Simon Thibault
The Differentiable Lens: Compound Lens Search over Glass Surfaces and Materials for Object Detection
Dec 08, 2022Abstract:Most camera lens systems are designed in isolation, separately from downstream computer vision methods. Recently, joint optimization approaches that design lenses alongside other components of the image acquisition and processing pipeline -- notably, downstream neural networks -- have achieved improved imaging quality or better performance on vision tasks. However, these existing methods optimize only a subset of lens parameters and cannot optimize glass materials given their categorical nature. In this work, we develop a differentiable spherical lens simulation model that accurately captures geometrical aberrations. We propose an optimization strategy to address the challenges of lens design -- notorious for non-convex loss function landscapes and many manufacturing constraints -- that are exacerbated in joint optimization tasks. Specifically, we introduce quantized continuous glass variables to facilitate the optimization and selection of glass materials in an end-to-end design context, and couple this with carefully designed constraints to support manufacturability. In automotive object detection, we show improved detection performance over existing designs even when simplifying designs to two- or three-element lenses, despite significantly degrading the image quality. Code and optical designs will be made publicly available.
The Surprising Creativity of Digital Evolution: A Collection of Anecdotes from the Evolutionary Computation and Artificial Life Research Communities
Aug 14, 2018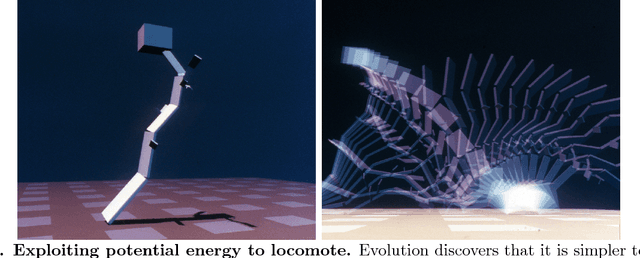
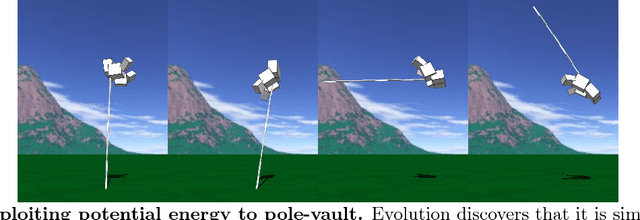
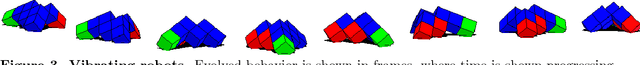

Abstract:Biological evolution provides a creative fount of complex and subtle adaptations, often surprising the scientists who discover them. However, because evolution is an algorithmic process that transcends the substrate in which it occurs, evolution's creativity is not limited to nature. Indeed, many researchers in the field of digital evolution have observed their evolving algorithms and organisms subverting their intentions, exposing unrecognized bugs in their code, producing unexpected adaptations, or exhibiting outcomes uncannily convergent with ones in nature. Such stories routinely reveal creativity by evolution in these digital worlds, but they rarely fit into the standard scientific narrative. Instead they are often treated as mere obstacles to be overcome, rather than results that warrant study in their own right. The stories themselves are traded among researchers through oral tradition, but that mode of information transmission is inefficient and prone to error and outright loss. Moreover, the fact that these stories tend to be shared only among practitioners means that many natural scientists do not realize how interesting and lifelike digital organisms are and how natural their evolution can be. To our knowledge, no collection of such anecdotes has been published before. This paper is the crowd-sourced product of researchers in the fields of artificial life and evolutionary computation who have provided first-hand accounts of such cases. It thus serves as a written, fact-checked collection of scientifically important and even entertaining stories. In doing so we also present here substantial evidence that the existence and importance of evolutionary surprises extends beyond the natural world, and may indeed be a universal property of all complex evolving systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge