Sridevi M
Modified RRT* for Path Planning in Autonomous Driving
Feb 19, 2024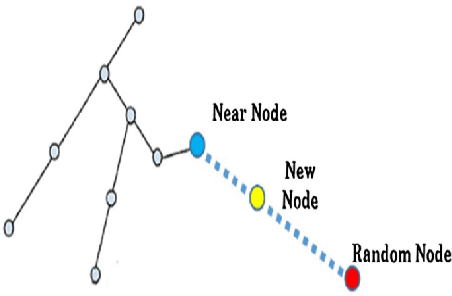
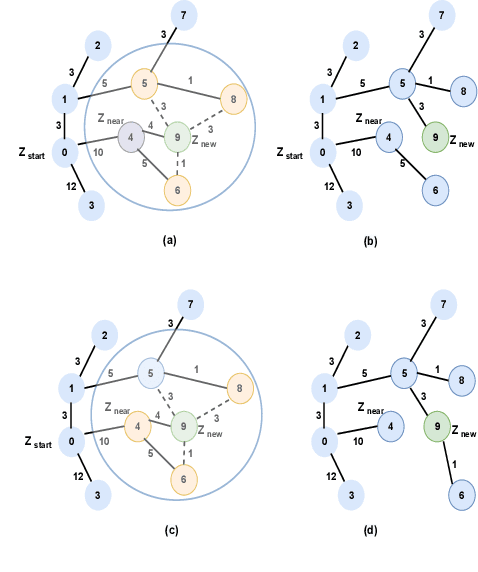
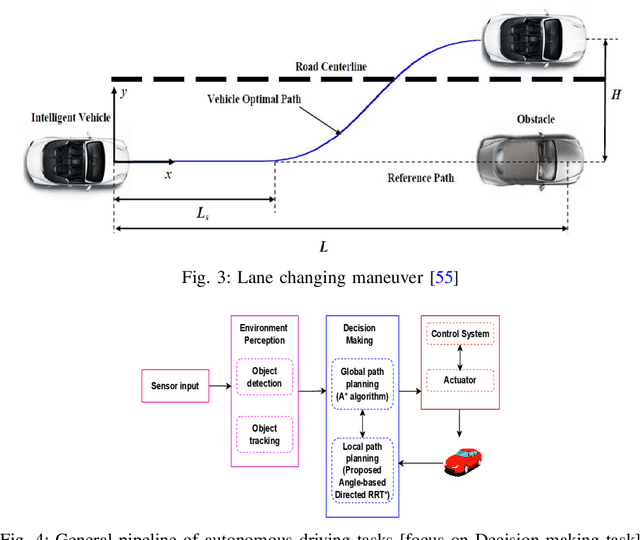
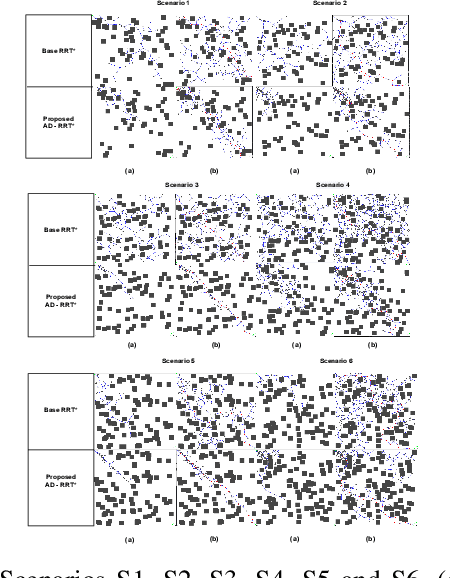
Abstract:Essential tasks in autonomous driving includes environment perception, detection and tracking, path planning and action control. This paper focus on path planning, which is one of the challenging task as it needs to find optimal path in highly complex and dynamic environments. Usually, a driving scenario has large number of obstacles in their route. In this paper, we propose a two-stage path planning algorithm named Angle-based Directed Rapidly exploring Random Trees (AD-RRT*) to address the problem of optimal path in complex environment. The proposed algorithm uses A* algorithm for global path planning and modifies RRT* to bound the samples using angle. The efficiency of the proposed algorithm is evaluated through experiments in different scenarios based on the location and number of obstacles. The proposed algorithm showed higher rate of convergence with reduced time and less number of nodes than the base RRT* algorithm.
Self-Supervised 3D Monocular Object Detection by Recycling Bounding Boxes
Jun 25, 2022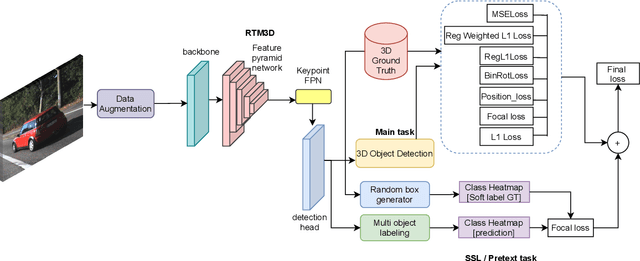
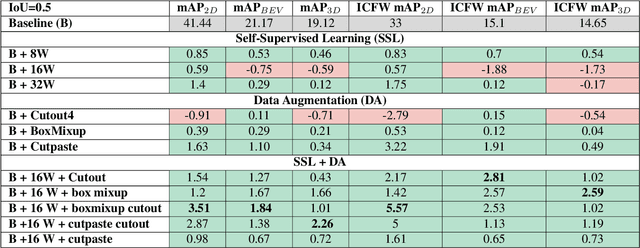
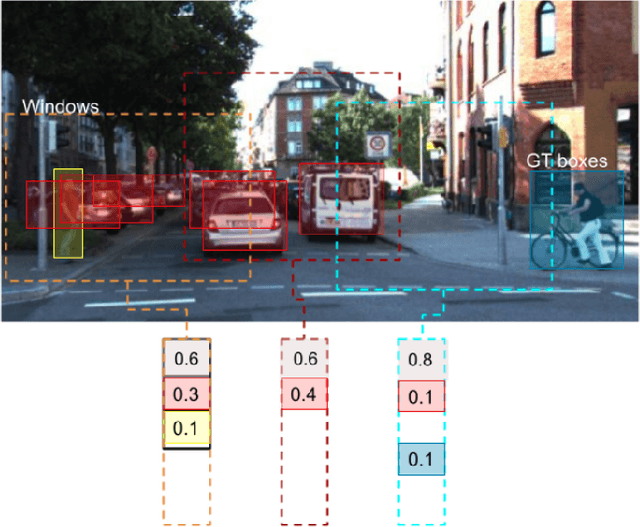
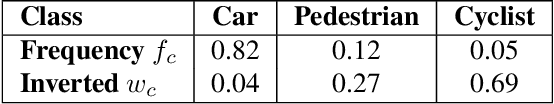
Abstract:Modern object detection architectures are moving towards employing self-supervised learning (SSL) to improve performance detection with related pretext tasks. Pretext tasks for monocular 3D object detection have not yet been explored yet in literature. The paper studies the application of established self-supervised bounding box recycling by labeling random windows as the pretext task. The classifier head of the 3D detector is trained to classify random windows containing different proportions of the ground truth objects, thus handling the foreground-background imbalance. We evaluate the pretext task using the RTM3D detection model as baseline, with and without the application of data augmentation. We demonstrate improvements of between 2-3 % in mAP 3D and 0.9-1.5 % BEV scores using SSL over the baseline scores. We propose the inverse class frequency re-weighted (ICFW) mAP score that highlights improvements in detection for low frequency classes in a class imbalanced dataset with long tails. We demonstrate improvements in ICFW both mAP 3D and BEV scores to take into account the class imbalance in the KITTI validation dataset. We see 4-5 % increase in ICFW metric with the pretext task.
Exploring 2D Data Augmentation for 3D Monocular Object Detection
Apr 21, 2021
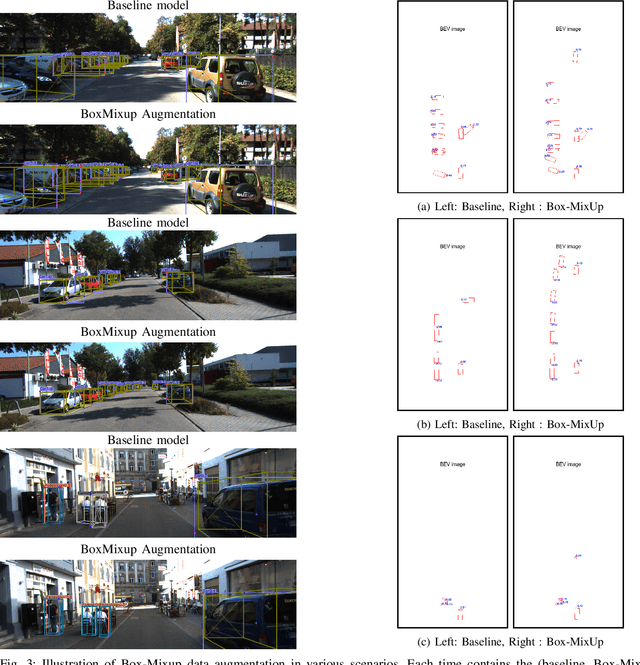
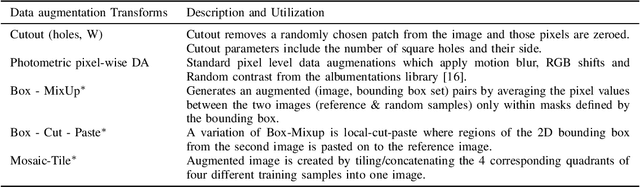
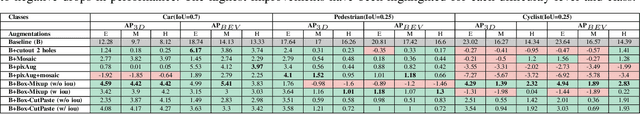
Abstract:Data augmentation is a key component of CNN based image recognition tasks like object detection. However, it is relatively less explored for 3D object detection. Many standard 2D object detection data augmentation techniques do not extend to 3D box. Extension of these data augmentations for 3D object detection requires adaptation of the 3D geometry of the input scene and synthesis of new viewpoints. This requires accurate depth information of the scene which may not be always available. In this paper, we evaluate existing 2D data augmentations and propose two novel augmentations for monocular 3D detection without a requirement for novel view synthesis. We evaluate these augmentations on the RTM3D detection model firstly due to the shorter training times . We obtain a consistent improvement by 4% in the 3D AP (@IoU=0.7) for cars, ~1.8% scores 3D AP (@IoU=0.25) for pedestrians & cyclists, over the baseline on KITTI car detection dataset. We also demonstrate a rigorous evaluation of the mAP scores by re-weighting them to take into account the class imbalance in the KITTI validation dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge