Szu-Lin Wu
Interrupted and cascaded permutation invariant training for speech separation
Oct 28, 2019
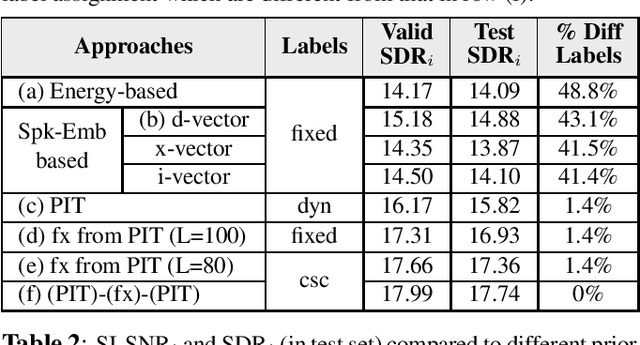
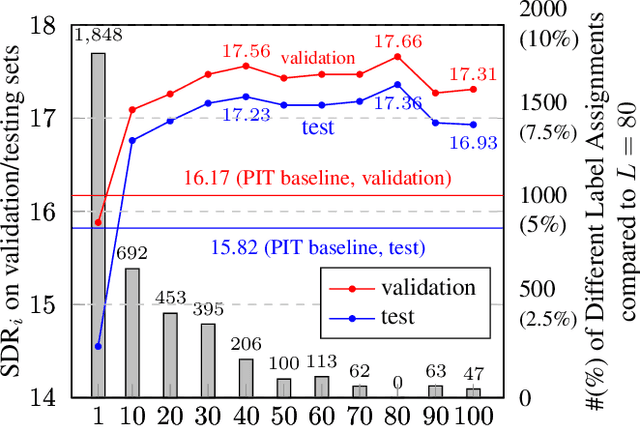
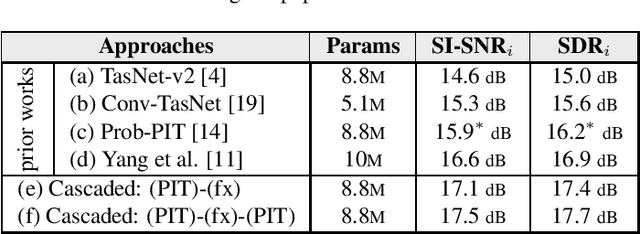
Abstract:Permutation Invariant Training (PIT) has long been a stepping stone method for training speech separation model in handling the label ambiguity problem. With PIT selecting the minimum cost label assignments dynamically, very few studies considered the separation problem to be optimizing both the model parameters and the label assignments, but focused on searching for good model architecture and parameters. In this paper, we investigate instead for a given model architecture the various flexible label assignment strategies for training the model, rather than directly using PIT. Surprisingly, we discover a significant performance boost compared to PIT is possible if the model is trained with fixed label assignments and a good set of labels is chosen. With fixed label training cascaded between two sections of PIT, we achieved the state-of-the-art performance on WSJ0-2mix without changing the model architecture at all.
Spoken SQuAD: A Study of Mitigating the Impact of Speech Recognition Errors on Listening Comprehension
Apr 01, 2018



Abstract:Reading comprehension has been widely studied. One of the most representative reading comprehension tasks is Stanford Question Answering Dataset (SQuAD), on which machine is already comparable with human. On the other hand, accessing large collections of multimedia or spoken content is much more difficult and time-consuming than plain text content for humans. It's therefore highly attractive to develop machines which can automatically understand spoken content. In this paper, we propose a new listening comprehension task - Spoken SQuAD. On the new task, we found that speech recognition errors have catastrophic impact on machine comprehension, and several approaches are proposed to mitigate the impact.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge