Sungwon Woo
A New Benchmark for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning: Redefining the Upper Bound
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Class-incremental learning (CIL) aims to continuously adapt to emerging classes while retaining knowledge of previously learned ones. Few-shot class-incremental learning (FSCIL) presents an even greater challenge which requires the model to learn incremental classes with only a limited number of samples. In conventional CIL, joint training is widely considered the upper bound, serving as both a benchmark and a methodological guide. However, we find that joint training fails to be a meaningful upper bound in FSCIL due to the inherent difficulty of inter-task class separation (ICS) caused by severe class imbalance. In this work, we introduce a new joint training benchmark tailored for FSCIL by integrating imbalance-aware techniques, effectively bridging the performance gap between base and incremental classes. Furthermore, we point out inconsistencies in the experimental setup and evaluation of existing FSCIL methods. To ensure fair comparisons between different FSCIL approaches and joint training, we standardize training conditions and propose a unified evaluation protocol that simultaneously considers the validation set and computational complexity. By establishing a reliable upper bound and a standardized evaluation framework for FSCIL, our work provides a clear benchmark and a practical foundation for future research.
Invisible Watermarks: Attacks and Robustness
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:As Generative AI continues to become more accessible, the case for robust detection of generated images in order to combat misinformation is stronger than ever. Invisible watermarking methods act as identifiers of generated content, embedding image- and latent-space messages that are robust to many forms of perturbations. The majority of current research investigates full-image attacks against images with a single watermarking method applied. We introduce novel improvements to watermarking robustness as well as minimizing degradation on image quality during attack. Firstly, we examine the application of both image-space and latent-space watermarking methods on a single image, where we propose a custom watermark remover network which preserves one of the watermarking modalities while completely removing the other during decoding. Then, we investigate localized blurring attacks (LBA) on watermarked images based on the GradCAM heatmap acquired from the watermark decoder in order to reduce the amount of degradation to the target image. Our evaluation suggests that 1) implementing the watermark remover model to preserve one of the watermark modalities when decoding the other modality slightly improves on the baseline performance, and that 2) LBA degrades the image significantly less compared to uniform blurring of the entire image. Code is available at: https://github.com/tomputer-g/IDL_WAR
Relational Self-supervised Distillation with Compact Descriptors for Image Copy Detection
May 29, 2024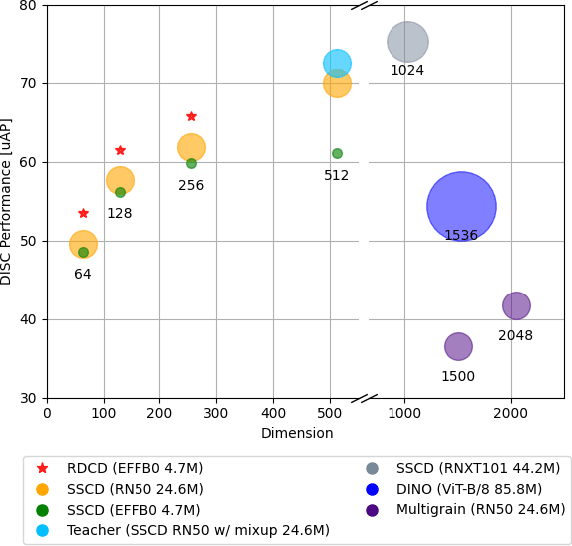
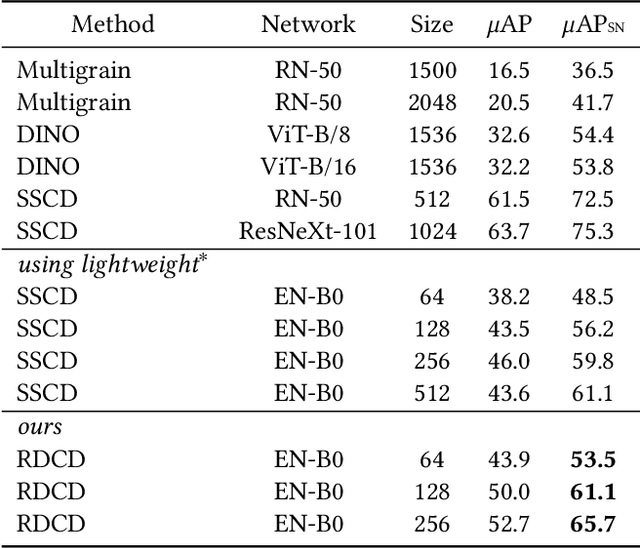
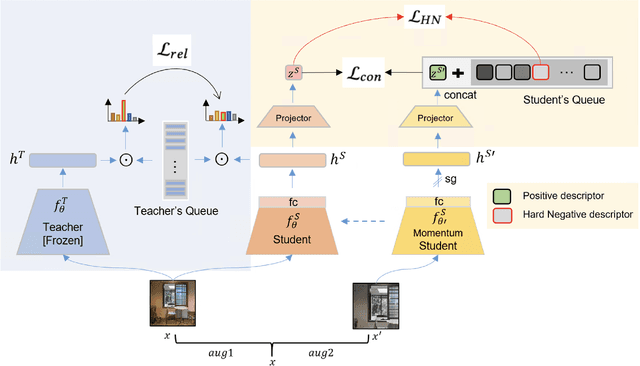

Abstract:This paper addresses image copy detection, a task in online sharing platforms for copyright protection. While previous approaches have performed exceptionally well, the large size of their networks and descriptors remains a significant disadvantage, complicating their practical application. In this paper, we propose a novel method that achieves a competitive performance by using a lightweight network and compact descriptors. By utilizing relational self-supervised distillation to transfer knowledge from a large network to a small network, we enable the training of lightweight networks with a small descriptor size. Our approach, which we call Relational selfsupervised Distillation with Compact Descriptors (RDCD), introduces relational self-supervised distillation (RSD) for flexible representation in a smaller feature space and applies contrastive learning with a hard negative (HN) loss to prevent dimensional collapse. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method using the DISC2021, Copydays, and NDEC benchmark datasets, with which our lightweight network with compact descriptors achieves a competitive performance. For the DISC2021 benchmark, ResNet-50/EfficientNet- B0 are used as a teacher and student respectively, the micro average precision improved by 5.0%/4.9%/5.9% for 64/128/256 descriptor sizes compared to the baseline method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge