Suleyman Cetintas
A Joint Probabilistic Classification Model of Relevant and Irrelevant Sentences in Mathematical Word Problems
Nov 21, 2014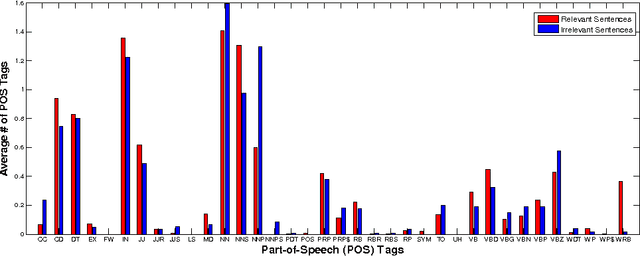


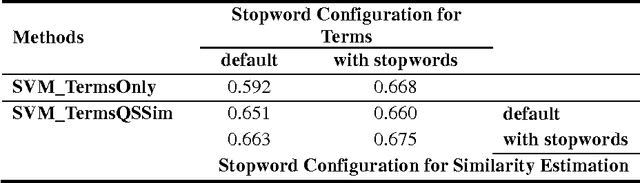
Abstract:Estimating the difficulty level of math word problems is an important task for many educational applications. Identification of relevant and irrelevant sentences in math word problems is an important step for calculating the difficulty levels of such problems. This paper addresses a novel application of text categorization to identify two types of sentences in mathematical word problems, namely relevant and irrelevant sentences. A novel joint probabilistic classification model is proposed to estimate the joint probability of classification decisions for all sentences of a math word problem by utilizing the correlation among all sentences along with the correlation between the question sentence and other sentences, and sentence text. The proposed model is compared with i) a SVM classifier which makes independent classification decisions for individual sentences by only using the sentence text and ii) a novel SVM classifier that considers the correlation between the question sentence and other sentences along with the sentence text. An extensive set of experiments demonstrates the effectiveness of the joint probabilistic classification model for identifying relevant and irrelevant sentences as well as the novel SVM classifier that utilizes the correlation between the question sentence and other sentences. Furthermore, empirical results and analysis show that i) it is highly beneficial not to remove stopwords and ii) utilizing part of speech tagging does not make a significant improvement although it has been shown to be effective for the related task of math word problem type classification.
Visual Sentiment Prediction with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 21, 2014
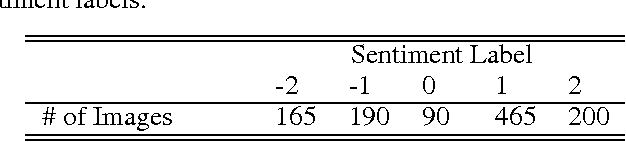
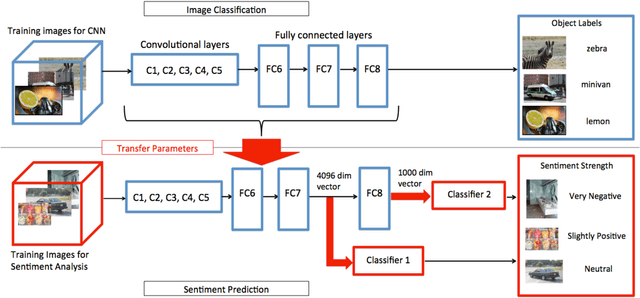
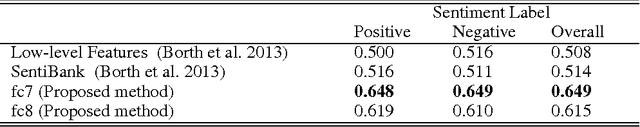
Abstract:Images have become one of the most popular types of media through which users convey their emotions within online social networks. Although vast amount of research is devoted to sentiment analysis of textual data, there has been very limited work that focuses on analyzing sentiment of image data. In this work, we propose a novel visual sentiment prediction framework that performs image understanding with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). Specifically, the proposed sentiment prediction framework performs transfer learning from a CNN with millions of parameters, which is pre-trained on large-scale data for object recognition. Experiments conducted on two real-world datasets from Twitter and Tumblr demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed visual sentiment analysis framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge