Slava Mikhaylov
Topology Analysis of International Networks Based on Debates in the United Nations
Jul 29, 2017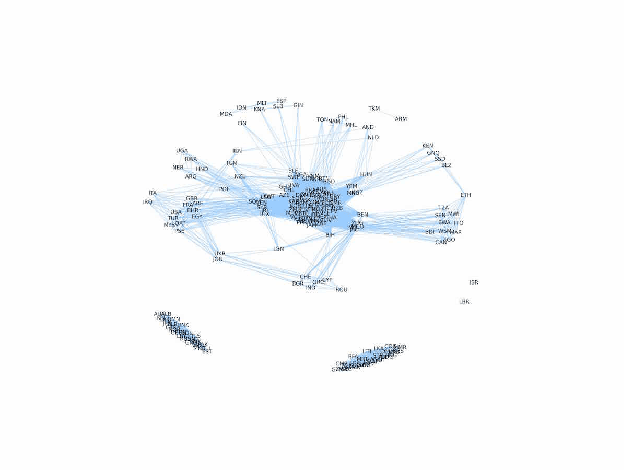


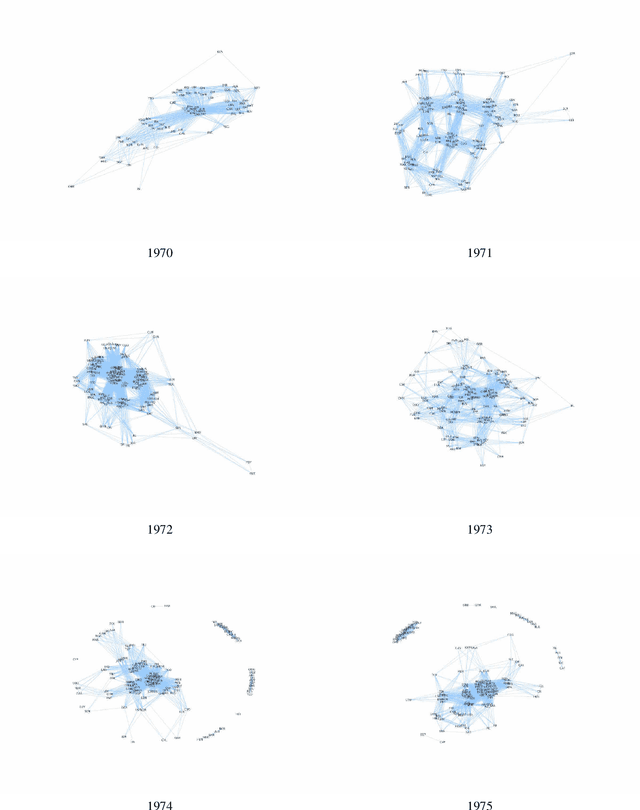
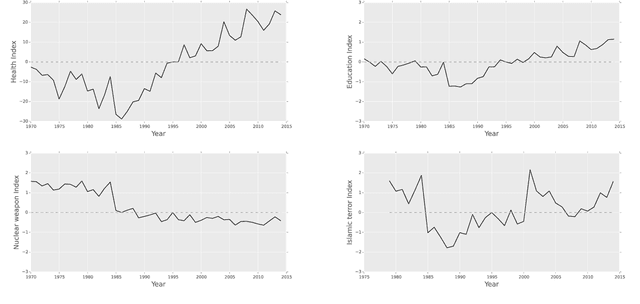
Abstract:In complex, high dimensional and unstructured data it is often difficult to extract meaningful patterns. This is especially the case when dealing with textual data. Recent studies in machine learning, information theory and network science have developed several novel instruments to extract the semantics of unstructured data, and harness it to build a network of relations. Such approaches serve as an efficient tool for dimensionality reduction and pattern detection. This paper applies semantic network science to extract ideological proximity in the international arena, by focusing on the data from General Debates in the UN General Assembly on the topics of high salience to international community. UN General Debate corpus (UNGDC) covers all high-level debates in the UN General Assembly from 1970 to 2014, covering all UN member states. The research proceeds in three main steps. First, Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) is used to extract the topics of the UN speeches, and therefore semantic information. Each country is then assigned a vector specifying the exposure to each of the topics identified. This intermediate output is then used in to construct a network of countries based on information theoretical metrics where the links capture similar vectorial patterns in the topic distributions. Topology of the networks is then analyzed through network properties like density, path length and clustering. Finally, we identify specific topological features of our networks using the map equation framework to detect communities in our networks of countries.
Detecting Policy Preferences and Dynamics in the UN General Debate with Neural Word Embeddings
Jul 11, 2017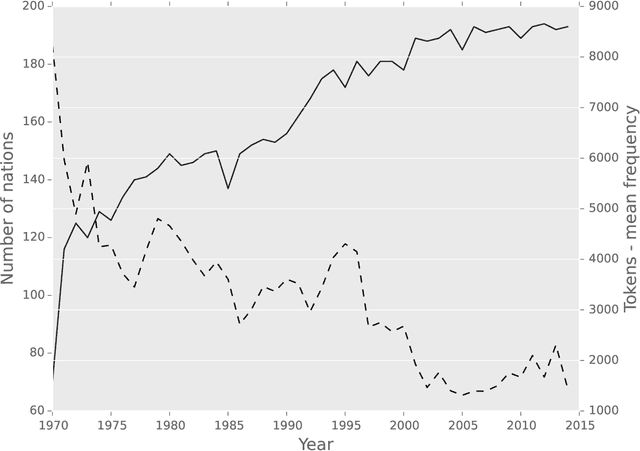

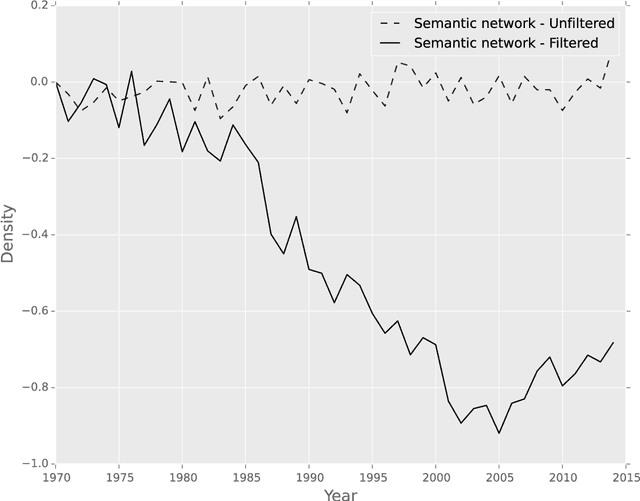
Abstract:Foreign policy analysis has been struggling to find ways to measure policy preferences and paradigm shifts in international political systems. This paper presents a novel, potential solution to this challenge, through the application of a neural word embedding (Word2vec) model on a dataset featuring speeches by heads of state or government in the United Nations General Debate. The paper provides three key contributions based on the output of the Word2vec model. First, it presents a set of policy attention indices, synthesizing the semantic proximity of political speeches to specific policy themes. Second, it introduces country-specific semantic centrality indices, based on topological analyses of countries' semantic positions with respect to each other. Third, it tests the hypothesis that there exists a statistical relation between the semantic content of political speeches and UN voting behavior, falsifying it and suggesting that political speeches contain information of different nature then the one behind voting outcomes. The paper concludes with a discussion of the practical use of its results and consequences for foreign policy analysis, public accountability, and transparency.
Complex Politics: A Quantitative Semantic and Topological Analysis of UK House of Commons Debates
Oct 13, 2015


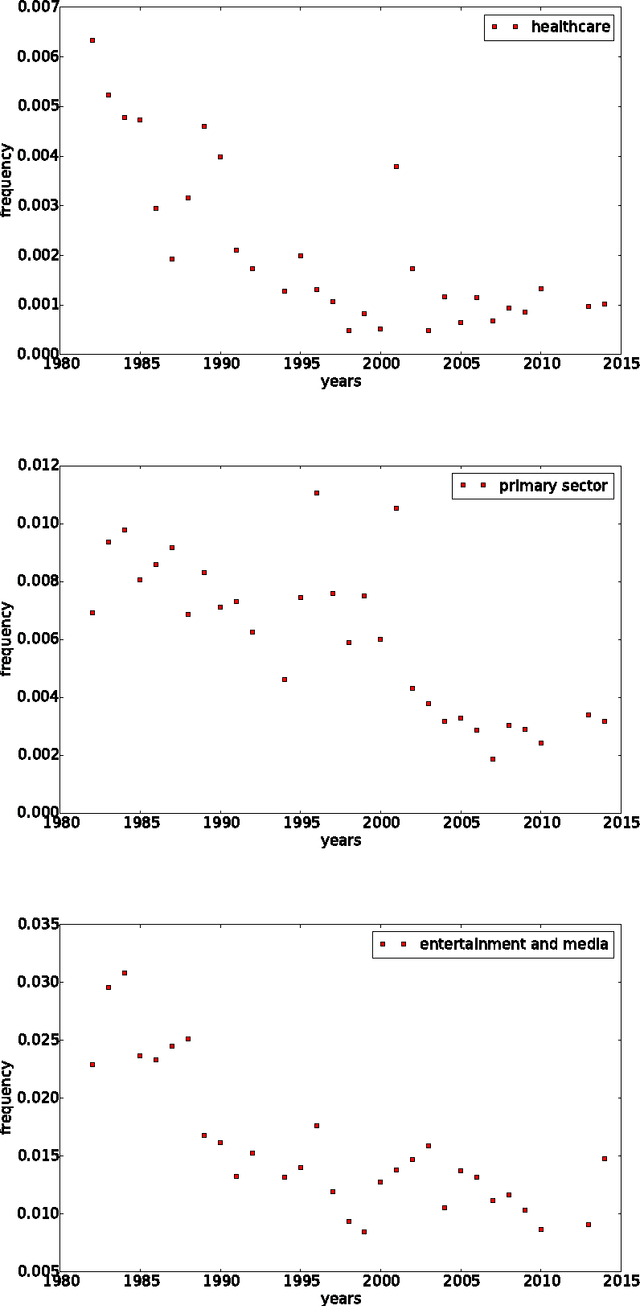
Abstract:This study is a first, exploratory attempt to use quantitative semantics techniques and topological analysis to analyze systemic patterns arising in a complex political system. In particular, we use a rich data set covering all speeches and debates in the UK House of Commons between 1975 and 2014. By the use of dynamic topic modeling (DTM) and topological data analysis (TDA) we show that both members and parties feature specific roles within the system, consistent over time, and extract global patterns indicating levels of political cohesion. Our results provide a wide array of novel hypotheses about the complex dynamics of political systems, with valuable policy applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge