Stephen Plaza
Janelia Farm Research Campus- HHMI
A Context-aware Delayed Agglomeration Framework for Electron Microscopy Segmentation
Mar 23, 2015



Abstract:Electron Microscopy (EM) image (or volume) segmentation has become significantly important in recent years as an instrument for connectomics. This paper proposes a novel agglomerative framework for EM segmentation. In particular, given an over-segmented image or volume, we propose a novel framework for accurately clustering regions of the same neuron. Unlike existing agglomerative methods, the proposed context-aware algorithm divides superpixels (over-segmented regions) of different biological entities into different subsets and agglomerates them separately. In addition, this paper describes a "delayed" scheme for agglomerative clustering that postpones some of the merge decisions, pertaining to newly formed bodies, in order to generate a more confident boundary prediction. We report significant improvements attained by the proposed approach in segmentation accuracy over existing standard methods on 2D and 3D datasets.
Identifying Synapses Using Deep and Wide Multiscale Recursive Networks
Sep 05, 2014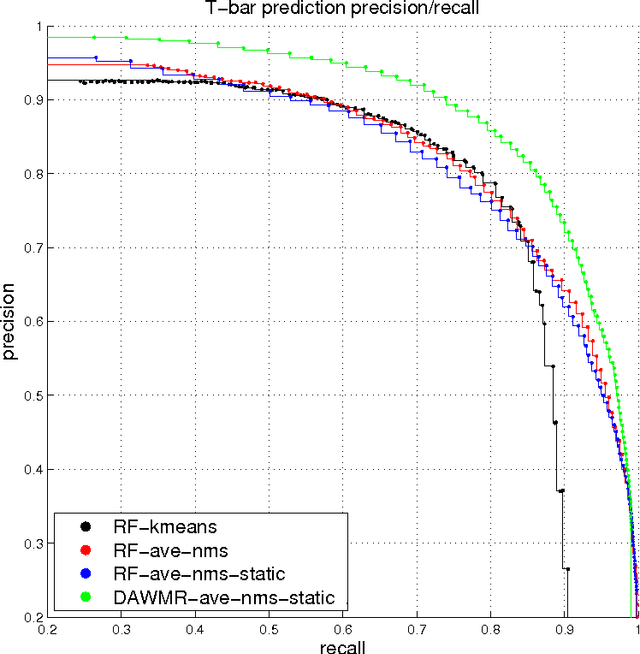
Abstract:In this work, we propose a learning framework for identifying synapses using a deep and wide multi-scale recursive (DAWMR) network, previously considered in image segmentation applications. We apply this approach on electron microscopy data from invertebrate fly brain tissue. By learning features directly from the data, we are able to achieve considerable improvements over existing techniques that rely on a small set of hand-designed features. We show that this system can reduce the amount of manual annotation required, in both acquisition of training data as well as verification of inferred detections.
Small Sample Learning of Superpixel Classifiers for EM Segmentation- Extended Version
Jun 13, 2014



Abstract:Pixel and superpixel classifiers have become essential tools for EM segmentation algorithms. Training these classifiers remains a major bottleneck primarily due to the requirement of completely annotating the dataset which is tedious, error-prone and costly. In this paper, we propose an interactive learning scheme for the superpixel classifier for EM segmentation. Our algorithm is "active semi-supervised" because it requests the labels of a small number of examples from user and applies label propagation technique to generate these queries. Using only a small set ($<20\%$) of all datapoints, the proposed algorithm consistently generates a classifier almost as accurate as that estimated from a complete groundtruth. We provide segmentation results on multiple datasets to show the strength of these classifiers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge