Simone Ricci
Mitigating Negative Flips via Margin Preserving Training
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Minimizing inconsistencies across successive versions of an AI system is as crucial as reducing the overall error. In image classification, such inconsistencies manifest as negative flips, where an updated model misclassifies test samples that were previously classified correctly. This issue becomes increasingly pronounced as the number of training classes grows over time, since adding new categories reduces the margin of each class and may introduce conflicting patterns that undermine their learning process, thereby degrading performance on the original subset. To mitigate negative flips, we propose a novel approach that preserves the margins of the original model while learning an improved one. Our method encourages a larger relative margin between the previously learned and newly introduced classes by introducing an explicit margin-calibration term on the logits. However, overly constraining the logit margin for the new classes can significantly degrade their accuracy compared to a new independently trained model. To address this, we integrate a double-source focal distillation loss with the previous model and a new independently trained model, learning an appropriate decision margin from both old and new data, even under a logit margin calibration. Extensive experiments on image classification benchmarks demonstrate that our approach consistently reduces the negative flip rate with high overall accuracy.
Backward-Compatible Aligned Representations via an Orthogonal Transformation Layer
Aug 16, 2024
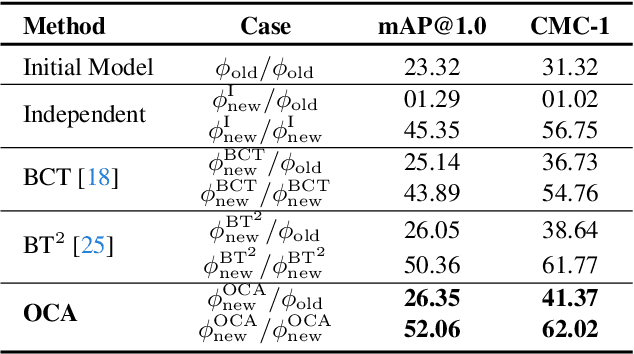

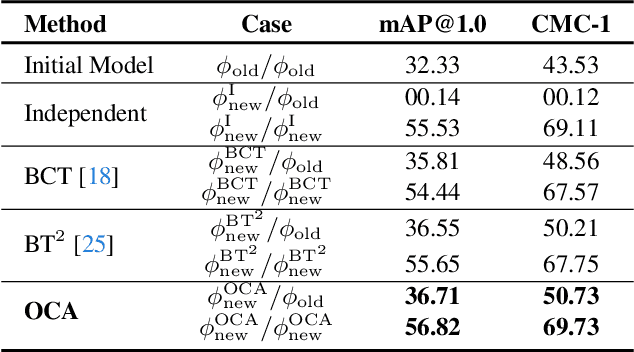
Abstract:Visual retrieval systems face significant challenges when updating models with improved representations due to misalignment between the old and new representations. The costly and resource-intensive backfilling process involves recalculating feature vectors for images in the gallery set whenever a new model is introduced. To address this, prior research has explored backward-compatible training methods that enable direct comparisons between new and old representations without backfilling. Despite these advancements, achieving a balance between backward compatibility and the performance of independently trained models remains an open problem. In this paper, we address it by expanding the representation space with additional dimensions and learning an orthogonal transformation to achieve compatibility with old models and, at the same time, integrate new information. This transformation preserves the original feature space's geometry, ensuring that our model aligns with previous versions while also learning new data. Our Orthogonal Compatible Aligned (OCA) approach eliminates the need for re-indexing during model updates and ensures that features can be compared directly across different model updates without additional mapping functions. Experimental results on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet-1k demonstrate that our method not only maintains compatibility with previous models but also achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, outperforming several existing methods.
Stationary Representations: Optimally Approximating Compatibility and Implications for Improved Model Replacements
May 04, 2024



Abstract:Learning compatible representations enables the interchangeable use of semantic features as models are updated over time. This is particularly relevant in search and retrieval systems where it is crucial to avoid reprocessing of the gallery images with the updated model. While recent research has shown promising empirical evidence, there is still a lack of comprehensive theoretical understanding about learning compatible representations. In this paper, we demonstrate that the stationary representations learned by the $d$-Simplex fixed classifier optimally approximate compatibility representation according to the two inequality constraints of its formal definition. This not only establishes a solid foundation for future works in this line of research but also presents implications that can be exploited in practical learning scenarios. An exemplary application is the now-standard practice of downloading and fine-tuning new pre-trained models. Specifically, we show the strengths and critical issues of stationary representations in the case in which a model undergoing sequential fine-tuning is asynchronously replaced by downloading a better-performing model pre-trained elsewhere. Such a representation enables seamless delivery of retrieval service (i.e., no reprocessing of gallery images) and offers improved performance without operational disruptions during model replacement. Code available at: https://github.com/miccunifi/iamcl2r.
Learning advisor networks for noisy image classification
Nov 08, 2022Abstract:In this paper, we introduced the novel concept of advisor network to address the problem of noisy labels in image classification. Deep neural networks (DNN) are prone to performance reduction and overfitting problems on training data with noisy annotations. Weighting loss methods aim to mitigate the influence of noisy labels during the training, completely removing their contribution. This discarding process prevents DNNs from learning wrong associations between images and their correct labels but reduces the amount of data used, especially when most of the samples have noisy labels. Differently, our method weighs the feature extracted directly from the classifier without altering the loss value of each data. The advisor helps to focus only on some part of the information present in mislabeled examples, allowing the classifier to leverage that data as well. We trained it with a meta-learning strategy so that it can adapt throughout the training of the main model. We tested our method on CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 with synthetic noise, and on Clothing1M which contains real-world noise, reporting state-of-the-art results.
* Paper published as Poster at ICIAP21
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge