Hwa Pyung Kim
CT sinogram-consistency learning for metal-induced beam hardening correction
Jan 12, 2018



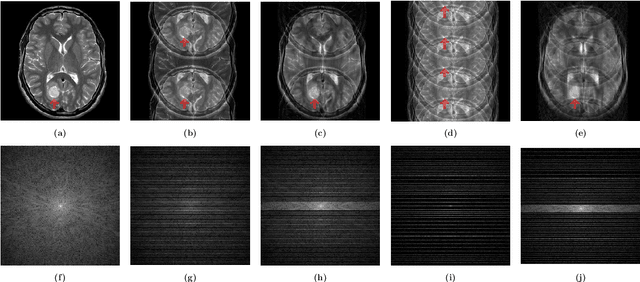
Abstract:This paper proposes a sinogram consistency learning method to deal with beam-hardening related artifacts in polychromatic computerized tomography (CT). The presence of highly attenuating materials in the scan field causes an inconsistent sinogram, that does not match the range space of the Radon transform. When the mismatched data are entered into the range space during CT reconstruction, streaking and shading artifacts are generated owing to the inherent nature of the inverse Radon transform. The proposed learning method aims to repair inconsistent sinograms by removing the primary metal-induced beam-hardening factors along the metal trace in the sinogram. Taking account of the fundamental difficulty in obtaining sufficient training data in a medical environment, the learning method is designed to use simulated training data and a patient-type specific learning model is used to simplify the learning process. The feasibility of the proposed method is investigated using a dataset, consisting of real CT scan of pelvises containing hip prostheses. The anatomical areas in training and test data are different, in order to demonstrate that the proposed method extracts the beam hardening features, selectively. The results show that our method successfully corrects sinogram inconsistency by extracting beam-hardening sources by means of deep learning. This paper proposed a deep learning method of sinogram correction for beam hardening reduction in CT for the first time. Conventional methods for beam hardening reduction are based on regularizations, and have the fundamental drawback of being not easily able to use manifold CT images, while a deep learning approach has the potential to do so.
Deep learning for undersampled MRI reconstruction
Sep 11, 2017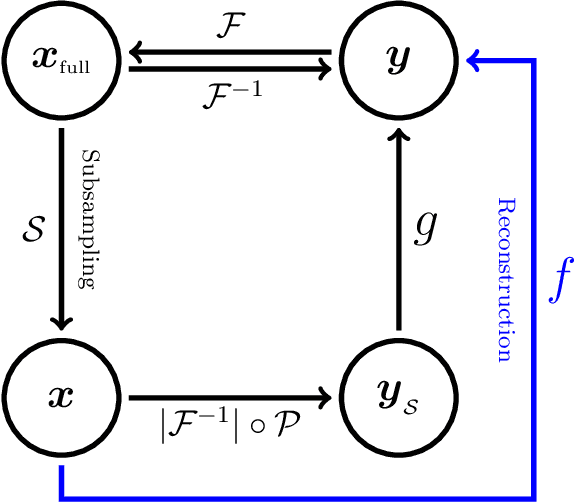

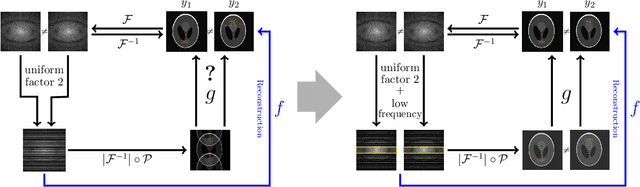
Abstract:This paper presents a deep learning method for faster magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) by reducing k-space data with sub-Nyquist sampling strategies and provides a rationale for why the proposed approach works well. Uniform subsampling is used in the time-consuming phase-encoding direction to capture high-resolution image information, while permitting the image-folding problem dictated by the Poisson summation formula. To deal with the localization uncertainty due to image folding, very few low-frequency k-space data are added. Training the deep learning net involves input and output images that are pairs of Fourier transforms of the subsampled and fully sampled k-space data. Numerous experiments show the remarkable performance of the proposed method; only 29% of k-space data can generate images of high quality as effectively as standard MRI reconstruction with fully sampled data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge