Fedor Kovalev
Multi-Domain Adaptation in Neural Machine Translation Through Multidimensional Tagging
Feb 19, 2021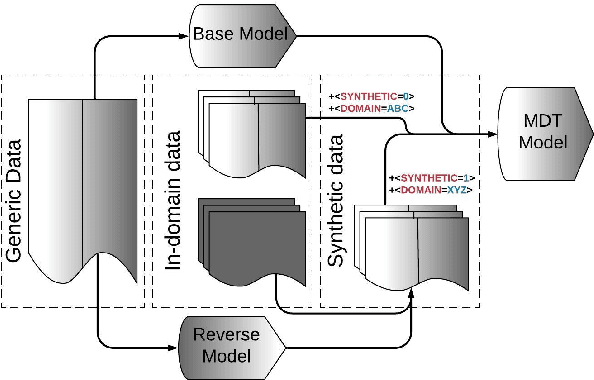
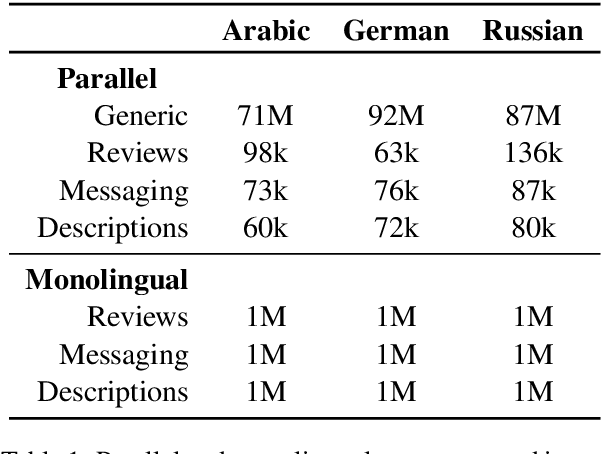
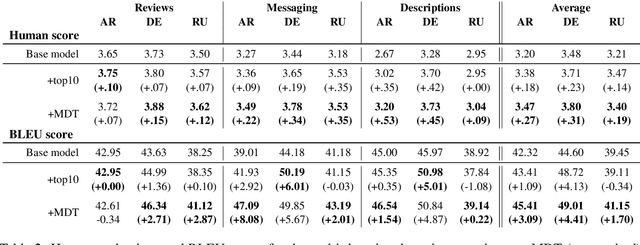
Abstract:Many modern Neural Machine Translation (NMT) systems are trained on nonhomogeneous datasets with several distinct dimensions of variation (e.g. domain, source, generation method, style, etc.). We describe and empirically evaluate multidimensional tagging (MDT), a simple yet effective method for passing sentence-level information to the model. Our human and BLEU evaluation results show that MDT can be applied to the problem of multi-domain adaptation and significantly reduce training costs without sacrificing the translation quality on any of the constituent domains.
Toward a full-scale neural machine translation in production: the Booking.com use case
Sep 25, 2017
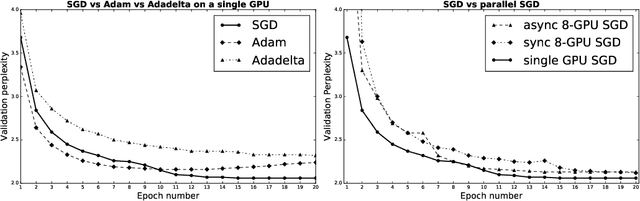
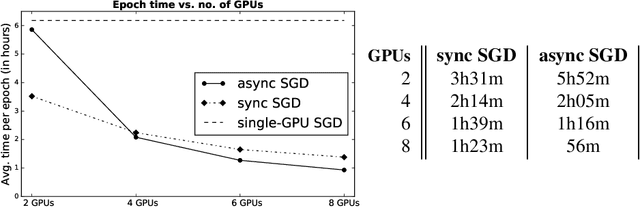

Abstract:While some remarkable progress has been made in neural machine translation (NMT) research, there have not been many reports on its development and evaluation in practice. This paper tries to fill this gap by presenting some of our findings from building an in-house travel domain NMT system in a large scale E-commerce setting. The three major topics that we cover are optimization and training (including different optimization strategies and corpus sizes), handling real-world content and evaluating results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge