Takahiro Ito
Frailty Care Robot for Elderly and Its Application for Physical and Psychological Support
Nov 20, 2021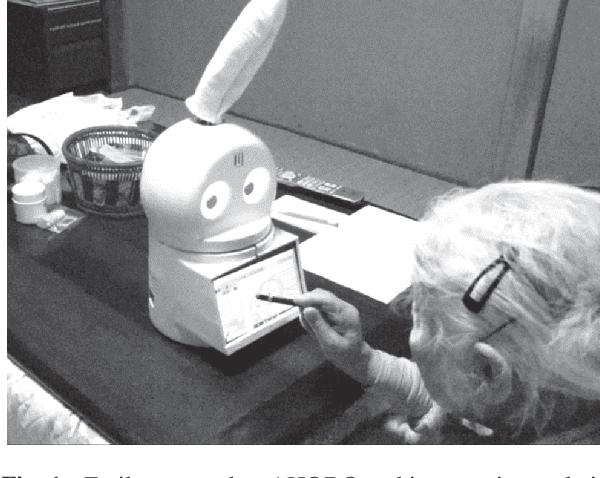

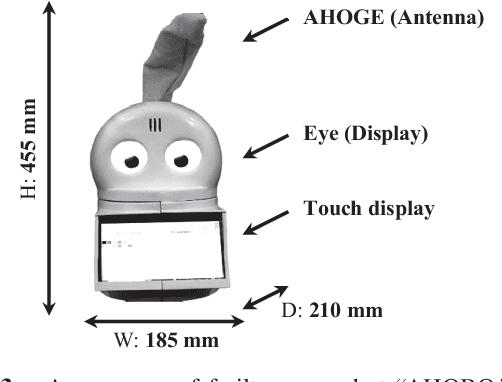
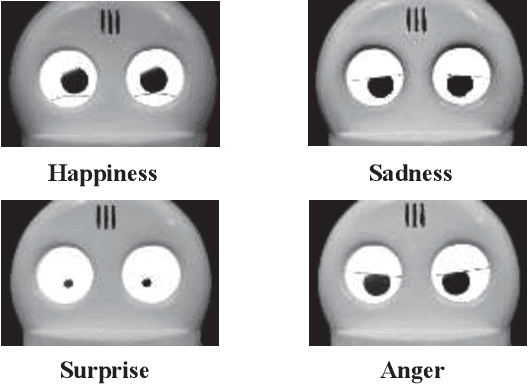
Abstract:To achieve continuous frail care in the daily lives of the elderly, we propose AHOBO, a frail care robot for the elderly at home. Two types of support systems by AHOBO were implemented to support the elderly in both physical health and psychological aspects. For physical health frailty care, we focused on blood pressure and developed a support system for blood pressure measurement with AHOBO. For psychological frailty care, we implemented reminiscent coloring with the AHOBO as a recreational activity with the robot. The usability of the system was evaluated based on the assumption of continuous use in daily life. For the support system in blood pressure measurement, we performed a qualitative evaluation using a questionnaire for 16 subjects, including elderly people under blood pressure measurement by the system. The results confirmed that the proposed robot does not affect the blood pressure readings and is acceptable in terms of ease of use based on subjective evaluation. For the reminiscent coloring interaction, a subjective evaluation was conducted on two elderly people under the verbal fluency task, and it has been confirmed that the interaction can be used continuously in daily life. The widespread use of the proposed robot as an interface for AI that supports daily life will lead to a society in which AI robots support people from the cradle to the grave.
* 9 pages, 15 figures, J. Adv. Comput. Intell. Intell. Inform.(JACIII)
Dense Pixel-wise Micro-motion Estimation of Object Surface by using Low Dimensional Embedding of Laser Speckle Pattern
Oct 31, 2020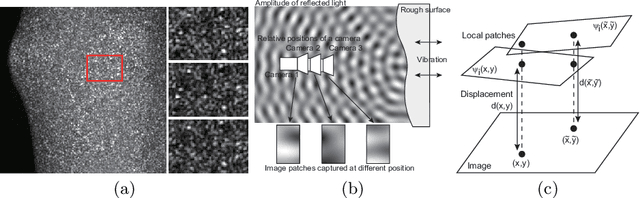
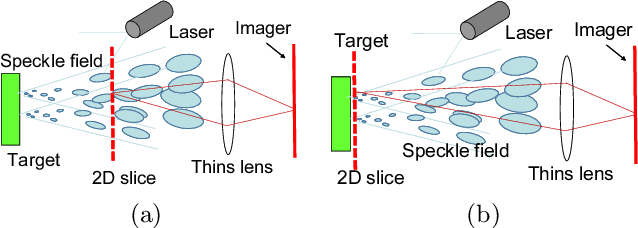

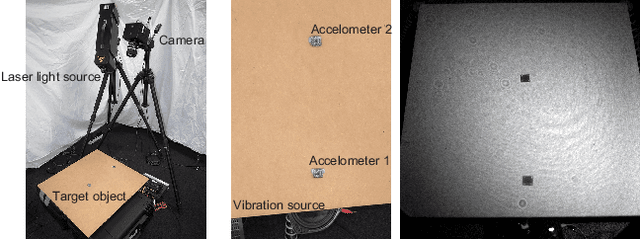
Abstract:This paper proposes a method of estimating micro-motion of an object at each pixel that is too small to detect under a common setup of camera and illumination. The method introduces an active-lighting approach to make the motion visually detectable. The approach is based on speckle pattern, which is produced by the mutual interference of laser light on object's surface and continuously changes its appearance according to the out-of-plane motion of the surface. In addition, speckle pattern becomes uncorrelated with large motion. To compensate such micro- and large motion, the method estimates the motion parameters up to scale at each pixel by nonlinear embedding of the speckle pattern into low-dimensional space. The out-of-plane motion is calculated by making the motion parameters spatially consistent across the image. In the experiments, the proposed method is compared with other measuring devices to prove the effectiveness of the method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge