Subhadip Paul
Fraud Analytics Using Machine-learning & Engineering on Big Data (FAME) for Telecom
Oct 31, 2023



Abstract:Telecom industries lose globally 46.3 Billion USD due to fraud. Data mining and machine learning techniques (apart from rules oriented approach) have been used in past, but efficiency has been low as fraud pattern changes very rapidly. This paper presents an industrialized solution approach with self adaptive data mining technique and application of big data technologies to detect fraud and discover novel fraud patterns in accurate, efficient and cost effective manner. Solution has been successfully demonstrated to detect International Revenue Share Fraud with <5% false positive. More than 1 Terra Bytes of Call Detail Record from a reputed wholesale carrier and overseas telecom transit carrier has been used to conduct this study.
Detecting Concept Drift in the Presence of Sparsity -- A Case Study of Automated Change Risk Assessment System
Jul 27, 2022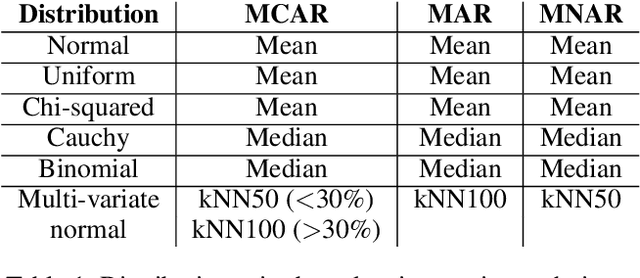
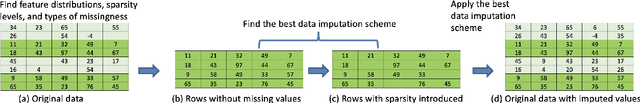
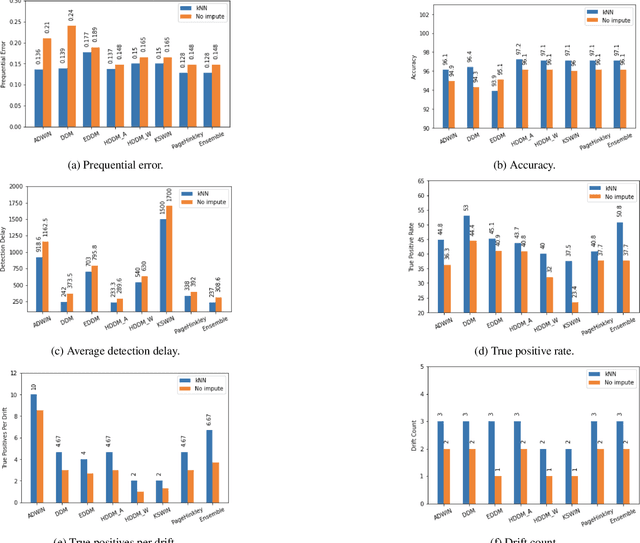
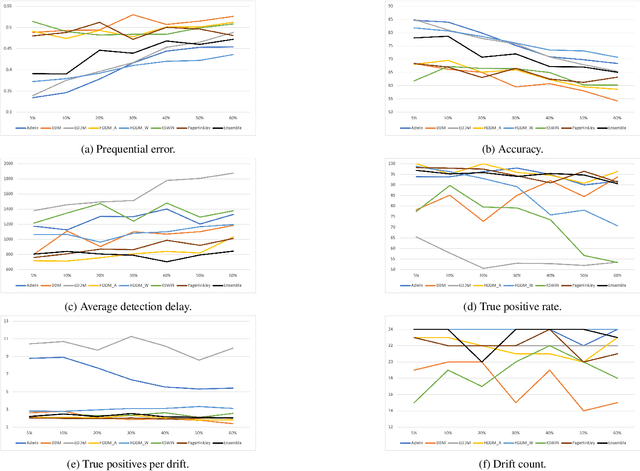
Abstract:Missing values, widely called as \textit{sparsity} in literature, is a common characteristic of many real-world datasets. Many imputation methods have been proposed to address this problem of data incompleteness or sparsity. However, the accuracy of a data imputation method for a given feature or a set of features in a dataset is highly dependent on the distribution of the feature values and its correlation with other features. Another problem that plagues industry deployments of machine learning (ML) solutions is concept drift detection, which becomes more challenging in the presence of missing values. Although data imputation and concept drift detection have been studied extensively, little work has attempted a combined study of the two phenomena, i.e., concept drift detection in the presence of sparsity. In this work, we carry out a systematic study of the following: (i) different patterns of missing values, (ii) various statistical and ML based data imputation methods for different kinds of sparsity, (iii) several concept drift detection methods, (iv) practical analysis of the various drift detection metrics, (v) selecting the best concept drift detector given a dataset with missing values based on the different metrics. We first analyze it on synthetic data and publicly available datasets, and finally extend the findings to our deployed solution of automated change risk assessment system. One of the major findings from our empirical study is the absence of supremacy of any one concept drift detection method across all the relevant metrics. Therefore, we adopt a majority voting based ensemble of concept drift detectors for abrupt and gradual concept drifts. Our experiments show optimal or near optimal performance can be achieved for this ensemble method across all the metrics.
Drift-Adjusted And Arbitrated Ensemble Framework For Time Series Forecasting
Mar 16, 2020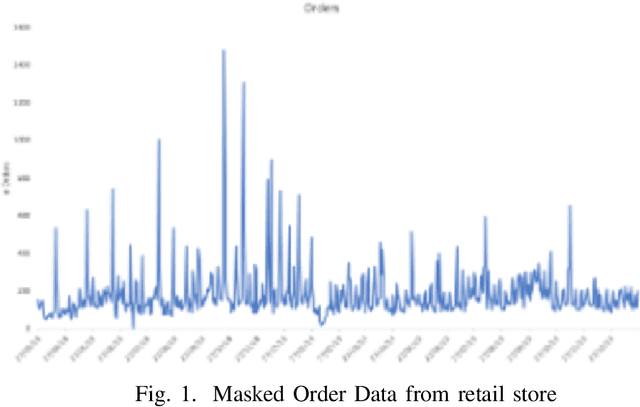
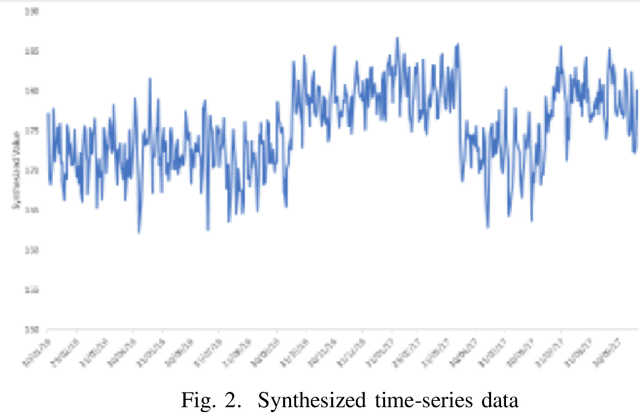
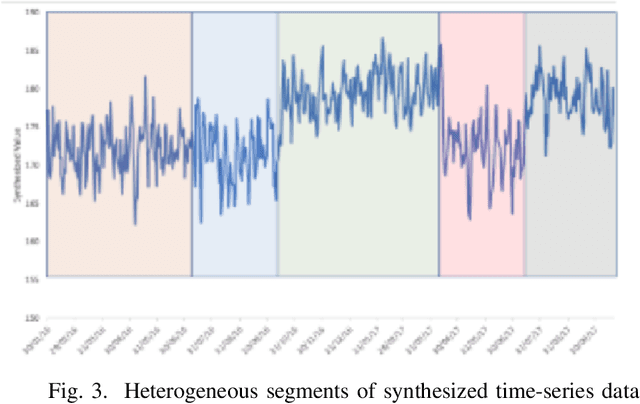
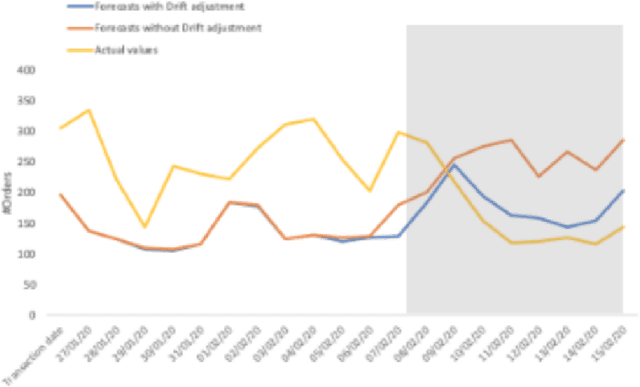
Abstract:Time Series Forecasting is at the core of many practical applications such as sales forecasting for business, rainfall forecasting for agriculture and many others. Though this problem has been extensively studied for years, it is still considered a challenging problem due to complex and evolving nature of time series data. Typical methods proposed for time series forecasting modeled linear or non-linear dependencies between data observations. However it is a generally accepted notion that no one method is universally effective for all kinds of time series data. Attempts have been made to use dynamic and weighted combination of heterogeneous and independent forecasting models and it has been found to be a promising direction to tackle this problem. This method is based on the assumption that different forecasters have different specialization and varying performance for different distribution of data and weights are dynamically assigned to multiple forecasters accordingly. However in many practical time series data-set, the distribution of data slowly evolves with time. We propose to employ a re-weighting based method to adjust the assigned weights to various forecasters in order to account for such distribution-drift. An exhaustive testing was performed against both real-world and synthesized time-series. Experimental results show the competitiveness of the method in comparison to state-of-the-art approaches for combining forecasters and handling drift.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge