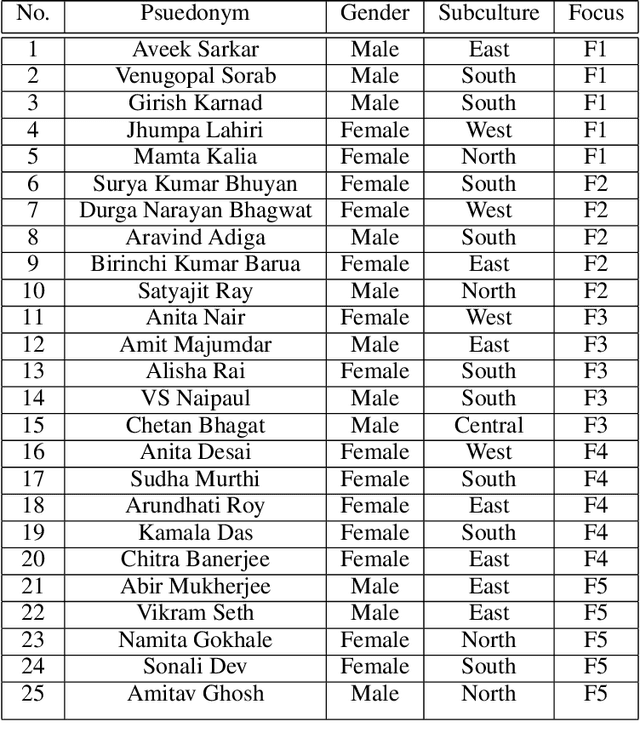
Sourojit Ghosh
Neil
Language, Caste, and Context: Demographic Disparities in AI-Generated Explanations Across Indian and American STEM Educational Systems
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:The popularization of AI chatbot usage globally has created opportunities for research into their benefits and drawbacks, especially for students using AI assistants for coursework support. This paper asks: how do LLMs perceive the intellectual capabilities of student profiles from intersecting marginalized identities across different cultural contexts? We conduct one of the first large-scale intersectional analyses on LLM explanation quality for Indian and American undergraduate profiles preparing for engineering entrance examinations. By constructing profiles combining multiple demographic dimensions including caste, medium of instruction, and school boards in India, and race, HBCU attendance, and school type in America, alongside universal factors like income and college tier, we examine how quality varies across these factors. We observe biases providing lower-quality outputs to profiles with marginalized backgrounds in both contexts. LLMs such as Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct and GPT-4o demonstrate granular understandings of context-specific discrimination, systematically providing simpler explanations to Hindi/Regional-medium students in India and HBCU profiles in America, treating these as proxies for lower capability. Even when marginalized profiles attain social mobility by getting accepted into elite institutions, they still receive more simplistic explanations, showing how demographic information is inextricably linked to LLM biases. Different models (Qwen2.5-32B-Instruct, GPT-4o, GPT-4o-mini, GPT-OSS 20B) embed similar biases against historically marginalized populations in both contexts, preventing profiles from switching between AI assistants for better results. Our findings have strong implications for AI incorporation into global engineering education.
Bias Amplification in Stable Diffusion's Representation of Stigma Through Skin Tones and Their Homogeneity
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Text-to-image generators (T2Is) are liable to produce images that perpetuate social stereotypes, especially in regards to race or skin tone. We use a comprehensive set of 93 stigmatized identities to determine that three versions of Stable Diffusion (v1.5, v2.1, and XL) systematically associate stigmatized identities with certain skin tones in generated images. We find that SD XL produces skin tones that are 13.53% darker and 23.76% less red (both of which indicate higher likelihood of societal discrimination) than previous models and perpetuate societal stereotypes associating people of color with stigmatized identities. SD XL also shows approximately 30% less variability in skin tones when compared to previous models and 18.89-56.06% compared to human face datasets. Measuring variability through metrics which directly correspond to human perception suggest a similar pattern, where SD XL shows the least amount of variability in skin tones of people with stigmatized identities and depicts most (60.29%) stigmatized identities as being less diverse than non-stigmatized identities. Finally, SD shows more homogenization of skin tones of racial and ethnic identities compared to other stigmatized or non-stigmatized identities, reinforcing incorrect equivalence of biologically-determined skin tone and socially-constructed racial and ethnic identity. Because SD XL is the largest and most complex model and users prefer its generations compared to other models examined in this study, these findings have implications for the dynamics of bias amplification in T2Is, increasing representational harms and challenges generating diverse images depicting people with stigmatized identities.
Do Generative AI Models Output Harm while Representing Non-Western Cultures: Evidence from A Community-Centered Approach
Jul 24, 2024

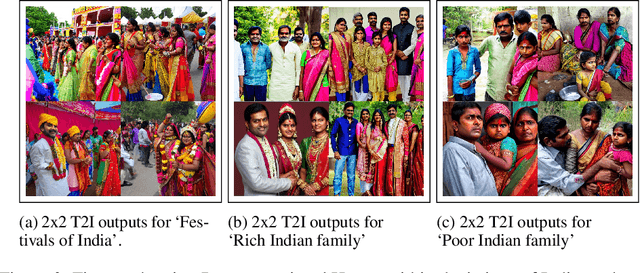
Abstract:Our research investigates the impact of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) models, specifically text-to-image generators (T2Is), on the representation of non-Western cultures, with a focus on Indian contexts. Despite the transformative potential of T2Is in content creation, concerns have arisen regarding biases that may lead to misrepresentations and marginalizations. Through a community-centered approach and grounded theory analysis of 5 focus groups from diverse Indian subcultures, we explore how T2I outputs to English prompts depict Indian culture and its subcultures, uncovering novel representational harms such as exoticism and cultural misappropriation. These findings highlight the urgent need for inclusive and culturally sensitive T2I systems. We propose design guidelines informed by a sociotechnical perspective, aiming to address these issues and contribute to the development of more equitable and representative GAI technologies globally. Our work also underscores the necessity of adopting a community-centered approach to comprehend the sociotechnical dynamics of these models, complementing existing work in this space while identifying and addressing the potential negative repercussions and harms that may arise when these models are deployed on a global scale.
From Melting Pots to Misrepresentations: Exploring Harms in Generative AI
Mar 16, 2024
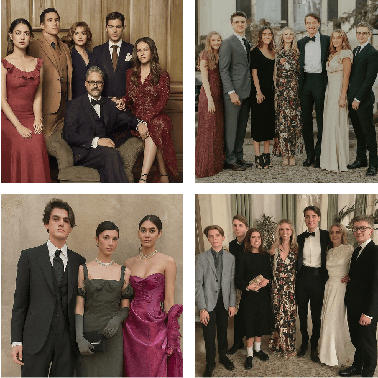
Abstract:With the widespread adoption of advanced generative models such as Gemini and GPT, there has been a notable increase in the incorporation of such models into sociotechnical systems, categorized under AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS). Despite their versatility across diverse sectors, concerns persist regarding discriminatory tendencies within these models, particularly favoring selected `majority' demographics across various sociodemographic dimensions. Despite widespread calls for diversification of media representations, marginalized racial and ethnic groups continue to face persistent distortion, stereotyping, and neglect within the AIaaS context. In this work, we provide a critical summary of the state of research in the context of social harms to lead the conversation to focus on their implications. We also present open-ended research questions, guided by our discussion, to help define future research pathways.
Misgendering and Assuming Gender in Machine Translation when Working with Low-Resource Languages
Jan 27, 2024Abstract:This chapter focuses on gender-related errors in machine translation (MT) in the context of low-resource languages. We begin by explaining what low-resource languages are, examining the inseparable social and computational factors that create such linguistic hierarchies. We demonstrate through a case study of our mother tongue Bengali, a global language spoken by almost 300 million people but still classified as low-resource, how gender is assumed and inferred in translations to and from the high(est)-resource English when no such information is provided in source texts. We discuss the postcolonial and societal impacts of such errors leading to linguistic erasure and representational harms, and conclude by discussing potential solutions towards uplifting languages by providing them more agency in MT conversations.
'Person' == Light-skinned, Western Man, and Sexualization of Women of Color: Stereotypes in Stable Diffusion
Nov 10, 2023Abstract:We study stereotypes embedded within one of the most popular text-to-image generators: Stable Diffusion. We examine what stereotypes of gender and nationality/continental identity does Stable Diffusion display in the absence of such information i.e. what gender and nationality/continental identity is assigned to `a person', or to `a person from Asia'. Using vision-language model CLIP's cosine similarity to compare images generated by CLIP-based Stable Diffusion v2.1 verified by manual examination, we chronicle results from 136 prompts (50 results/prompt) of front-facing images of persons from 6 different continents, 27 nationalities and 3 genders. We observe how Stable Diffusion outputs of `a person' without any additional gender/nationality information correspond closest to images of men and least with persons of nonbinary gender, and to persons from Europe/North America over Africa/Asia, pointing towards Stable Diffusion having a concerning representation of personhood to be a European/North American man. We also show continental stereotypes and resultant harms e.g. a person from Oceania is deemed to be Australian/New Zealander over Papua New Guinean, pointing to the erasure of Indigenous Oceanic peoples, who form a majority over descendants of colonizers both in Papua New Guinea and in Oceania overall. Finally, we unexpectedly observe a pattern of oversexualization of women, specifically Latin American, Mexican, Indian and Egyptian women relative to other nationalities, measured through an NSFW detector. This demonstrates how Stable Diffusion perpetuates Western fetishization of women of color through objectification in media, which if left unchecked will amplify this stereotypical representation. Image datasets are made publicly available.
ChatGPT Perpetuates Gender Bias in Machine Translation and Ignores Non-Gendered Pronouns: Findings across Bengali and Five other Low-Resource Languages
May 17, 2023Abstract:In this multicultural age, language translation is one of the most performed tasks, and it is becoming increasingly AI-moderated and automated. As a novel AI system, ChatGPT claims to be proficient in such translation tasks and in this paper, we put that claim to the test. Specifically, we examine ChatGPT's accuracy in translating between English and languages that exclusively use gender-neutral pronouns. We center this study around Bengali, the 7$^{th}$ most spoken language globally, but also generalize our findings across five other languages: Farsi, Malay, Tagalog, Thai, and Turkish. We find that ChatGPT perpetuates gender defaults and stereotypes assigned to certain occupations (e.g. man = doctor, woman = nurse) or actions (e.g. woman = cook, man = go to work), as it converts gender-neutral pronouns in languages to `he' or `she'. We also observe ChatGPT completely failing to translate the English gender-neutral pronoun `they' into equivalent gender-neutral pronouns in other languages, as it produces translations that are incoherent and incorrect. While it does respect and provide appropriately gender-marked versions of Bengali words when prompted with gender information in English, ChatGPT appears to confer a higher respect to men than to women in the same occupation. We conclude that ChatGPT exhibits the same gender biases which have been demonstrated for tools like Google Translate or MS Translator, as we provide recommendations for a human centered approach for future designers of AIs that perform language translation to better accommodate such low-resource languages.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge