Sungchul Lee
Forecasting VIX using interpretable Kolmogorov-Arnold networks
Feb 03, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents the use of Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for forecasting the CBOE Volatility Index (VIX). Unlike traditional MLP-based neural networks that are often criticized for their black-box nature, KAN offers an interpretable approach via learnable spline-based activation functions and symbolification. Based on a parsimonious architecture with symbolic functions, KAN expresses a forecast of the VIX as a closed-form in terms of explanatory variables, and provide interpretable insights into key characteristics of the VIX, including mean reversion and the leverage effect. Through in-depth empirical analysis across multiple datasets and periods, we show that KANs achieve competitive forecasting performance while requiring significantly fewer parameters compared to MLP-based neural network models. Our findings demonstrate the capacity and potential of KAN as an interpretable financial time-series forecasting method.
Deep learning for undersampled MRI reconstruction
Sep 11, 2017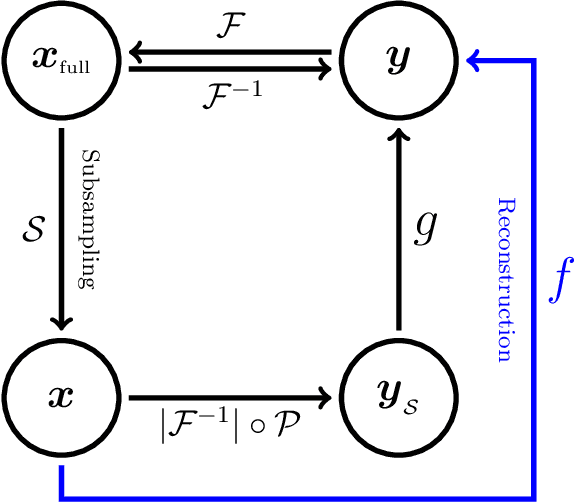

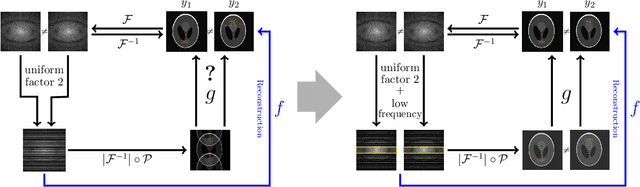
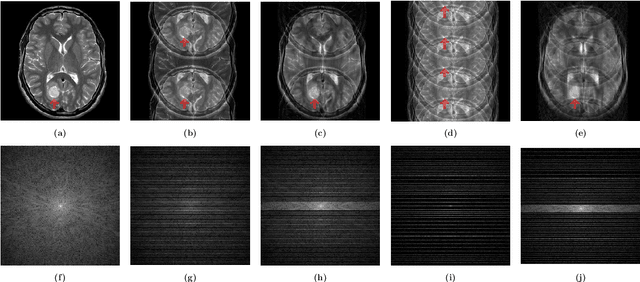
Abstract:This paper presents a deep learning method for faster magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by reducing k-space data with sub-Nyquist sampling strategies and provides a rationale for why the proposed approach works well. Uniform subsampling is used in the time-consuming phase-encoding direction to capture high-resolution image information, while permitting the image-folding problem dictated by the Poisson summation formula. To deal with the localization uncertainty due to image folding, very few low-frequency k-space data are added. Training the deep learning net involves input and output images that are pairs of Fourier transforms of the subsampled and fully sampled k-space data. Numerous experiments show the remarkable performance of the proposed method; only 29% of k-space data can generate images of high quality as effectively as standard MRI reconstruction with fully sampled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge