Suhail Barot
Question Answering via Web Extracted Tables and Pipelined Models
Apr 16, 2019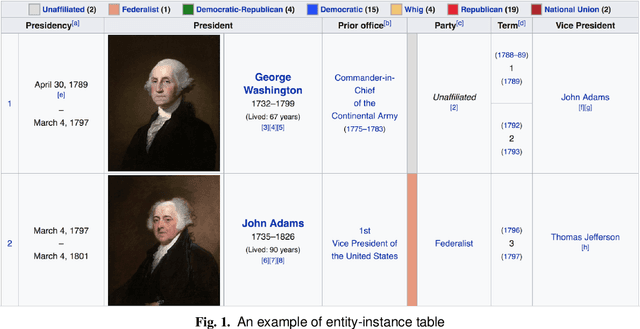
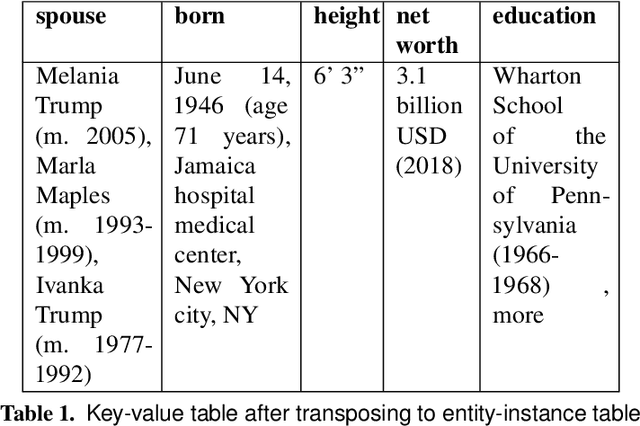
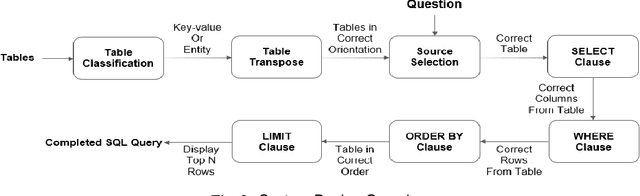
Abstract:In this paper, we describe a dataset and baseline result for a question answering that utilizes web tables. It contains commonly asked questions on the web and their corresponding answers found in tables on websites. Our dataset is novel in that every question is paired with a table of a different signature. In particular, the dataset contains two classes of tables: entity-instance tables and the key-value tables. Each QA instance comprises a table of either kind, a natural language question, and a corresponding structured SQL query. We build our model by dividing question answering into several tasks, including table retrieval and question element classification, and conduct experiments to measure the performance of each task. We extract various features specific to each task and compose a full pipeline which constructs the SQL query from its parts. Our work provides qualitative results and error analysis for each task, and identifies in detail the reasoning required to generate SQL expressions from natural language questions. This analysis of reasoning informs future models based on neural machine learning.
Acronym Disambiguation: A Domain Independent Approach
Dec 17, 2017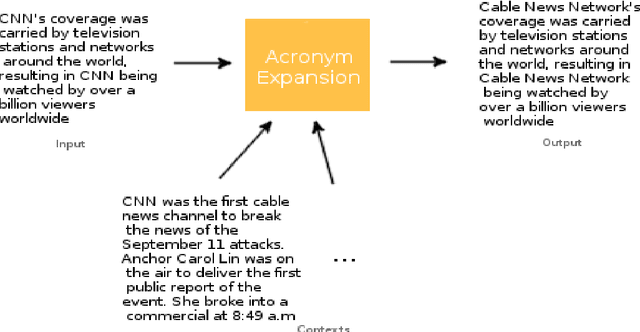
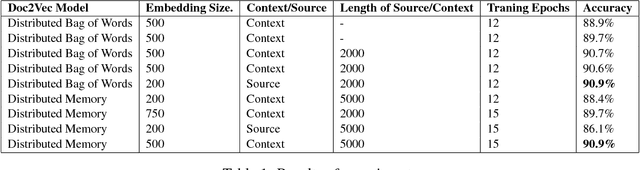
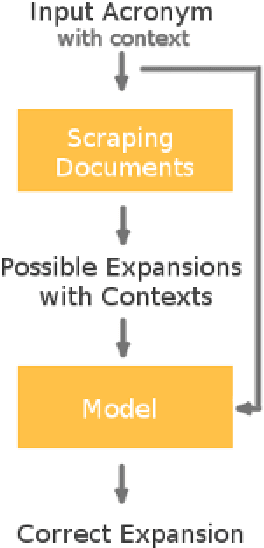
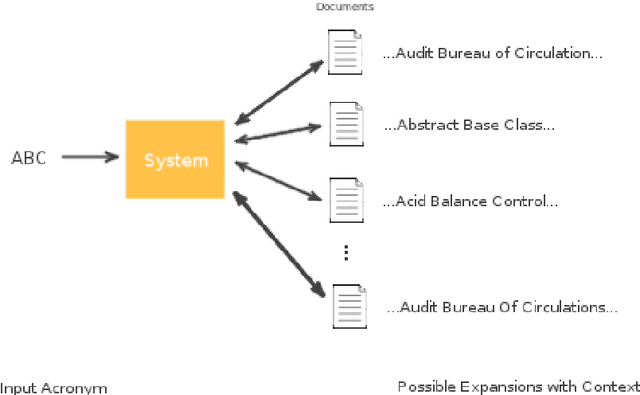
Abstract:Acronyms are omnipresent. They usually express information that is repetitive and well known. But acronyms can also be ambiguous because there can be multiple expansions for the same acronym. In this paper, we propose a general system for acronym disambiguation that can work on any acronym given some context information. We present methods for retrieving all the possible expansions of an acronym from Wikipedia and AcronymsFinder.com. We propose to use these expansions to collect all possible contexts in which these acronyms are used and then score them using a paragraph embedding technique called Doc2Vec. This method collectively led to achieving an accuracy of 90.9% in selecting the correct expansion for given acronym, on a dataset we scraped from Wikipedia with 707 distinct acronyms and 14,876 disambiguations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge