Tarun Gogineni
OpenAI GPT-5 System Card
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This is the system card published alongside the OpenAI GPT-5 launch, August 2025. GPT-5 is a unified system with a smart and fast model that answers most questions, a deeper reasoning model for harder problems, and a real-time router that quickly decides which model to use based on conversation type, complexity, tool needs, and explicit intent (for example, if you say 'think hard about this' in the prompt). The router is continuously trained on real signals, including when users switch models, preference rates for responses, and measured correctness, improving over time. Once usage limits are reached, a mini version of each model handles remaining queries. This system card focuses primarily on gpt-5-thinking and gpt-5-main, while evaluations for other models are available in the appendix. The GPT-5 system not only outperforms previous models on benchmarks and answers questions more quickly, but -- more importantly -- is more useful for real-world queries. We've made significant advances in reducing hallucinations, improving instruction following, and minimizing sycophancy, and have leveled up GPT-5's performance in three of ChatGPT's most common uses: writing, coding, and health. All of the GPT-5 models additionally feature safe-completions, our latest approach to safety training to prevent disallowed content. Similarly to ChatGPT agent, we have decided to treat gpt-5-thinking as High capability in the Biological and Chemical domain under our Preparedness Framework, activating the associated safeguards. While we do not have definitive evidence that this model could meaningfully help a novice to create severe biological harm -- our defined threshold for High capability -- we have chosen to take a precautionary approach.
GPT-4o System Card
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:GPT-4o is an autoregressive omni model that accepts as input any combination of text, audio, image, and video, and generates any combination of text, audio, and image outputs. It's trained end-to-end across text, vision, and audio, meaning all inputs and outputs are processed by the same neural network. GPT-4o can respond to audio inputs in as little as 232 milliseconds, with an average of 320 milliseconds, which is similar to human response time in conversation. It matches GPT-4 Turbo performance on text in English and code, with significant improvement on text in non-English languages, while also being much faster and 50\% cheaper in the API. GPT-4o is especially better at vision and audio understanding compared to existing models. In line with our commitment to building AI safely and consistent with our voluntary commitments to the White House, we are sharing the GPT-4o System Card, which includes our Preparedness Framework evaluations. In this System Card, we provide a detailed look at GPT-4o's capabilities, limitations, and safety evaluations across multiple categories, focusing on speech-to-speech while also evaluating text and image capabilities, and measures we've implemented to ensure the model is safe and aligned. We also include third-party assessments on dangerous capabilities, as well as discussion of potential societal impacts of GPT-4o's text and vision capabilities.
TorsionNet: A Reinforcement Learning Approach to Sequential Conformer Search
Jun 12, 2020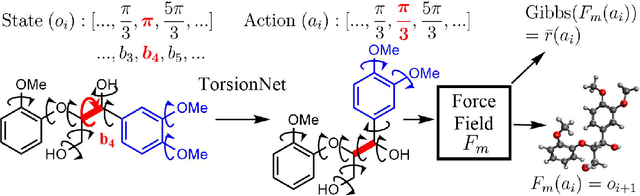
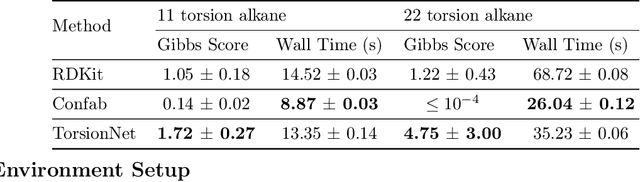
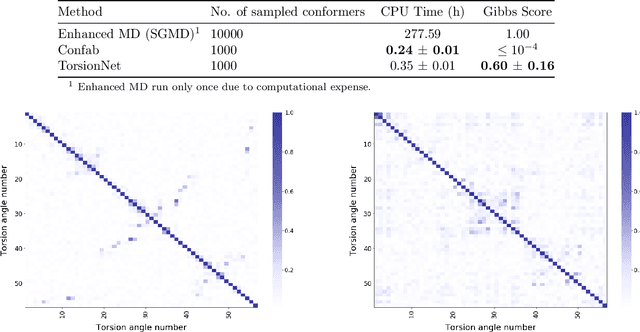
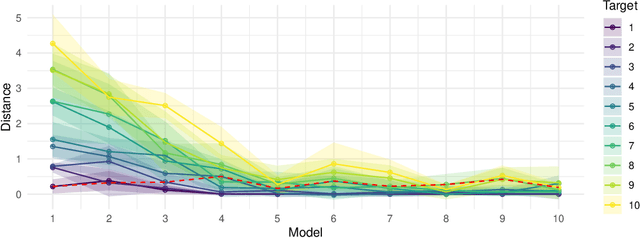
Abstract:Molecular geometry prediction of flexible molecules, or conformer search, is a long-standing challenge in computational chemistry. This task is of great importance for predicting structure-activity relationships for a wide variety of substances ranging from biomolecules to ubiquitous materials. Substantial computational resources are invested in Monte Carlo and Molecular Dynamics methods to generate diverse and representative conformer sets for medium to large molecules, which are yet intractable to chemoinformatic conformer search methods. We present TorsionNet, an efficient sequential conformer search technique based on reinforcement learning under the rigid rotor approximation. The model is trained via curriculum learning, whose theoretical benefit is explored in detail, to maximize a novel metric grounded in thermodynamics called the Gibbs Score. Our experimental results show that TorsionNet outperforms the highest scoring chemoinformatics method by 4x on large branched alkanes, and by several orders of magnitude on the previously unexplored biopolymer lignin, with applications in renewable energy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge