Suo Qiu
Global Weighted Average Pooling Bridges Pixel-level Localization and Image-level Classification
Sep 21, 2018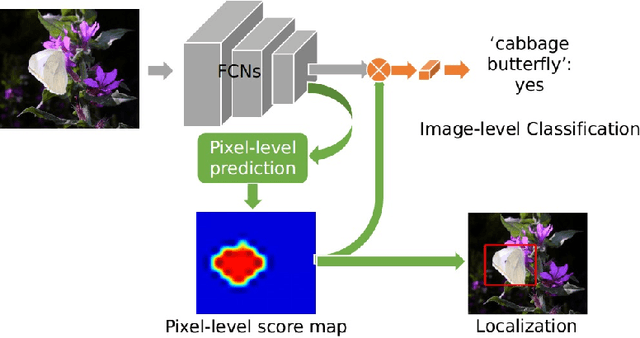
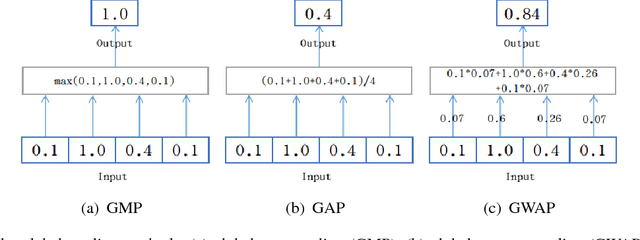
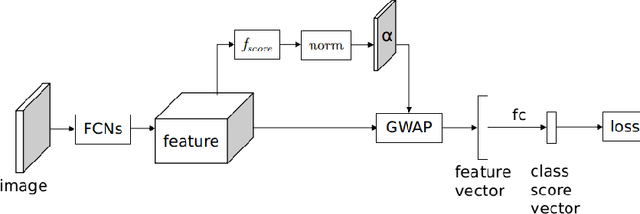
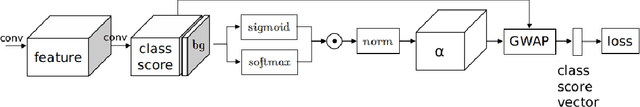
Abstract:In this work, we first tackle the problem of simultaneous pixel-level localization and image-level classification with only image-level labels for fully convolutional network training. We investigate the global pooling method which plays a vital role in this task. Classical global max pooling and average pooling methods are hard to indicate the precise regions of objects. Therefore, we revisit the global weighted average pooling (GWAP) method for this task and propose the class-agnostic GWAP module and the class-specific GWAP module in this paper. We evaluate the classification and pixel-level localization ability on the ILSVRC benchmark dataset. Experimental results show that the proposed GWAP module can better capture the regions of the foreground objects. We further explore the knowledge transfer between the image classification task and the region-based object detection task. We propose a multi-task framework that combines our class-specific GWAP module with R-FCN. The framework is trained with few ground truth bounding boxes and large-scale image-level labels. We evaluate this framework on PASCAL VOC dataset. Experimental results show that this framework can use the data with only image-level labels to improve the generalization of the object detection model.
FReLU: Flexible Rectified Linear Units for Improving Convolutional Neural Networks
Jan 29, 2018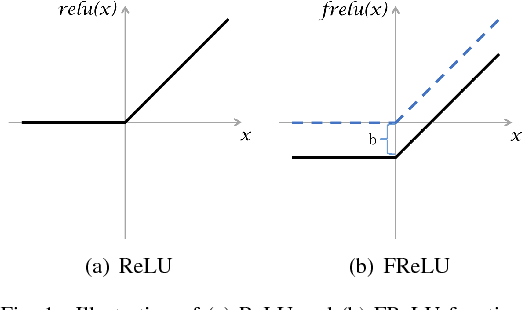
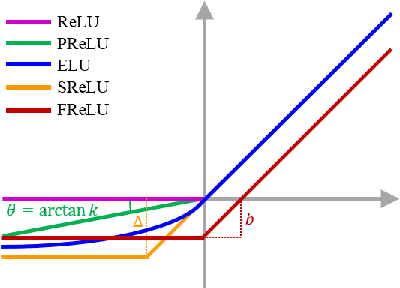

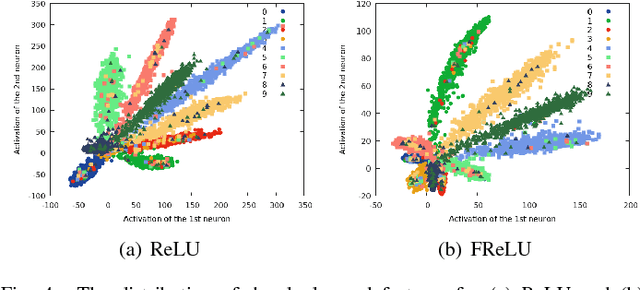
Abstract:Rectified linear unit (ReLU) is a widely used activation function for deep convolutional neural networks. However, because of the zero-hard rectification, ReLU networks miss the benefits from negative values. In this paper, we propose a novel activation function called \emph{flexible rectified linear unit (FReLU)} to further explore the effects of negative values. By redesigning the rectified point of ReLU as a learnable parameter, FReLU expands the states of the activation output. When the network is successfully trained, FReLU tends to converge to a negative value, which improves the expressiveness and thus the performance. Furthermore, FReLU is designed to be simple and effective without exponential functions to maintain low cost computation. For being able to easily used in various network architectures, FReLU does not rely on strict assumptions by self-adaption. We evaluate FReLU on three standard image classification datasets, including CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves fast convergence and higher performances on both plain and residual networks.
Multi-scale Convolutional Neural Networks for Crowd Counting
Feb 08, 2017
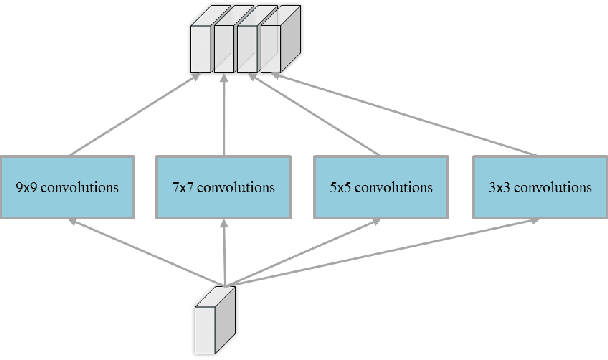
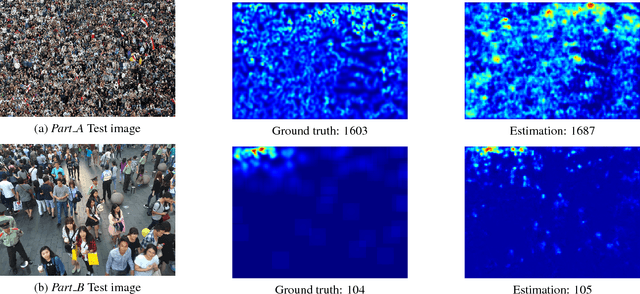
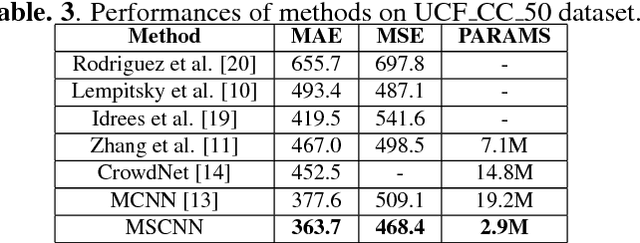
Abstract:Crowd counting on static images is a challenging problem due to scale variations. Recently deep neural networks have been shown to be effective in this task. However, existing neural-networks-based methods often use the multi-column or multi-network model to extract the scale-relevant features, which is more complicated for optimization and computation wasting. To this end, we propose a novel multi-scale convolutional neural network (MSCNN) for single image crowd counting. Based on the multi-scale blobs, the network is able to generate scale-relevant features for higher crowd counting performances in a single-column architecture, which is both accuracy and cost effective for practical applications. Complemental results show that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on both accuracy and robustness with far less number of parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge