it enables machines to comprehend and process human language, leading to improved human-computer interactions and advancements in fields such as virtual assistants, chatbots, and language-based AI systems. This paper highlights the significance of advancing the field of NLU for low-resource languages. With intent detection and slot filling being crucial tasks in NLU, the widely used datasets ATIS and SNIPS have been utilized in the past. However, these datasets only cater to the English language and do not support other languages. In this work, we aim to address this gap by creating a Persian benchmark for joint intent detection and slot filling based on the ATIS dataset. To evaluate the effectiveness of our benchmark, we employ state-of-the-art methods for intent detection and slot filling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge