Talaat Khalil
Combining Lexical Features and a Supervised Learning Approach for Arabic Sentiment Analysis
Oct 23, 2017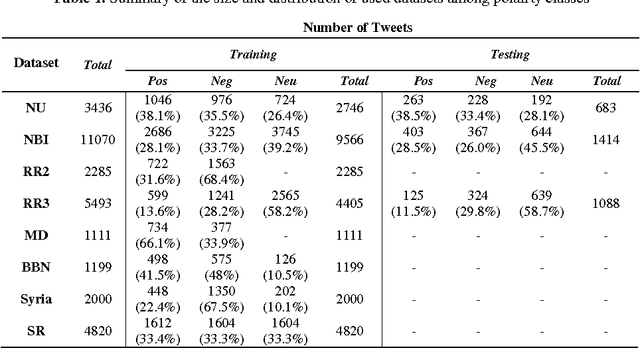
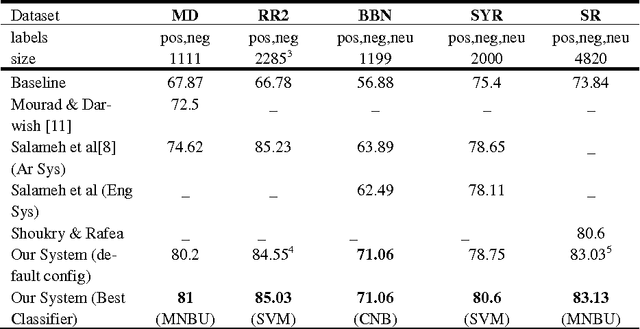
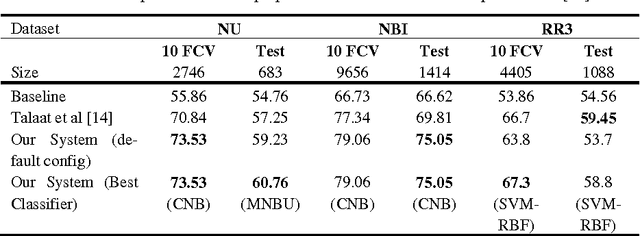
Abstract:The importance of building sentiment analysis tools for Arabic social media has been recognized during the past couple of years, especially with the rapid increase in the number of Arabic social media users. One of the main difficulties in tackling this problem is that text within social media is mostly colloquial, with many dialects being used within social media platforms. In this paper, we present a set of features that were integrated with a machine learning based sentiment analysis model and applied on Egyptian, Saudi, Levantine, and MSA Arabic social media datasets. Many of the proposed features were derived through the use of an Arabic Sentiment Lexicon. The model also presents emoticon based features, as well as input text related features such as the number of segments within the text, the length of the text, whether the text ends with a question mark or not, etc. We show that the presented features have resulted in an increased accuracy across six of the seven datasets we've experimented with and which are all benchmarked. Since the developed model out-performs all existing Arabic sentiment analysis systems that have publicly available datasets, we can state that this model presents state-of-the-art in Arabic sentiment analysis.
Toward a full-scale neural machine translation in production: the Booking.com use case
Sep 25, 2017
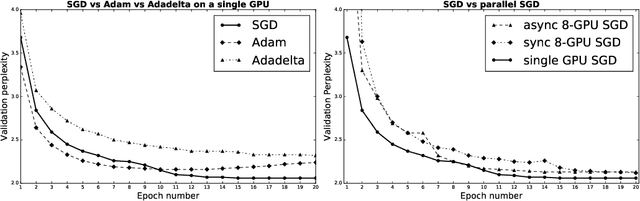
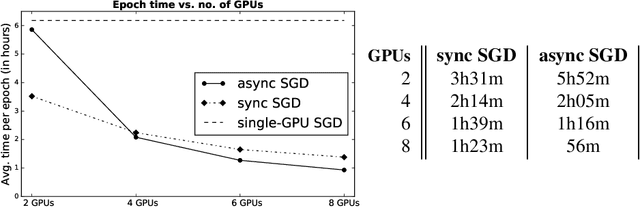

Abstract:While some remarkable progress has been made in neural machine translation (NMT) research, there have not been many reports on its development and evaluation in practice. This paper tries to fill this gap by presenting some of our findings from building an in-house travel domain NMT system in a large scale E-commerce setting. The three major topics that we cover are optimization and training (including different optimization strategies and corpus sizes), handling real-world content and evaluating results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge