Taylan Sen
AI Standardized Patient Improves Human Conversations in Advanced Cancer Care
May 05, 2025Abstract:Serious illness communication (SIC) in end-of-life care faces challenges such as emotional stress, cultural barriers, and balancing hope with honesty. Despite its importance, one of the few available ways for clinicians to practice SIC is with standardized patients, which is expensive, time-consuming, and inflexible. In this paper, we present SOPHIE, an AI-powered standardized patient simulation and automated feedback system. SOPHIE combines large language models (LLMs), a lifelike virtual avatar, and automated, personalized feedback based on clinical literature to provide remote, on-demand SIC training. In a randomized control study with healthcare students and professionals, SOPHIE users demonstrated significant improvement across three critical SIC domains: Empathize, Be Explicit, and Empower. These results suggest that AI-driven tools can enhance complex interpersonal communication skills, offering scalable, accessible solutions to address a critical gap in clinician education.
A Mental Trespass? Unveiling Truth, Exposing Thoughts and Threatening Civil Liberties with Non-Invasive AI Lie Detection
Feb 16, 2021


Abstract:Imagine an app on your phone or computer that can tell if you are being dishonest, just by processing affective features of your facial expressions, body movements, and voice. People could ask about your political preferences, your sexual orientation, and immediately determine which of your responses are honest and which are not. In this paper we argue why artificial intelligence-based, non-invasive lie detection technologies are likely to experience a rapid advancement in the coming years, and that it would be irresponsible to wait any longer before discussing its implications. Legal and popular perspectives are reviewed to evaluate the potential for these technologies to cause societal harm. To understand the perspective of a reasonable person, we conducted a survey of 129 individuals, and identified consent and accuracy as the major factors in their decision-making process regarding the use of these technologies. In our analysis, we distinguish two types of lie detection technology, accurate truth metering and accurate thought exposing. We generally find that truth metering is already largely within the scope of existing US federal and state laws, albeit with some notable exceptions. In contrast, we find that current regulation of thought exposing technologies is ambiguous and inadequate to safeguard civil liberties. In order to rectify these shortcomings, we introduce the legal concept of mental trespass and use this concept as the basis for proposed regulation.
Are you really looking at me? A Framework for Extracting Interpersonal Eye Gaze from Conventional Video
Jun 21, 2019
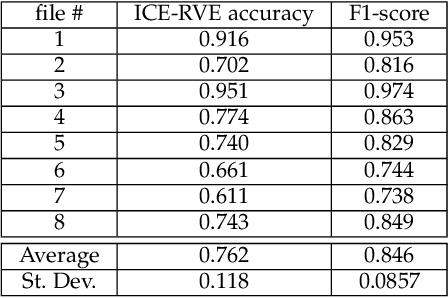
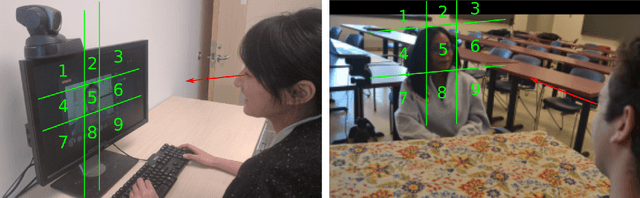

Abstract:Despite a revolution in the pervasiveness of video cameras in our daily lives, one of the most meaningful forms of nonverbal affective communication, interpersonal eye gaze, i.e. eye gaze relative to a conversation partner, is not available from common video. We introduce the Interpersonal-Calibrating Eye-gaze Encoder (ICE), which automatically extracts interpersonal gaze from video recordings without specialized hardware and without prior knowledge of participant locations. Leveraging the intuition that individuals spend a large portion of a conversation looking at each other enables the ICE dynamic clustering algorithm to extract interpersonal gaze. We validate ICE in both video chat using an objective metric with an infrared gaze tracker (F1=0.846, N=8), as well as in face-to-face communication with expert-rated evaluations of eye contact (r= 0.37, N=170). We then use ICE to analyze behavior in two different, yet important affective communication domains: interrogation-based deception detection, and communication skill assessment in speed dating. We find that honest witnesses break interpersonal gaze contact and look down more often than deceptive witnesses when answering questions (p=0.004, d=0.79). In predicting expert communication skill ratings in speed dating videos, we demonstrate that interpersonal gaze alone has more predictive power than facial expressions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge