Syed Kazmi
A Concurrent CNN-RNN Approach for Multi-Step Wind Power Forecasting
Jan 02, 2023Abstract:Wind power forecasting helps with the planning for the power systems by contributing to having a higher level of certainty in decision-making. Due to the randomness inherent to meteorological events (e.g., wind speeds), making highly accurate long-term predictions for wind power can be extremely difficult. One approach to remedy this challenge is to utilize weather information from multiple points across a geographical grid to obtain a holistic view of the wind patterns, along with temporal information from the previous power outputs of the wind farms. Our proposed CNN-RNN architecture combines convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to extract spatial and temporal information from multi-dimensional input data to make day-ahead predictions. In this regard, our method incorporates an ultra-wide learning view, combining data from multiple numerical weather prediction models, wind farms, and geographical locations. Additionally, we experiment with global forecasting approaches to understand the impact of training the same model over the datasets obtained from multiple different wind farms, and we employ a method where spatial information extracted from convolutional layers is passed to a tree ensemble (e.g., Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM)) instead of fully connected layers. The results show that our proposed CNN-RNN architecture outperforms other models such as LGBM, Extra Tree regressor and linear regression when trained globally, but fails to replicate such performance when trained individually on each farm. We also observe that passing the spatial information from CNN to LGBM improves its performance, providing further evidence of CNN's spatial feature extraction capabilities.
Auto Response Generation in Online Medical Chat Services
Apr 26, 2021

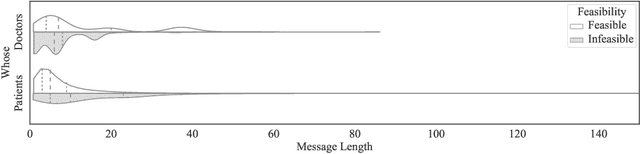
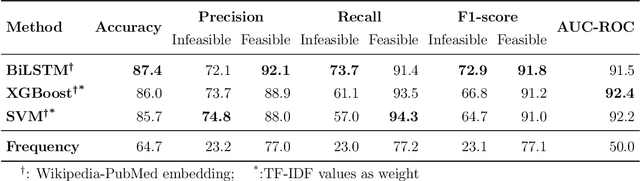
Abstract:Telehealth helps to facilitate access to medical professionals by enabling remote medical services for the patients. These services have become gradually popular over the years with the advent of necessary technological infrastructure. The benefits of telehealth have been even more apparent since the beginning of the COVID-19 crisis, as people have become less inclined to visit doctors in person during the pandemic. In this paper, we focus on facilitating the chat sessions between a doctor and a patient. We note that the quality and efficiency of the chat experience can be critical as the demand for telehealth services increases. Accordingly, we develop a smart auto-response generation mechanism for medical conversations that helps doctors respond to consultation requests efficiently, particularly during busy sessions. We explore over 900,000 anonymous, historical online messages between doctors and patients collected over nine months. We implement clustering algorithms to identify the most frequent responses by doctors and manually label the data accordingly. We then train machine learning algorithms using this preprocessed data to generate the responses. The considered algorithm has two steps: a filtering (i.e., triggering) model to filter out infeasible patient messages and a response generator to suggest the top-3 doctor responses for the ones that successfully pass the triggering phase. The method provides an accuracy of 83.28\% for precision@3 and shows robustness to its parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge