Su Kim
Learning Topology-Specific Experts for Molecular Property Prediction
Mar 12, 2023Abstract:Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have been successfully applied to predicting molecular properties, which is one of the most classical cheminformatics tasks with various applications. Despite their effectiveness, we empirically observe that training a single GNN model for diverse molecules with distinct structural patterns limits its prediction performance. In this paper, motivated by this observation, we propose TopExpert to leverage topology-specific prediction models (referred to as experts), each of which is responsible for each molecular group sharing similar topological semantics. That is, each expert learns topology-specific discriminative features while being trained with its corresponding topological group. To tackle the key challenge of grouping molecules by their topological patterns, we introduce a clustering-based gating module that assigns an input molecule into one of the clusters and further optimizes the gating module with two different types of self-supervision: topological semantics induced by GNNs and molecular scaffolds, respectively. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TopExpert has boosted the performance for molecular property prediction and also achieved better generalization for new molecules with unseen scaffolds than baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/kimsu55/ToxExpert.
* 11 pages with 8 figures
Learnable Structural Semantic Readout for Graph Classification
Nov 22, 2021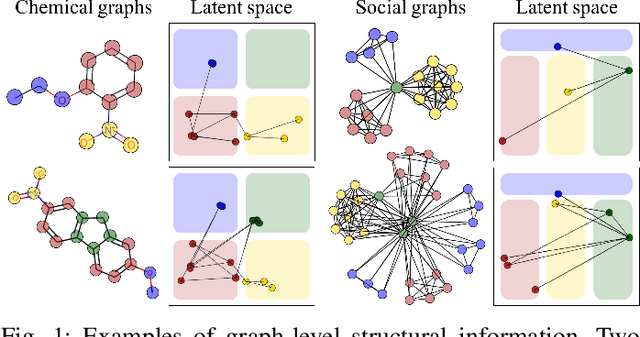
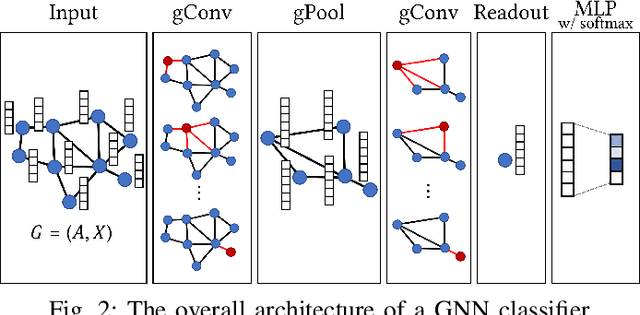
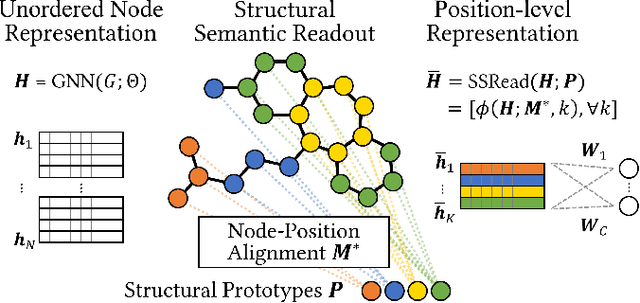
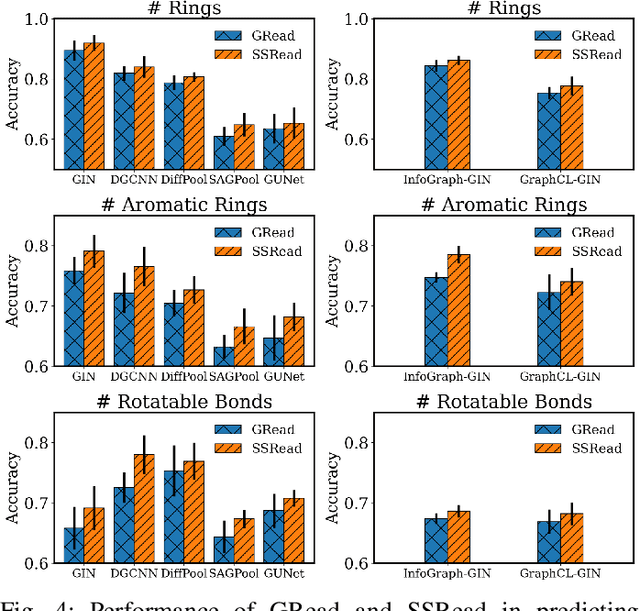
Abstract:With the great success of deep learning in various domains, graph neural networks (GNNs) also become a dominant approach to graph classification. By the help of a global readout operation that simply aggregates all node (or node-cluster) representations, existing GNN classifiers obtain a graph-level representation of an input graph and predict its class label using the representation. However, such global aggregation does not consider the structural information of each node, which results in information loss on the global structure. Particularly, it limits the discrimination power by enforcing the same weight parameters of the classifier for all the node representations; in practice, each of them contributes to target classes differently depending on its structural semantic. In this work, we propose structural semantic readout (SSRead) to summarize the node representations at the position-level, which allows to model the position-specific weight parameters for classification as well as to effectively capture the graph semantic relevant to the global structure. Given an input graph, SSRead aims to identify structurally-meaningful positions by using the semantic alignment between its nodes and structural prototypes, which encode the prototypical features of each position. The structural prototypes are optimized to minimize the alignment cost for all training graphs, while the other GNN parameters are trained to predict the class labels. Our experimental results demonstrate that SSRead significantly improves the classification performance and interpretability of GNN classifiers while being compatible with a variety of aggregation functions, GNN architectures, and learning frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge