Soumitra Kundu
LifWavNet: Lifting Wavelet-based Network for Non-contact ECG Reconstruction from Radar
Oct 31, 2025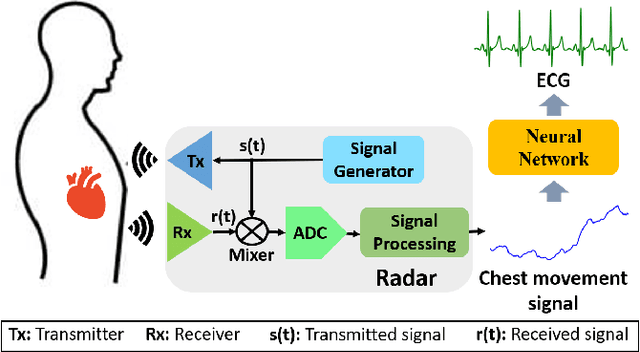
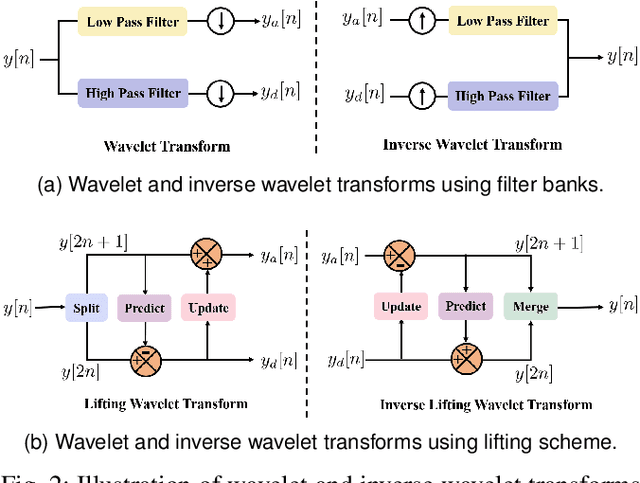
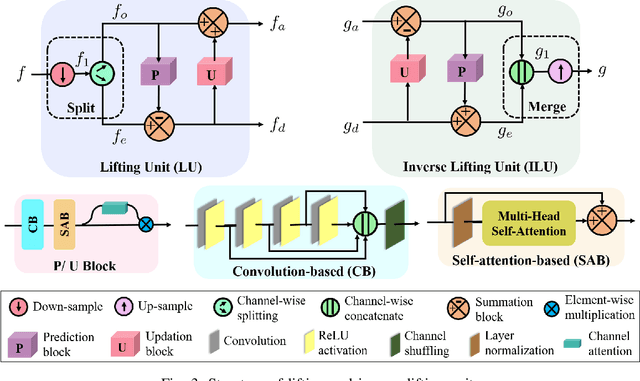
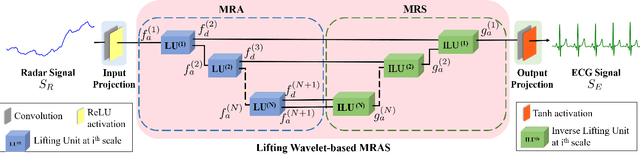
Abstract:Non-contact electrocardiogram (ECG) reconstruction from radar signals offers a promising approach for unobtrusive cardiac monitoring. We present LifWavNet, a lifting wavelet network based on a multi-resolution analysis and synthesis (MRAS) model for radar-to-ECG reconstruction. Unlike prior models that use fixed wavelet approaches, LifWavNet employs learnable lifting wavelets with lifting and inverse lifting units to adaptively capture radar signal features and synthesize physiologically meaningful ECG waveforms. To improve reconstruction fidelity, we introduce a multi-resolution short-time Fourier transform (STFT) loss, that enforces consistency with the ground-truth ECG in both temporal and spectral domains. Evaluations on two public datasets demonstrate that LifWavNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods in ECG reconstruction and downstream vital sign estimation (heart rate and heart rate variability). Furthermore, intermediate feature visualization highlights the interpretability of multi-resolution decomposition and synthesis in radar-to-ECG reconstruction. These results establish LifWavNet as a robust framework for radar-based non-contact ECG measurement.
SSNet: Saliency Prior and State Space Model-based Network for Salient Object Detection in RGB-D Images
Mar 04, 2025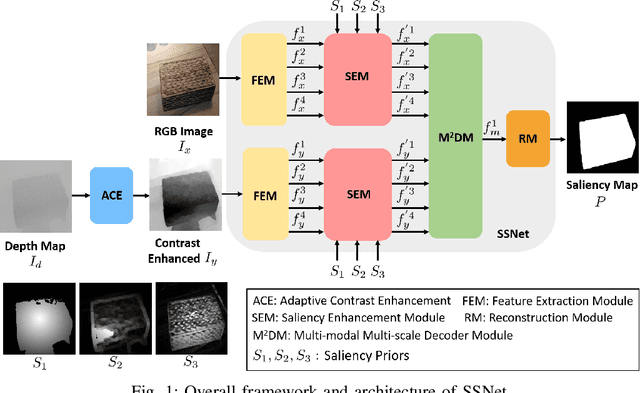
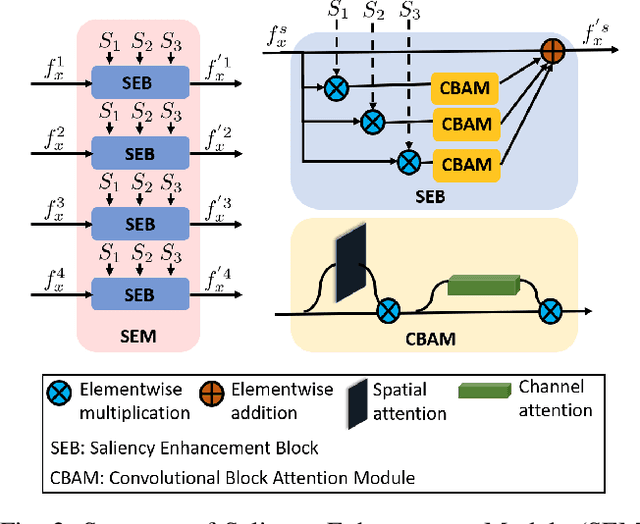
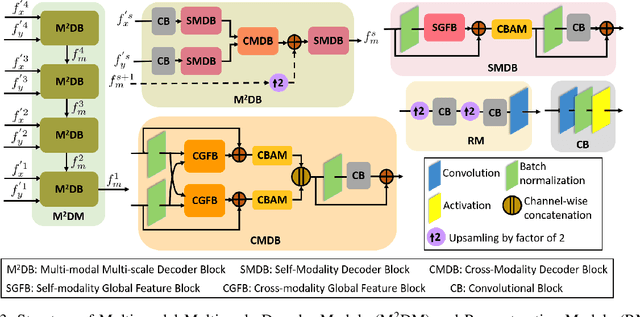
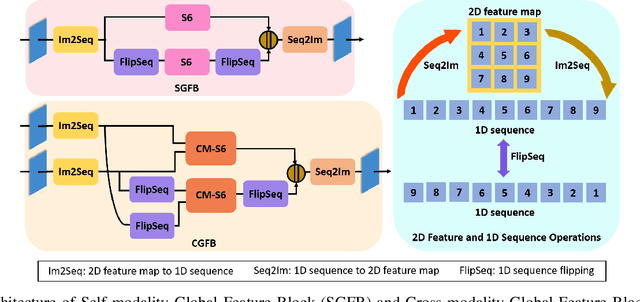
Abstract:Salient object detection (SOD) in RGB-D images is an essential task in computer vision, enabling applications in scene understanding, robotics, and augmented reality. However, existing methods struggle to capture global dependency across modalities, lack comprehensive saliency priors from both RGB and depth data, and are ineffective in handling low-quality depth maps. To address these challenges, we propose SSNet, a saliency-prior and state space model (SSM)-based network for the RGB-D SOD task. Unlike existing convolution- or transformer-based approaches, SSNet introduces an SSM-based multi-modal multi-scale decoder module to efficiently capture both intra- and inter-modal global dependency with linear complexity. Specifically, we propose a cross-modal selective scan SSM (CM-S6) mechanism, which effectively captures global dependency between different modalities. Furthermore, we introduce a saliency enhancement module (SEM) that integrates three saliency priors with deep features to refine feature representation and improve the localization of salient objects. To further address the issue of low-quality depth maps, we propose an adaptive contrast enhancement technique that dynamically refines depth maps, making them more suitable for the RGB-D SOD task. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments on seven benchmark datasets demonstrate that SSNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
l0-Regularized Sparse Coding-based Interpretable Network for Multi-Modal Image Fusion
Nov 07, 2024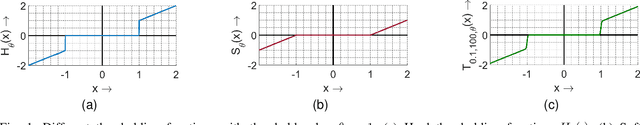
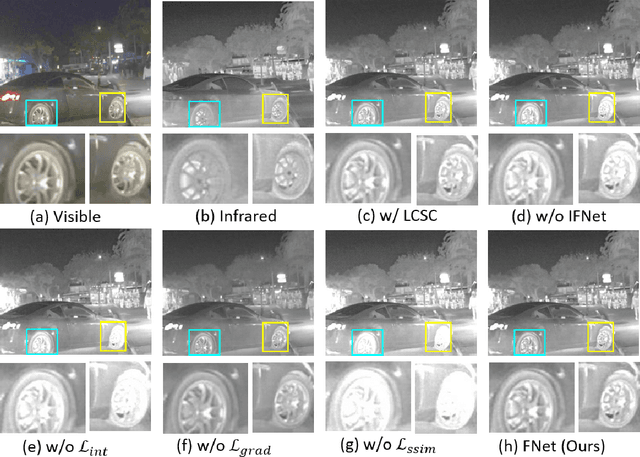
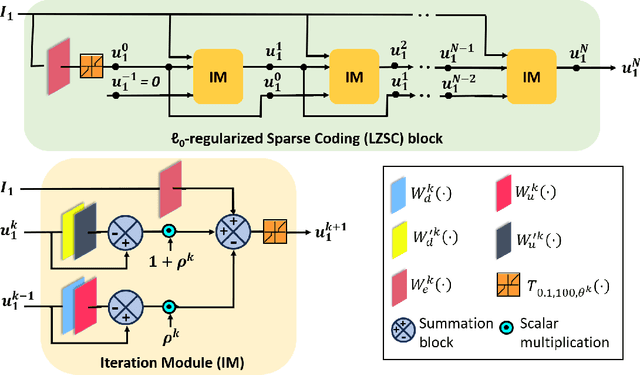
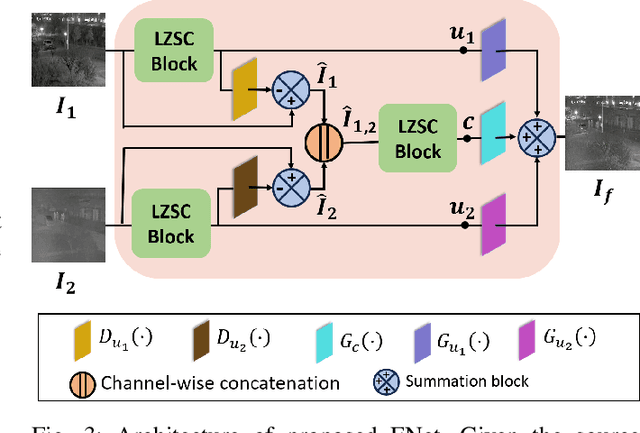
Abstract:Multi-modal image fusion (MMIF) enhances the information content of the fused image by combining the unique as well as common features obtained from different modality sensor images, improving visualization, object detection, and many more tasks. In this work, we introduce an interpretable network for the MMIF task, named FNet, based on an l0-regularized multi-modal convolutional sparse coding (MCSC) model. Specifically, for solving the l0-regularized CSC problem, we develop an algorithm unrolling-based l0-regularized sparse coding (LZSC) block. Given different modality source images, FNet first separates the unique and common features from them using the LZSC block and then these features are combined to generate the final fused image. Additionally, we propose an l0-regularized MCSC model for the inverse fusion process. Based on this model, we introduce an interpretable inverse fusion network named IFNet, which is utilized during FNet's training. Extensive experiments show that FNet achieves high-quality fusion results across five different MMIF tasks. Furthermore, we show that FNet enhances downstream object detection in visible-thermal image pairs. We have also visualized the intermediate results of FNet, which demonstrates the good interpretability of our network.
INN-PAR: Invertible Neural Network for PPG to ABP Reconstruction
Sep 13, 2024Abstract:Non-invasive and continuous blood pressure (BP) monitoring is essential for the early prevention of many cardiovascular diseases. Estimating arterial blood pressure (ABP) from photoplethysmography (PPG) has emerged as a promising solution. However, existing deep learning approaches for PPG-to-ABP reconstruction (PAR) encounter certain information loss, impacting the precision of the reconstructed signal. To overcome this limitation, we introduce an invertible neural network for PPG to ABP reconstruction (INN-PAR), which employs a series of invertible blocks to jointly learn the mapping between PPG and its gradient with the ABP signal and its gradient. INN-PAR efficiently captures both forward and inverse mappings simultaneously, thereby preventing information loss. By integrating signal gradients into the learning process, INN-PAR enhances the network's ability to capture essential high-frequency details, leading to more accurate signal reconstruction. Moreover, we propose a multi-scale convolution module (MSCM) within the invertible block, enabling the model to learn features across multiple scales effectively. We have experimented on two benchmark datasets, which show that INN-PAR significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in both waveform reconstruction and BP measurement accuracy.
SINET: Sparsity-driven Interpretable Neural Network for Underwater Image Enhancement
Sep 02, 2024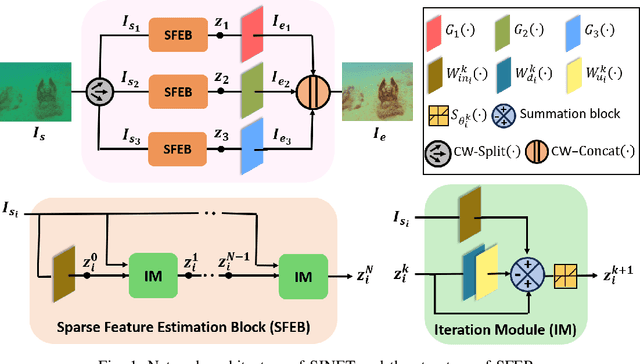
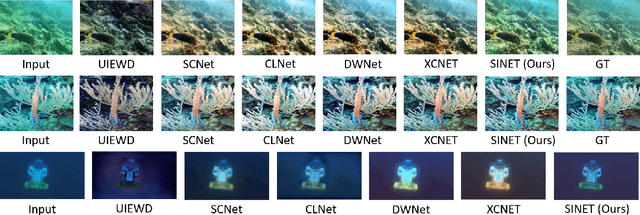
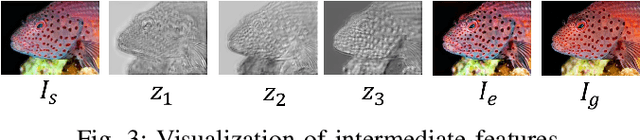
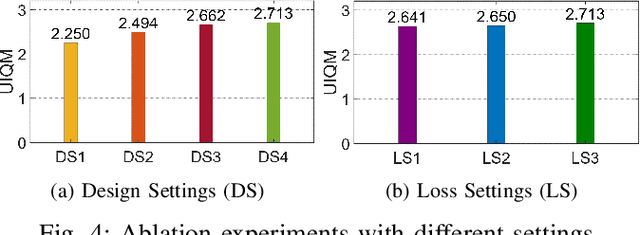
Abstract:Improving the quality of underwater images is essential for advancing marine research and technology. This work introduces a sparsity-driven interpretable neural network (SINET) for the underwater image enhancement (UIE) task. Unlike pure deep learning methods, our network architecture is based on a novel channel-specific convolutional sparse coding (CCSC) model, ensuring good interpretability of the underlying image enhancement process. The key feature of SINET is that it estimates the salient features from the three color channels using three sparse feature estimation blocks (SFEBs). The architecture of SFEB is designed by unrolling an iterative algorithm for solving the $\ell_1$ regulaized convolutional sparse coding (CSC) problem. Our experiments show that SINET surpasses state-of-the-art PSNR value by $1.05$ dB with $3873$ times lower computational complexity.
LATIS: Lambda Abstraction-based Thermal Image Super-resolution
Nov 18, 2023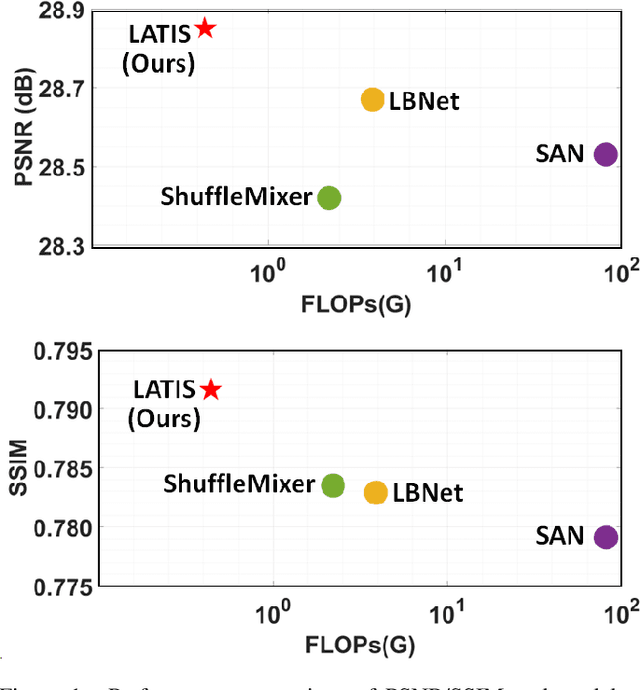
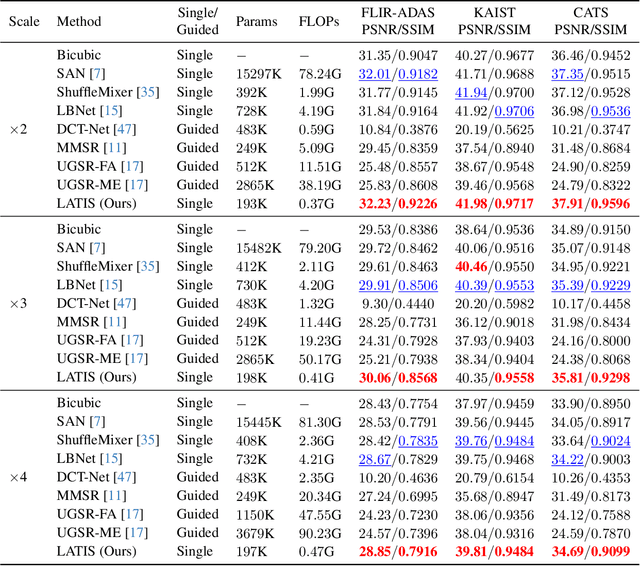
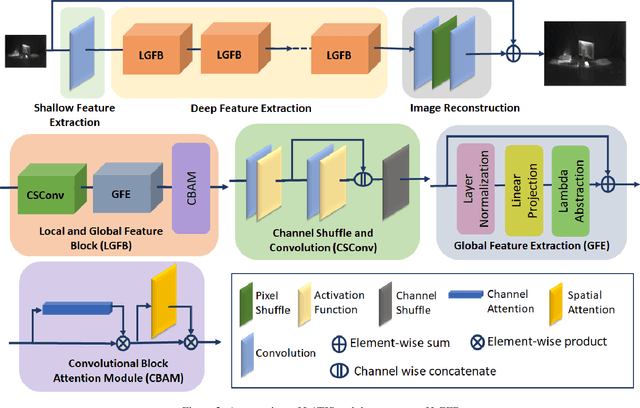

Abstract:Single image super-resolution (SISR) is an effective technique to improve the quality of low-resolution thermal images. Recently, transformer-based methods have achieved significant performance in SISR. However, in the SR task, only a small number of pixels are involved in the transformers self-attention (SA) mechanism due to the computational complexity of the attention mechanism. The lambda abstraction is a promising alternative to SA in modeling long-range interactions while being computationally more efficient. This paper presents lambda abstraction-based thermal image super-resolution (LATIS), a novel lightweight architecture for SISR of thermal images. LATIS sequentially captures local and global information using the local and global feature block (LGFB). In LGFB, we introduce a global feature extraction (GFE) module based on the lambda abstraction mechanism, channel-shuffle and convolution (CSConv) layer to encode local context. Besides, to improve the performance further, we propose a differentiable patch-wise histogram-based loss function. Experimental results demonstrate that our LATIS, with the least model parameters and complexity, achieves better or comparable performance with state-of-the-art methods across multiple datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge