Stephan K. Chalup
Comparing Computing Platforms for Deep Learning on a Humanoid Robot
Jan 20, 2019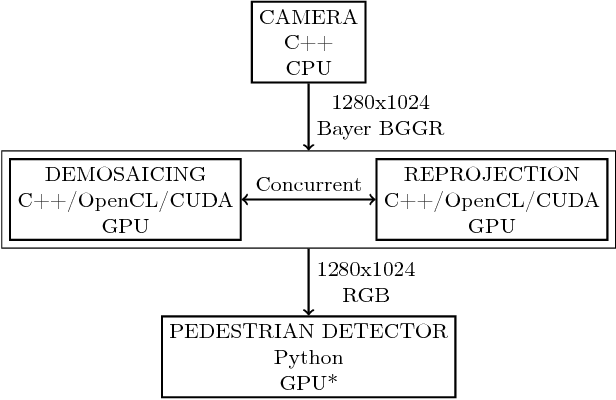
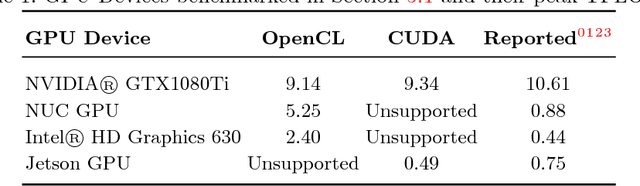
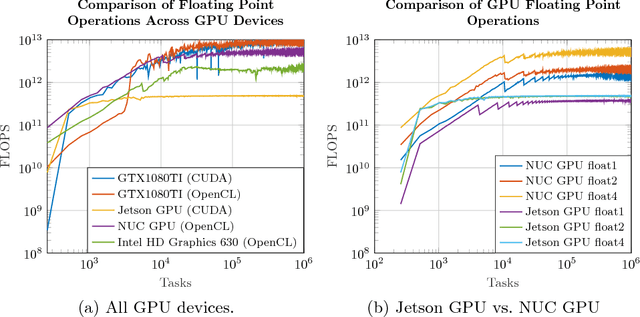

Abstract:The goal of this study is to test two different computing platforms with respect to their suitability for running deep networks as part of a humanoid robot software system. One of the platforms is the CPU-centered Intel NUC7i7BNH and the other is a NVIDIA Jetson TX2 system that puts more emphasis on GPU processing. The experiments addressed a number of benchmarking tasks including pedestrian detection using deep neural networks. Some of the results were unexpected but demonstrate that platforms exhibit both advantages and disadvantages when taking computational performance and electrical power requirements of such a system into account.
* 12 pages, 5 figures
RoboCup Junior in the Hunter Region: Driving the Future of Robotic STEM Education
Dec 04, 2018


Abstract:RoboCup Junior is a project-oriented educational initiative that sponsors regional, national and international robotic events for young students in primary and secondary school. It leads children to the fundamentals of teamwork and complex problem solving through step-by-step logical thinking using computers and robots. The Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment at the University of Newcastle in Australia has hosted and organized the Hunter regional tournament since 2012. This paper presents an analysis of data collected from RoboCup Junior in the Hunter Region, New South Wales, Australia, for a period of six years 2012-2017 inclusive. Our study evaluates the effectiveness of the competition in terms of geographical spread, participation numbers, and gender balance. We also present a case study about current university students who have previously participated in RoboCup Junior.
Aligning Manifolds of Double Pendulum Dynamics Under the Influence of Noise
Sep 20, 2018



Abstract:This study presents the results of a series of simulation experiments that evaluate and compare four different manifold alignment methods under the influence of noise. The data was created by simulating the dynamics of two slightly different double pendulums in three-dimensional space. The method of semi-supervised feature-level manifold alignment using global distance resulted in the most convincing visualisations. However, the semi-supervised feature-level local alignment methods resulted in smaller alignment errors. These local alignment methods were also more robust to noise and faster than the other methods.
Visual Mesh: Real-time Object Detection Using Constant Sample Density
Jul 23, 2018



Abstract:This paper proposes an enhancement of convolutional neural networks for object detection in resource-constrained robotics through a geometric input transformation called Visual Mesh. It uses object geometry to create a graph in vision space, reducing computational complexity by normalizing the pixel and feature density of objects. The experiments compare the Visual Mesh with several other fast convolutional neural networks. The results demonstrate execution times sixteen times quicker than the fastest competitor tested, while achieving outstanding accuracy.
The NUbots Team Description Paper 2015
Feb 11, 2015
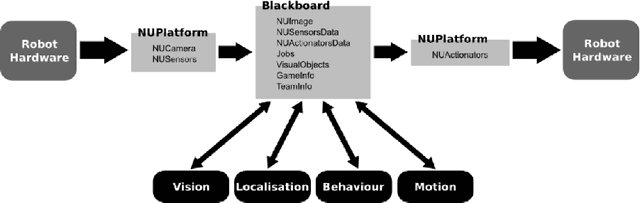
Abstract:The NUbots are an interdisciplinary RoboCup team from The University of Newcastle, Australia. The team has a history of strong contributions in the areas of machine learning and computer vision. The NUbots have participated in RoboCup leagues since 2002, placing first several times in the past. In 2014 the NUbots also partnered with the University of Newcastle Mechatronics Laboratory to participate in the RobotX Marine Robotics Challenge, which resulted in several new ideas and improvements to the NUbots vision system for RoboCup. This paper summarizes the history of the NUbots team, describes the roles and research of the team members, gives an overview of the NUbots' robots, their software system, and several associated research projects.
The NUbots Team Description Paper 2014
Mar 27, 2014

Abstract:The NUbots team, from The University of Newcastle, Australia, has had a strong record of success in the RoboCup Standard Platform League since first entering in 2002. The team has also competed within the RoboCup Humanoid Kid-Size League since 2012. The 2014 team brings a renewed focus on software architecture, modularity, and the ability to easily share code. This paper summarizes the history of the NUbots team, describes the roles and research of the team members, gives an overview of the NUbots' robots and software system, and addresses relevant research projects within the the Newcastle Robotics Laboratory.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge