Stuart E. Middleton
Prompt position really matters in few-shot and zero-shot NLU tasks
May 23, 2023Abstract:Prompt-based models have made remarkable advancements in the fields of zero-shot and few-shot learning, attracting a lot of attention from researchers. Developing an effective prompt template plays a critical role. However, prior studies have mainly focused on prompt vocabulary selection or embedding initialization with the reserved prompt position fixed. In this empirical study, we conduct the most comprehensive analysis to date of prompt position option for natural language understanding tasks. Our findings quantify the substantial impact prompt position has on model performance. We observe that the prompt position used in prior studies is often sub-optimal for both zero-shot and few-shot settings. These findings suggest prompt position optimisation as an interesting research direction alongside the existing focus on prompt engineering.
Combining Machine Learning and Human Experts to Predict Match Outcomes in Football: A Baseline Model
Dec 08, 2020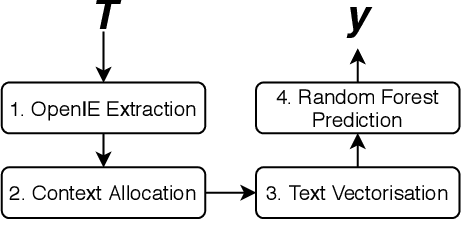
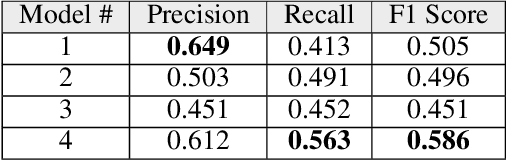
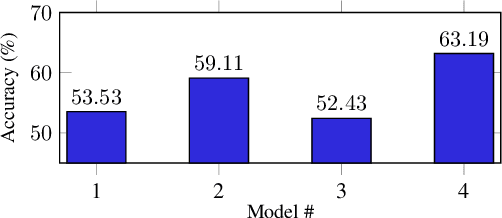
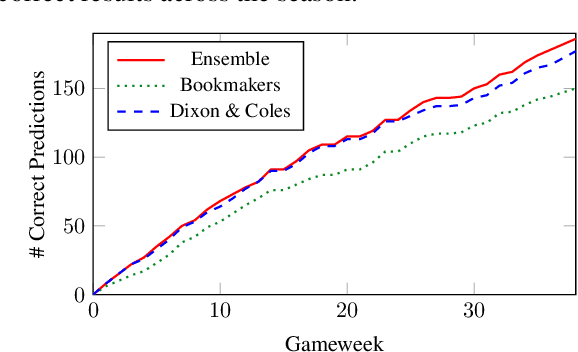
Abstract:In this paper, we present a new application-focused benchmark dataset and results from a set of baseline Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning models for prediction of match outcomes for games of football (soccer). By doing so we give a baseline for the prediction accuracy that can be achieved exploiting both statistical match data and contextual articles from human sports journalists. Our dataset is focuses on a representative time-period over 6 seasons of the English Premier League, and includes newspaper match previews from The Guardian. The models presented in this paper achieve an accuracy of 63.18% showing a 6.9% boost on the traditional statistical methods.
Exploiting Synergy Between Ontologies and Recommender Systems
Apr 08, 2002Abstract:Recommender systems learn about user preferences over time, automatically finding things of similar interest. This reduces the burden of creating explicit queries. Recommender systems do, however, suffer from cold-start problems where no initial information is available early on upon which to base recommendations. Semantic knowledge structures, such as ontologies, can provide valuable domain knowledge and user information. However, acquiring such knowledge and keeping it up to date is not a trivial task and user interests are particularly difficult to acquire and maintain. This paper investigates the synergy between a web-based research paper recommender system and an ontology containing information automatically extracted from departmental databases available on the web. The ontology is used to address the recommender systems cold-start problem. The recommender system addresses the ontology's interest-acquisition problem. An empirical evaluation of this approach is conducted and the performance of the integrated systems measured.
Interface agents: A review of the field
Mar 09, 2002
Abstract:This paper reviews the origins of interface agents, discusses challenges that exist within the interface agent field and presents a survey of current attempts to find solutions to these challenges. A history of agent systems from their birth in the 1960's to the current day is described, along with the issues they try to address. A taxonomy of interface agent systems is presented, and today's agent systems categorized accordingly. Lastly, an analysis of the machine learning and user modelling techniques used by today's agents is presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge