Suling Jia
fETSmcs: Feature-based ETS model component selection
Jun 26, 2022



Abstract:The well-developed ETS (ExponenTial Smoothing or Error, Trend, Seasonality) method incorporating a family of exponential smoothing models in state space representation has been widely used for automatic forecasting. The existing ETS method uses information criteria for model selection by choosing an optimal model with the smallest information criterion among all models fitted to a given time series. The ETS method under such a model selection scheme suffers from computational complexity when applied to large-scale time series data. To tackle this issue, we propose an efficient approach for ETS model selection by training classifiers on simulated data to predict appropriate model component forms for a given time series. We provide a simulation study to show the model selection ability of the proposed approach on simulated data. We evaluate our approach on the widely used forecasting competition data set M4, in terms of both point forecasts and prediction intervals. To demonstrate the practical value of our method, we showcase the performance improvements from our approach on a monthly hospital data set.
Enhancing the Diversity of Predictions Combination by Negative Correlation Learning
Apr 06, 2021
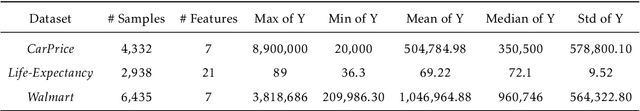
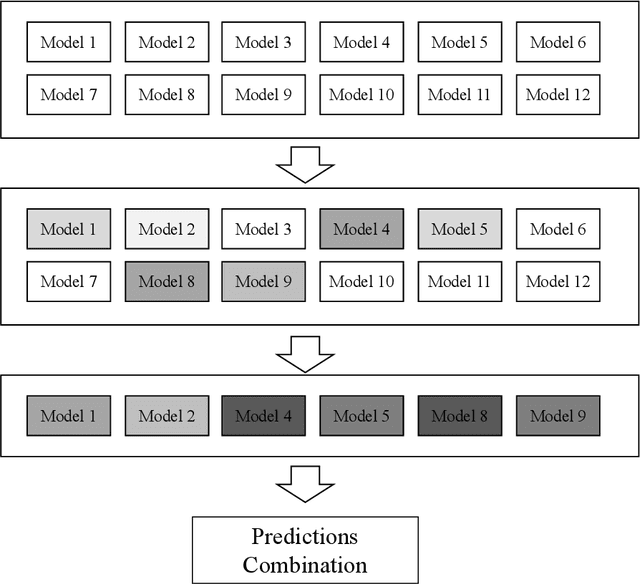
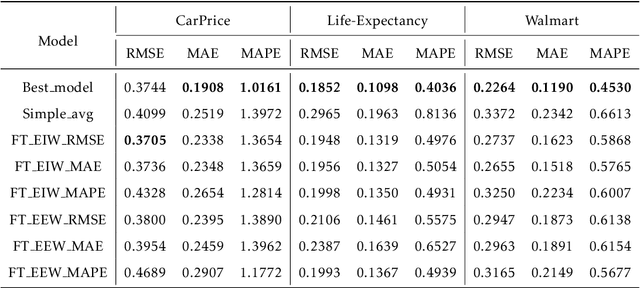
Abstract:Predictions combination, as a combination model approach with adjustments in the output space, has flourished in recent years in research and competitions. Simple average is intuitive and robust, and is often used as a benchmark in predictions combination. However, some poorly performing sub-models can reduce the overall accuracy because the sub-models are not selected in advance. Even though some studies have selected the top sub-models for the combination after ranking them by mean square error, the covariance of them causes this approach to not yield much benefit. In this paper, we suggest to consider the diversity of sub-models in the predictions combination, which can be adopted to assist in selecting the most diverse model subset in the model pool using negative correlation learning. Three publicly available datasets are applied to evaluate the approach. The experimental results not only show the diversity of sub-models in the predictions combination incorporating negative correlation learning, but also produce predictions with accuracy far exceeding that of the simple average benchmark and some weighted average methods. Furthermore, by adjusting the penalty strength for negative correlation, the predictions combination also outperform the best sub-model. The value of this paper lies in its ease of use and effectiveness, allowing the predictions combination to embrace both diversity and accuracy.
Research and application of time series algorithms in centralized purchasing data
Nov 01, 2019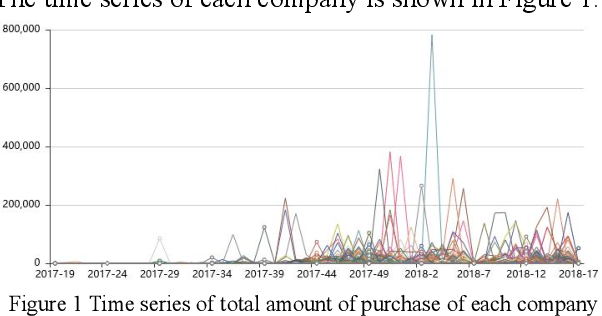
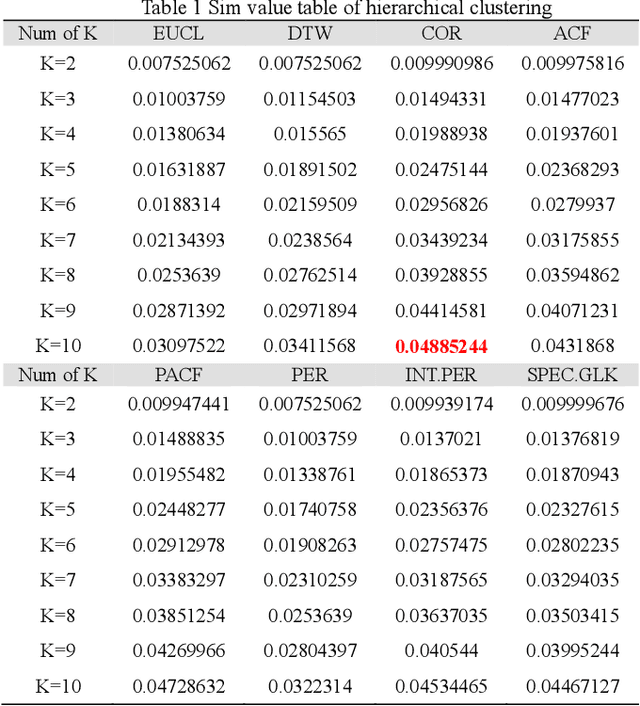
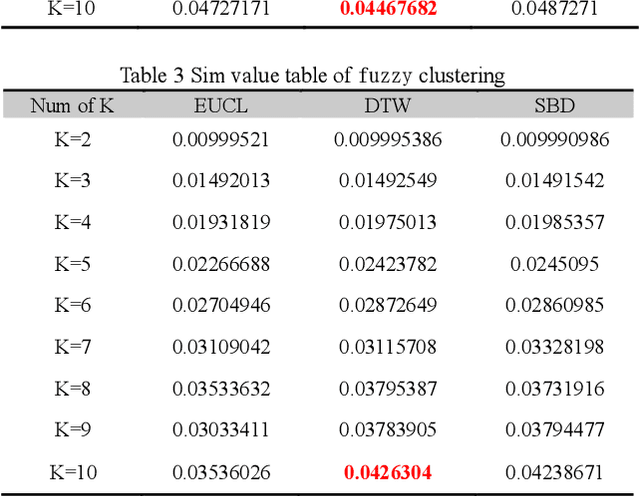
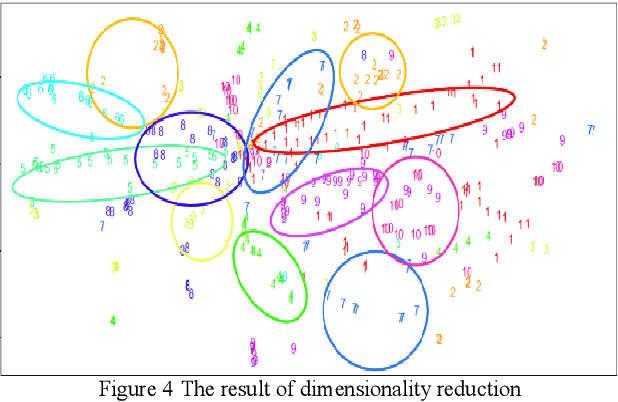
Abstract:Based on the online transaction data of COSCO group's centralized procurement platform, this paper studies the clustering method of time series type data. The different methods of similarity calculation, different clustering methods with different K values are analysed, and the best clustering method suitable for centralized purchasing data is determined. The company list under the corresponding cluster is obtained. The time series motif discovery algorithm is used to model the centroid of each cluster. Through ARIMA method, we also made 12 periods of prediction for the centroid of each category. This paper constructs a matrix of "Customer Lifecycle Theory - Five Elements of Marketing ", and puts forward corresponding marketing suggestions for customers at different life cycle stages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge