Tahir Syed
Efficient Learning Under Density Shift in Incremental Settings Using Cramér-Rao-Based Regularization
Feb 18, 2025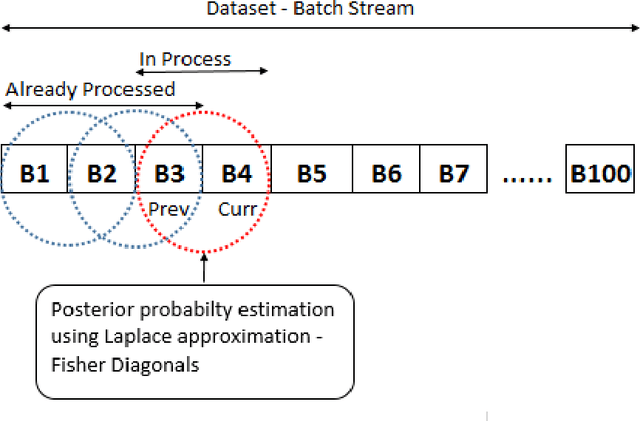
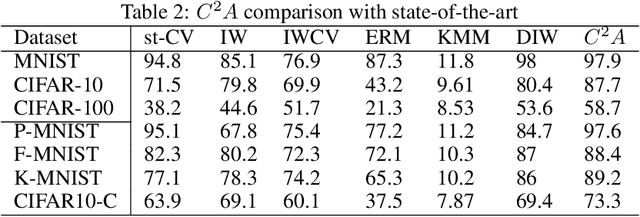
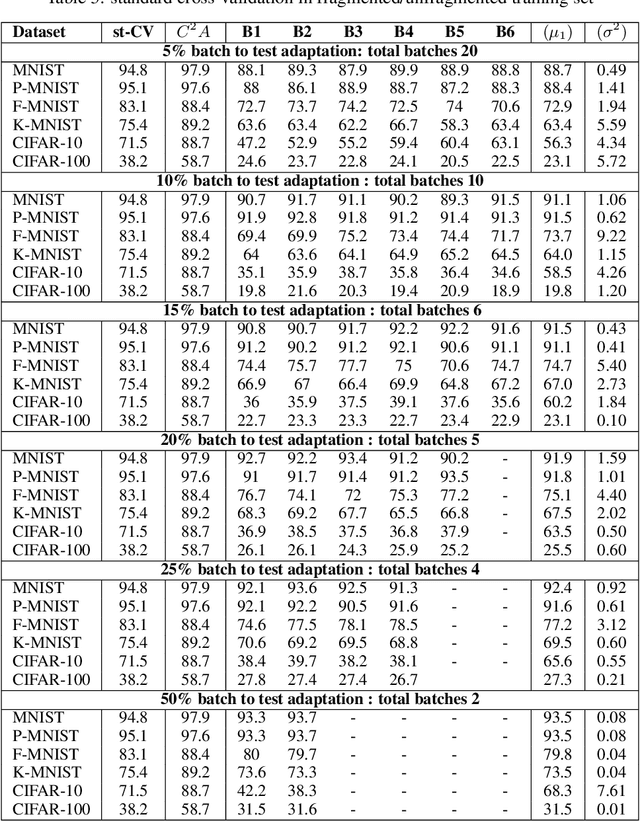
Abstract:The continuous surge in data volume and velocity is often dealt with using data orchestration and distributed processing approaches, abstracting away the machine learning challenges that exist at the algorithmic level. With growing interest in automating the learning loop, training with data that arrive in a sequence rather than in the classical in-memory training data form will face a machine learning challenge because of evolving feature distributions across batches of training data biasing the cross-validation step (\cite{sugiyama2012machine}). This work takes a distributed density estimation angle to the problem where data are temporally distributed. It processes data in batches and allows a neural network to treat a batch as training data. The method accumulates knowledge about the data density via posterior probability absorption using the Fisher Information Matrix, which contains information about the local optimization gradients for the batch. This is then used as a regularizer for the loss in the following batch, and therefore the density estimate for the entire dataset constructively gets more robust to the non-iid distribution shift. This needs the presence of a pair of batches in memory at a time, so the space cost is not a function of the size of the complete, distributed dataset. We proposed a novel regularization-based approach Covariate Shift Correction $C^{2}A$ that leverages Fisher information and Kullback-Leibler divergence to adapt to both natural and sequential covariate shift caused by dataset fragmentation. $C^{2}A$ achieves $19\%$ accuracy at maximum against state-of-the-art methods.
Multimodal HIE Lesion Segmentation in Neonates: A Comparative Study of Loss Functions
Feb 13, 2025


Abstract:Segmentation of Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) lesions in neonatal MRI is a crucial but challenging task due to diffuse multifocal lesions with varying volumes and the limited availability of annotated HIE lesion datasets. Using the BONBID-HIE dataset, we implemented a 3D U-Net with optimized preprocessing, augmentation, and training strategies to overcome data constraints. The goal of this study is to identify the optimal loss function specifically for the HIE lesion segmentation task. To this end, we evaluated various loss functions, including Dice, Dice-Focal, Tversky, Hausdorff Distance (HausdorffDT) Loss, and two proposed compound losses -- Dice-Focal-HausdorffDT and Tversky-HausdorffDT -- to enhance segmentation performance. The results show that different loss functions predict distinct segmentation masks, with compound losses outperforming standalone losses. Tversky-HausdorffDT Loss achieves the highest Dice and Normalized Surface Dice scores, while Dice-Focal-HausdorffDT Loss minimizes Mean Surface Distance. This work underscores the significance of task-specific loss function optimization, demonstrating that combining region-based and boundary-aware losses leads to more accurate HIE lesion segmentation, even with limited training data.
Latents of latents to delineate pixels: hybrid Matryoshka autoencoder-to-U-Net pairing for segmenting large medical images in GPU-poor and low-data regimes
Feb 13, 2025

Abstract:Medical images are often high-resolution and lose important detail if downsampled, making pixel-level methods such as semantic segmentation much less efficient if performed on a low-dimensional image. We propose a low-rank Matryoshka projection and a hybrid segmenting architecture that preserves important information while retaining sufficient pixel geometry for pixel-level tasks. We design the Matryoshka Autoencoder (MatAE-U-Net) which combines the hierarchical encoding of the Matryoshka Autoencoder with the spatial reconstruction capabilities of a U-Net decoder, leveraging multi-scale feature extraction and skip connections to enhance accuracy and generalisation. We apply it to the problem of segmenting the left ventricle (LV) in echocardiographic images using the Stanford EchoNet-D dataset, including 1,000 standardised video-mask pairs of cardiac ultrasound videos resized to 112x112 pixels. The MatAE-UNet model achieves a Mean IoU of 77.68\%, Mean Pixel Accuracy of 97.46\%, and Dice Coefficient of 86.91\%, outperforming the baseline U-Net, which attains a Mean IoU of 74.70\%, Mean Pixel Accuracy of 97.31\%, and Dice Coefficient of 85.20\%. The results highlight the potential of using the U-Net in the recursive Matroshka latent space for imaging problems with low-contrast such as echocardiographic analysis.
Technical note on calibrating vision-language models under covariate shift
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Despite being a successful example of emerging capability, vision-language foundation models for low-shot vision classification have a limited ability to sufficiently generalize to the target data distribution due to sample poverty, leading to sensitivity to variations in the data. A popular mitigation strategy is finetuning over multiple datasets, but domain generalization is expensive when practiced in this manner. This work examines both covariate shift between pre-training data and the underspecified target data, and \textit{confidence misalignment}, where the model's prediction confidence amplified by the limited data availability. We propose \textit{Confidence-Calibrated Covariate Shift Correction ($C3SC$)}, a unified framework to mitigate both covariate shift and confidence misalignment. $C3SC$ leverages Fisher information penalty for covariate shift correction and confidence misalignment penalty (CMP) to lower confidence on misclassified examples. Experimental results across various vision and covariate shift datasets demonstrates that $C3SC$ significantly improves in calibration (ECE) by $5.82\%$ at maximum. $C3SC$ shows better robustness as well by showing $3.5\%$ improvement in accuracy metric on challenging covariate shift datasets, making $C3SC$ a promising solution for reliable real-world vision-language low-shot applications under distribution shift.
Technical report on label-informed logit redistribution for better domain generalization in low-shot classification with foundation models
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Confidence calibration is an emerging challenge in real-world decision systems based on foundations models when used for downstream vision classification tasks. Due to various reasons exposed, logit scores on the CLIP head remain large irrespective of whether the image-language pairs reconcile. It is difficult to address in data space, given the few-shot regime. We propose a penalty incorporated into loss objective that penalizes incorrect classifications whenever one is made during finetuning, by moving an amount of log-likelihood to the true class commensurate to the relative amplitudes of the two likelihoods. We refer to it as \textit{confidence misalignment penalty (CMP)}. Extensive experiments on $12$ vision datasets and $5$ domain generalization datasets supports the calibration performance of our method against stat-of-the-art. CMP outperforms the benchmarked prompt learning methods, demonstrating average improvement in Expected Calibration Error (ECE) by average $6.01$\%, $4.01$ \% at minimum and $9.72$\% at maximum.
Mitigating covariate shift in non-colocated data with learned parameter priors
Nov 10, 2024Abstract:When training data are distributed across{ time or space,} covariate shift across fragments of training data biases cross-validation, compromising model selection and assessment. We present \textit{Fragmentation-Induced covariate-shift Remediation} ($FIcsR$), which minimizes an $f$-divergence between a fragment's covariate distribution and that of the standard cross-validation baseline. We s{how} an equivalence with popular importance-weighting methods. {The method}'s numerical solution poses a computational challenge owing to the overparametrized nature of a neural network, and we derive a Fisher Information approximation. When accumulated over fragments, this provides a global estimate of the amount of shift remediation thus far needed, and we incorporate that as a prior via the minimization objective. In the paper, we run extensive classification experiments on multiple data classes, over $40$ datasets, and with data batched over multiple sequence lengths. We extend the study to the $k$-fold cross-validation setting through a similar set of experiments. An ablation study exposes the method to varying amounts of shift and demonstrates slower degradation with $FIcsR$ in place. The results are promising under all these conditions; with improved accuracy against batch and fold state-of-the-art by more than $5\%$ and $10\%$, respectively.
Textual analysis of End User License Agreement for red-flagging potentially malicious software
Mar 11, 2024Abstract:New software and updates are downloaded by end users every day. Each dowloaded software has associated with it an End Users License Agreements (EULA), but this is rarely read. An EULA includes information to avoid legal repercussions. However,this proposes a host of potential problems such as spyware or producing an unwanted affect in the target system. End users do not read these EULA's because of length of the document and users find it extremely difficult to understand. Text summarization is one of the relevant solution to these kind of problems. This require a solution which can summarize the EULA and classify the EULA as "Benign" or "Malicious". We propose a solution in which we have summarize the EULA and classify the EULA as "Benign" or "Malicious". We extract EULA text of different sofware's then we classify the text using eight different supervised classifiers. we use ensemble learning to classify the EULA as benign or malicious using five different text summarization methods. An accuracy of $95.8$\% shows the effectiveness of the presented approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge