Sriram Krishna
BG-HOP: A Bimanual Generative Hand-Object Prior
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present BG-HOP, a generative prior that seeks to model bimanual hand-object interactions in 3D. We address the challenge of limited bimanual interaction data by extending existing single-hand generative priors, demonstrating preliminary results in capturing the joint distribution of hands and objects. Our experiments showcase the model's capability to generate bimanual interactions and synthesize grasps for given objects. We make code and models publicly available.
Using Sampling to Estimate and Improve Performance of Automated Scoring Systems with Guarantees
Nov 17, 2021
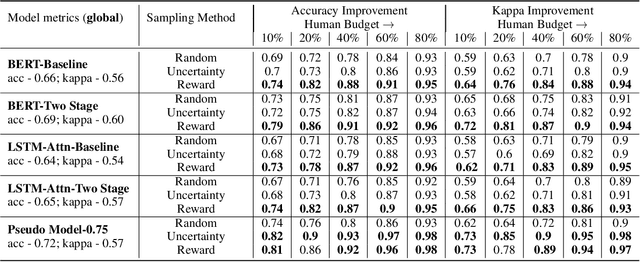
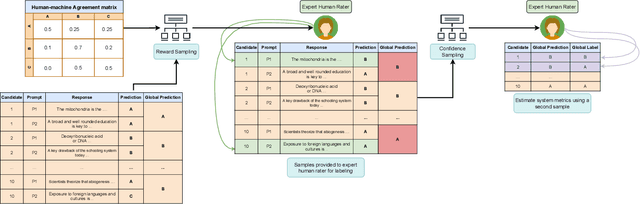
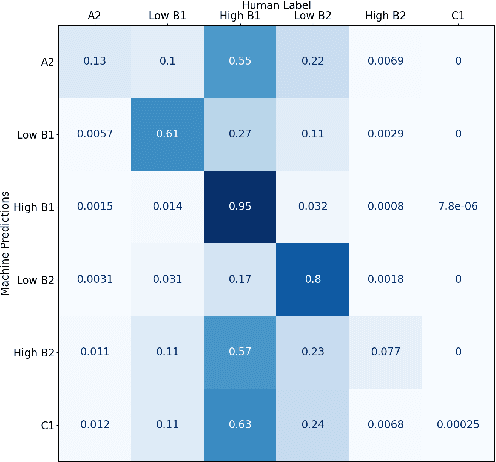
Abstract:Automated Scoring (AS), the natural language processing task of scoring essays and speeches in an educational testing setting, is growing in popularity and being deployed across contexts from government examinations to companies providing language proficiency services. However, existing systems either forgo human raters entirely, thus harming the reliability of the test, or score every response by both human and machine thereby increasing costs. We target the spectrum of possible solutions in between, making use of both humans and machines to provide a higher quality test while keeping costs reasonable to democratize access to AS. In this work, we propose a combination of the existing paradigms, sampling responses to be scored by humans intelligently. We propose reward sampling and observe significant gains in accuracy (19.80% increase on average) and quadratic weighted kappa (QWK) (25.60% on average) with a relatively small human budget (30% samples) using our proposed sampling. The accuracy increase observed using standard random and importance sampling baselines are 8.6% and 12.2% respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate the system's model agnostic nature by measuring its performance on a variety of models currently deployed in an AS setting as well as pseudo models. Finally, we propose an algorithm to estimate the accuracy/QWK with statistical guarantees (Our code is available at https://git.io/J1IOy).
Searching a Raw Video Database using Natural Language Queries
Dec 31, 2020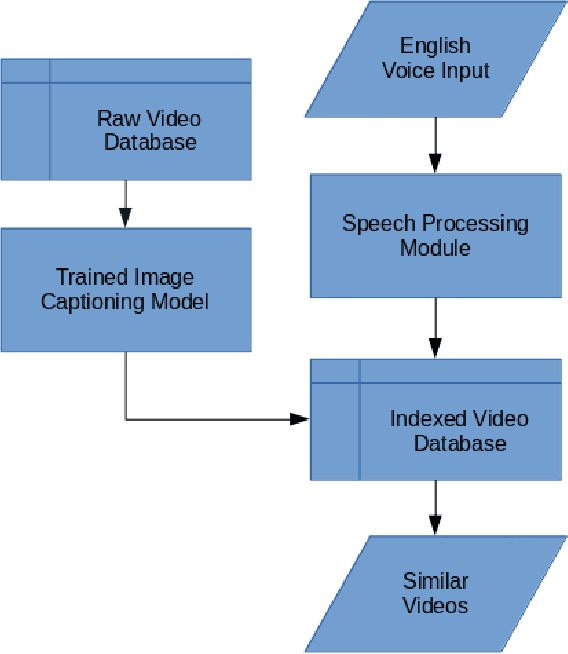


Abstract:The number of videos being produced and consequently stored in databases for video streaming platforms has been increasing exponentially over time. This vast database should be easily index-able to find the requisite clip or video to match the given search specification, preferably in the form of a textual query. This work aims to provide an end-to-end pipeline to search a video database with a voice query from the end user. The pipeline makes use of Recurrent Neural Networks in combination with Convolutional Neural Networks to generate captions of the video clips present in the database.
Gestop : Customizable Gesture Control of Computer Systems
Oct 25, 2020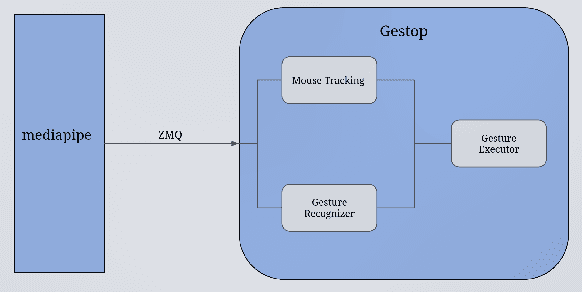

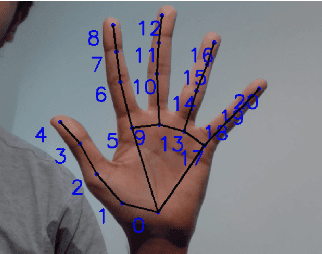
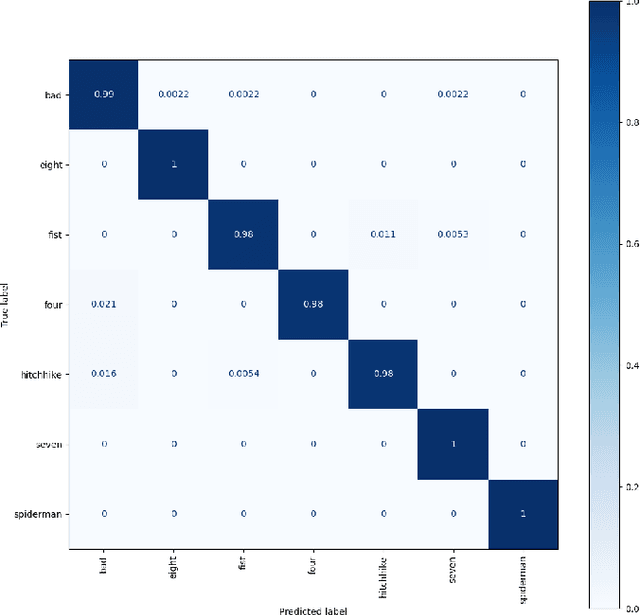
Abstract:The established way of interfacing with most computer systems is a mouse and keyboard. Hand gestures are an intuitive and effective touchless way to interact with computer systems. However, hand gesture based systems have seen low adoption among end-users primarily due to numerous technical hurdles in detecting in-air gestures accurately. This paper presents Gestop, a framework developed to bridge this gap. The framework learns to detect gestures from demonstrations, is customizable by end-users and enables users to interact in real-time with computers having only RGB cameras, using gestures.
Genetic Bi-objective Optimization Approach to Habitability Score
Oct 12, 2020



Abstract:The search for life outside the Solar System is an endeavour of astronomers all around the world. With hundreds of exoplanets being discovered due to advances in astronomy, there is a need to classify the habitability of these exoplanets. This is typically done using various metrics such as the Earth Similarity Index or the Planetary Habitability Index. In this paper, Genetic Algorithms are used to evaluate the best possible habitability scores using the Cobb-Douglas Habitability Score. Genetic Algorithm is a classic evolutionary algorithm used for solving optimization problems. It is based on Darwin's theory of evolution, "Survival of the fittest". The working of the algorithm is established through comparison with various benchmark functions and extended its functionality to Multi-Objective optimization. The Cobb-Douglas Habitability Function is formulated as a bi-objective as well as a single objective optimization problem to find the optimal values to maximize the Cobb-Douglas Habitability Score for a set of promising exoplanets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge