Susmita Ghosh
Revisiting Aerial Scene Classification on the AID Benchmark
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Aerial images play a vital role in urban planning and environmental preservation, as they consist of various structures, representing different types of buildings, forests, mountains, and unoccupied lands. Due to its heterogeneous nature, developing robust models for scene classification remains a challenge. In this study, we conduct a literature review of various machine learning methods for aerial image classification. Our survey covers a range of approaches from handcrafted features (e.g., SIFT, LBP) to traditional CNNs (e.g., VGG, GoogLeNet), and advanced deep hybrid networks. In this connection, we have also designed Aerial-Y-Net, a spatial attention-enhanced CNN with multi-scale feature fusion mechanism, which acts as an attention-based model and helps us to better understand the complexities of aerial images. Evaluated on the AID dataset, our model achieves 91.72% accuracy, outperforming several baseline architectures.
Automated COVID-19 CT Image Classification using Multi-head Channel Attention in Deep CNN
Aug 12, 2023



Abstract:The rapid spread of COVID-19 has necessitated efficient and accurate diagnostic methods. Computed Tomography (CT) scan images have emerged as a valuable tool for detecting the disease. In this article, we present a novel deep learning approach for automated COVID-19 CT scan classification where a modified Xception model is proposed which incorporates a newly designed channel attention mechanism and weighted global average pooling to enhance feature extraction thereby improving classification accuracy. The channel attention module selectively focuses on informative regions within each channel, enabling the model to learn discriminative features for COVID-19 detection. Experiments on a widely used COVID-19 CT scan dataset demonstrate a very good accuracy of 96.99% and show its superiority to other state-of-the-art techniques. This research can contribute to the ongoing efforts in using artificial intelligence to combat current and future pandemics and can offer promising and timely solutions for efficient medical image analysis tasks.
Introducing Feature Attention Module on Convolutional Neural Network for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a leading cause of blindness among diabetic patients. Deep learning models have shown promising results in automating the detection of DR. In the present work, we propose a new methodology that integrates a feature attention module with a pretrained VGG19 convolutional neural network (CNN) for more accurate DR detection. Here, the pretrained net is fine-tuned with the proposed feature attention block. The proposed module aims to leverage the complementary information from various regions of fundus images to enhance the discriminative power of the CNN. The said feature attention module incorporates an attention mechanism which selectively highlights salient features from images and fuses them with the original input. The simultaneous learning of attention weights for the features and thereupon the combination of attention-modulated features within the feature attention block facilitates the network's ability to focus on relevant information while reducing the impact of noisy or irrelevant features. Performance of the proposed method has been evaluated on a widely used dataset for diabetic retinopathy classification e.g., the APTOS (Asia Pacific Tele-Ophthalmology Society) DR Dataset. Results are compared with/without attention module, as well as with other state-of-the-art approaches. Results confirm that the introduction of the fusion module (fusing of feature attention module with CNN) improves the accuracy of DR detection achieving an accuracy of 95.70%.
Transfer-Ensemble Learning based Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Diabetic Retinopathy Classification
Aug 01, 2023



Abstract:This article aims to classify diabetic retinopathy (DR) disease into five different classes using an ensemble approach based on two popular pre-trained convolutional neural networks: VGG16 and Inception V3. The proposed model aims to leverage the strengths of the two individual nets to enhance the classification performance for diabetic retinopathy. The ensemble model architecture involves freezing a portion of the layers in each pre-trained model to utilize their learned representations effectively. Global average pooling layers are added to transform the output feature maps into fixed-length vectors. These vectors are then concatenated to form a consolidated representation of the input image. The ensemble model is trained using a dataset of diabetic retinopathy images (APTOS), divided into training and validation sets. During the training process, the model learns to classify the retinal images into the corresponding diabetic retinopathy classes. Experimental results on the test set demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed ensemble model for DR classification achieving an accuracy of 96.4%.
T-Fusion Net: A Novel Deep Neural Network Augmented with Multiple Localizations based Spatial Attention Mechanisms for Covid-19 Detection
Jul 31, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, deep neural networks are yielding better performance in image classification tasks. However, the increasing complexity of datasets and the demand for improved performance necessitate the exploration of innovative techniques. The present work proposes a new deep neural network (called as, T-Fusion Net) that augments multiple localizations based spatial attention. This attention mechanism allows the network to focus on relevant image regions, improving its discriminative power. A homogeneous ensemble of the said network is further used to enhance image classification accuracy. For ensembling, the proposed approach considers multiple instances of individual T-Fusion Net. The model incorporates fuzzy max fusion to merge the outputs of individual nets. The fusion process is optimized through a carefully chosen parameter to strike a balance on the contributions of the individual models. Experimental evaluations on benchmark Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2 CT scan) dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed T-Fusion Net as well as its ensemble. The proposed T-Fusion Net and the homogeneous ensemble model exhibit better performance, as compared to other state-of-the-art methods, achieving accuracy of 97.59% and 98.4%, respectively.
Mutual Information and Ensemble Based Feature Recommender for Renal Cancer Stage Classification
Sep 28, 2022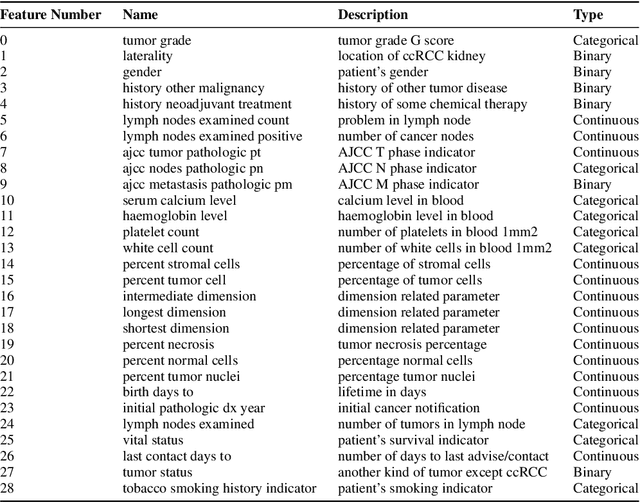
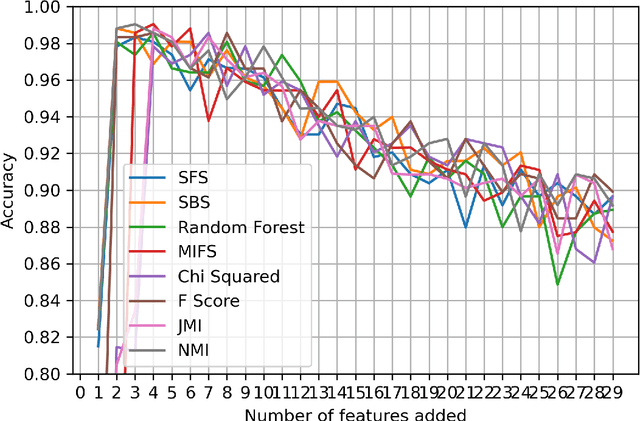
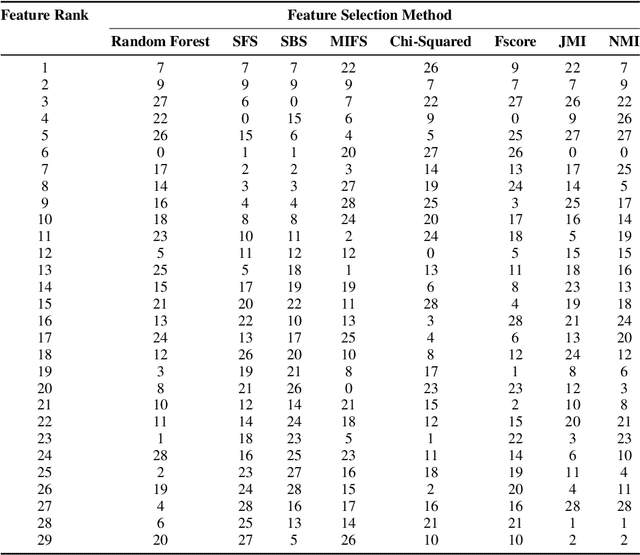
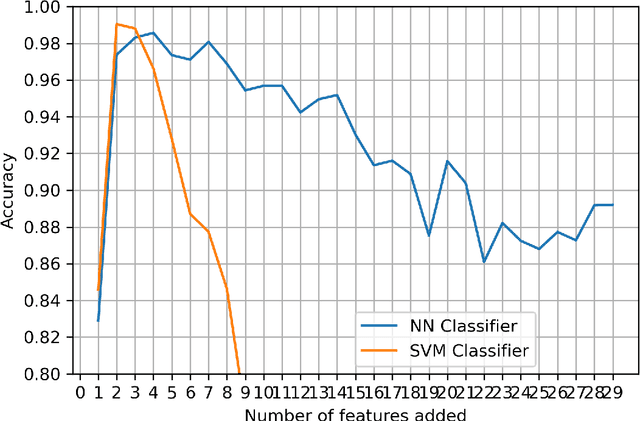
Abstract:Kidney is an essential organ in human body. It maintains homeostasis and removes harmful substances through urine. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common form of kidney cancer. Around 90\% of all kidney cancers are attributed to RCC. Most harmful type of RCC is clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) that makes up about 80\% of all RCC cases. Early and accurate detection of ccRCC is necessary to prevent further spreading of the disease in other organs. In this article, a detailed experimentation is done to identify important features which can aid in diagnosing ccRCC at different stages. The ccRCC dataset is obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). A novel mutual information and ensemble based feature ranking approach considering the order of features obtained from 8 popular feature selection methods is proposed. Performance of the proposed method is evaluated by overall classification accuracy obtained using 2 different classifiers (ANN and SVM). Experimental results show that the proposed feature ranking method is able to attain a higher accuracy (96.6\% and 98.6\% using SVM and NN, respectively) for classifying different stages of ccRCC with a reduced feature set as compared to existing work. It is also to be noted that, out of 3 distinguishing features as mentioned by the existing TNM system (proposed by AJCC and UICC), our proposed method was able to select two of them (size of tumour, metastasis status) as the top-most ones. This establishes the efficacy of our proposed approach.
Autoencoder based Hybrid Multi-Task Predictor Network for Daily Open-High-Low-Close Prices Prediction of Indian Stocks
Apr 28, 2022



Abstract:Stock prices are highly volatile and sudden changes in trends are often very problematic for traditional forecasting models to handle. The standard Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks are regarded as the state-of-the-art models for such predictions. But, these models fail to handle sudden and drastic changes in the price trend. Moreover, there are some inherent constraints with the open, high, low and close (OHLC) prices of the stocks. Literature lacks the study on the inherent property of OHLC prices. We argue that predicting the OHLC prices for the next day is much more informative than predicting the trends of the stocks as the trend is mostly calculated using these OHLC prices only. The problem mainly is focused on Buy-Today Sell-Tomorrow (BTST) trading. In this regard, AEs when pre-trained with the stock prices, may be beneficial. A novel framework is proposed where a pre-trained encoder is cascaded in front of the multi-task predictor network. This hybrid network can leverage the power of a combination of networks and can both handle the OHLC constraints as well as capture any sudden drastic changes in the prices. It is seen that such a network is much more efficient at predicting stock prices. The experiments have been extended to recommend the most profitable and most overbought stocks on the next day. The model has been tested for multiple Indian companies and it is found that the recommendations from the proposed model have not resulted in a single loss for a test period of 300 days.
Combination of Transfer Learning, Recursive Learning and Ensemble Learning for Multi-Day Ahead COVID-19 Cases Prediction in India using Gated Recurrent Unit Networks
Aug 20, 2021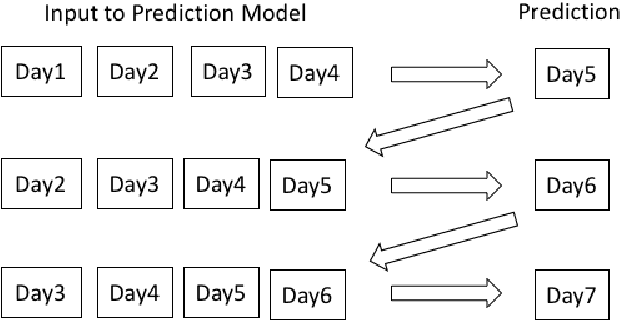



Abstract:The current COVID-19 pandemic has put a huge challenge on the Indian health infrastructure. With more and more people getting affected during the second wave, the hospitals were over-burdened, running out of supplies and oxygen. In this scenario, prediction of the number of COVID-19 cases beforehand might have helped in the better utilization of limited resources and supplies. This manuscript deals with the prediction of new COVID-19 cases, new deaths and total active cases for multiple days in advance. The proposed method uses gated recurrent unit networks as the main predicting model. A study is conducted by building four models that are pre-trained on the data from four different countries (United States of America, Brazil, Spain and Bangladesh) and are fine-tuned or retrained on India's data. Since the four countries chosen have experienced different types of infection curves, the pre-training provides a transfer learning to the models incorporating diverse situations into account. Each of the four models then give a multiple days ahead predictions using recursive learning method for the Indian test data. The final prediction comes from an ensemble of the predictions of the combination of different models. This method with two countries, Spain and Brazil, is seen to achieve the best performance amongst all the combinations as well as compared to other traditional regression models.
Proprties of biclustering algorithms and a novel biclustering technique based on relative density
Nov 12, 2018



Abstract:Biclustering is found to be useful in areas like data mining and bioinformatics. The term biclustering involves searching subsets of observations and features forming coherent structure. This can be interpreted in different ways like spatial closeness, relation between features for selected observations etc. This paper discusses different properties, objectives and approaches of biclustering algorithms. We also present an algorithm which detects feature relation based biclusters using density based techniques. Here we use relative density of regions to identify biclusters embedded in the data. Properties of this algorithm are discussed and demonstrated using artificial datasets. Proposed method is seen to give better results on these datasets using paired right tailed t test. Usefulness of proposed method is also demonstrated using real life datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge