Talgat Saparov
The impact of deep learning aid on the workload and interpretation accuracy of radiologists on chest computed tomography: a cross-over reader study
Jun 12, 2024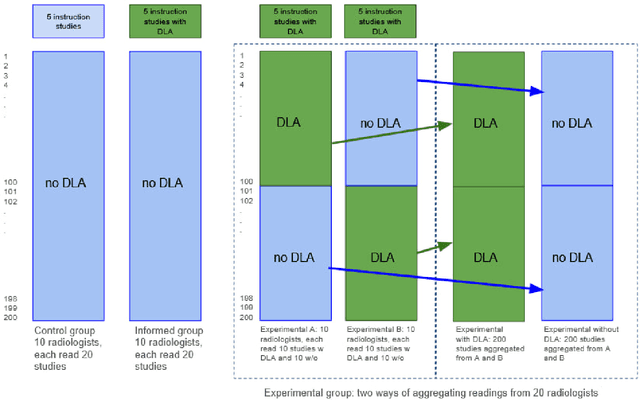
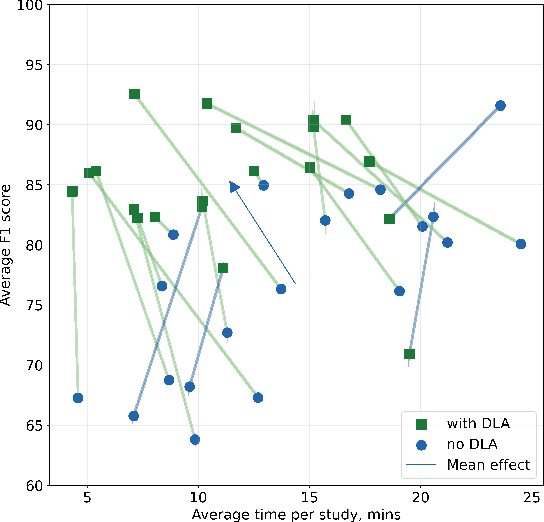
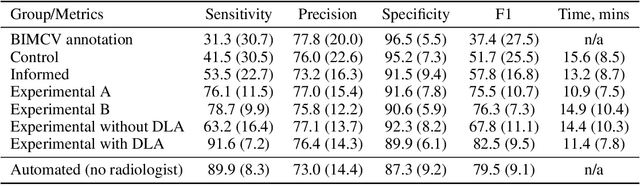
Abstract:Interpretation of chest computed tomography (CT) is time-consuming. Previous studies have measured the time-saving effect of using a deep-learning-based aid (DLA) for CT interpretation. We evaluated the joint impact of a multi-pathology DLA on the time and accuracy of radiologists' reading. 40 radiologists were randomly split into three experimental arms: control (10), who interpret studies without assistance; informed group (10), who were briefed about DLA pathologies, but performed readings without it; and the experimental group (20), who interpreted half studies with DLA, and half without. Every arm used the same 200 CT studies retrospectively collected from BIMCV-COVID19 dataset; each radiologist provided readings for 20 CT studies. We compared interpretation time, and accuracy of participants diagnostic report with respect to 12 pathological findings. Mean reading time per study was 15.6 minutes [SD 8.5] in the control arm, 13.2 minutes [SD 8.7] in the informed arm, 14.4 [SD 10.3] in the experimental arm without DLA, and 11.4 minutes [SD 7.8] in the experimental arm with DLA. Mean sensitivity and specificity were 41.5 [SD 30.4], 86.8 [SD 28.3] in the control arm; 53.5 [SD 22.7], 92.3 [SD 9.4] in the informed non-assisted arm; 63.2 [SD 16.4], 92.3 [SD 8.2] in the experimental arm without DLA; and 91.6 [SD 7.2], 89.9 [SD 6.0] in the experimental arm with DLA. DLA speed up interpretation time per study by 2.9 minutes (CI95 [1.7, 4.3], p<0.0005), increased sensitivity by 28.4 (CI95 [23.4, 33.4], p<0.0005), and decreased specificity by 2.4 (CI95 [0.6, 4.3], p=0.13). Of 20 radiologists in the experimental arm, 16 have improved reading time and sensitivity, two improved their time with a marginal drop in sensitivity, and two participants improved sensitivity with increased time. Overall, DLA introduction decreased reading time by 20.6%.
Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation in CT Segmentation by Filtered Back Projection Augmentation
Aug 03, 2021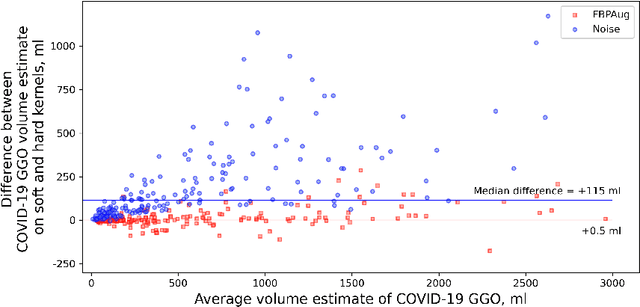
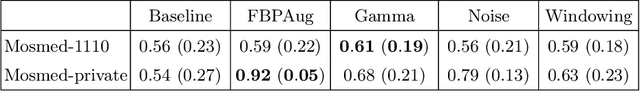
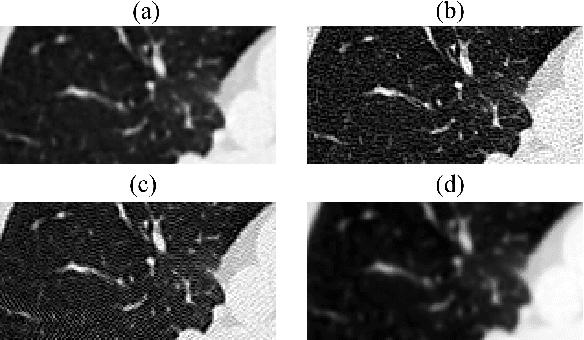
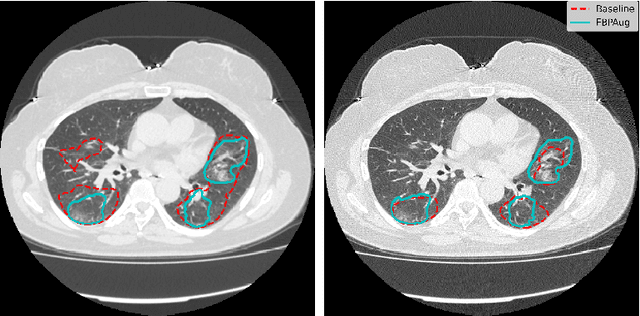
Abstract:Domain shift is one of the most salient challenges in medical computer vision. Due to immense variability in scanners' parameters and imaging protocols, even images obtained from the same person and the same scanner could differ significantly. We address variability in computed tomography (CT) images caused by different convolution kernels used in the reconstruction process, the critical domain shift factor in CT. The choice of a convolution kernel affects pixels' granularity, image smoothness, and noise level. We analyze a dataset of paired CT images, where smooth and sharp images were reconstructed from the same sinograms with different kernels, thus providing identical anatomy but different style. Though identical predictions are desired, we show that the consistency, measured as the average Dice between predictions on pairs, is just 0.54. We propose Filtered Back-Projection Augmentation (FBPAug), a simple and surprisingly efficient approach to augment CT images in sinogram space emulating reconstruction with different kernels. We apply the proposed method in a zero-shot domain adaptation setup and show that the consistency boosts from 0.54 to 0.92 outperforming other augmentation approaches. Neither specific preparation of source domain data nor target domain data is required, so our publicly released FBPAug can be used as a plug-and-play module for zero-shot domain adaptation in any CT-based task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge