l0-Regularized Sparse Coding-based Interpretable Network for Multi-Modal Image Fusion
Paper and Code
Nov 07, 2024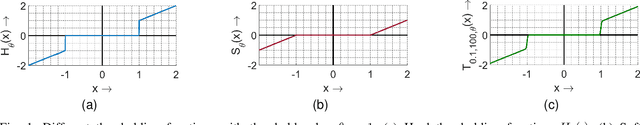
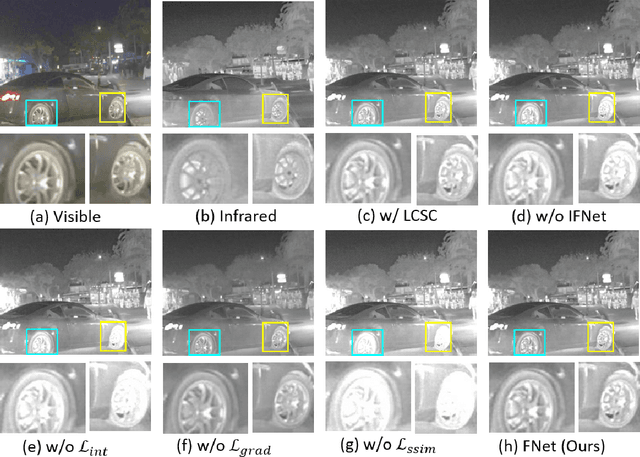
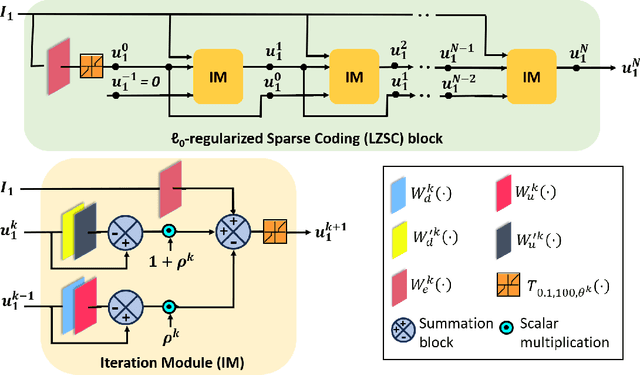
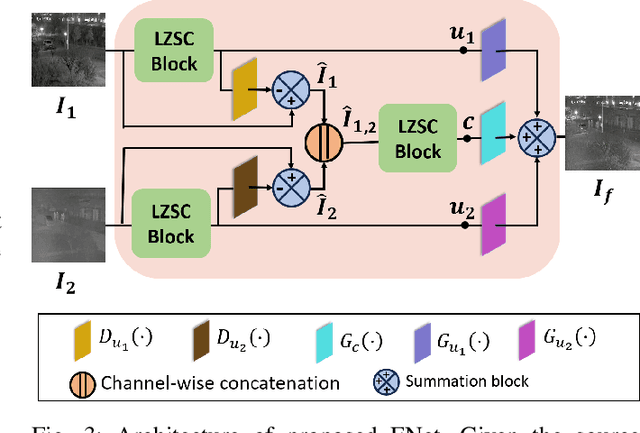
Multi-modal image fusion (MMIF) enhances the information content of the fused image by combining the unique as well as common features obtained from different modality sensor images, improving visualization, object detection, and many more tasks. In this work, we introduce an interpretable network for the MMIF task, named FNet, based on an l0-regularized multi-modal convolutional sparse coding (MCSC) model. Specifically, for solving the l0-regularized CSC problem, we develop an algorithm unrolling-based l0-regularized sparse coding (LZSC) block. Given different modality source images, FNet first separates the unique and common features from them using the LZSC block and then these features are combined to generate the final fused image. Additionally, we propose an l0-regularized MCSC model for the inverse fusion process. Based on this model, we introduce an interpretable inverse fusion network named IFNet, which is utilized during FNet's training. Extensive experiments show that FNet achieves high-quality fusion results across five different MMIF tasks. Furthermore, we show that FNet enhances downstream object detection in visible-thermal image pairs. We have also visualized the intermediate results of FNet, which demonstrates the good interpretability of our network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge