Simeon Bamford
An Event-Based Opto-Tactile Skin
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:This paper presents a neuromorphic, event-driven tactile sensing system for soft, large-area skin, based on the Dynamic Vision Sensors (DVS) integrated with a flexible silicone optical waveguide skin. Instead of repetitively scanning embedded photoreceivers, this design uses a stereo vision setup comprising two DVS cameras looking sideways through the skin. Such a design produces events as changes in brightness are detected, and estimates press positions on the 2D skin surface through triangulation, utilizing Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (DBSCAN) to find the center of mass of contact events resulting from pressing actions. The system is evaluated over a 4620 mm2 probed area of the skin using a meander raster scan. Across 95 % of the presses visible to both cameras, the press localization achieved a Root-Mean-Squared Error (RMSE) of 4.66 mm. The results highlight the potential of this approach for wide-area flexible and responsive tactile sensors in soft robotics and interactive environments. Moreover, we examined how the system performs when the amount of event data is strongly reduced. Using stochastic down-sampling, the event stream was reduced to 1/1024 of its original size. Under this extreme reduction, the average localization error increased only slightly (from 4.66 mm to 9.33 mm), and the system still produced valid press localizations for 85 % of the trials. This reduction in pass rate is expected, as some presses no longer produce enough events to form a reliable cluster for triangulation. These results show that the sensing approach remains functional even with very sparse event data, which is promising for reducing power consumption and computational load in future implementations. The system exhibits a detection latency distribution with a characteristic width of 31 ms.
luvHarris: A Practical Corner Detector for Event-cameras
May 24, 2021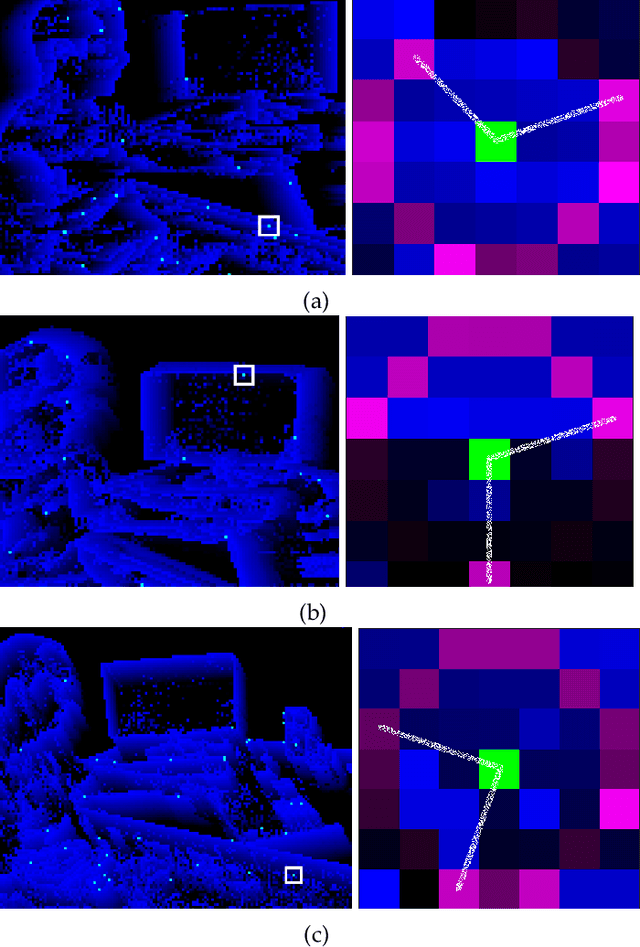
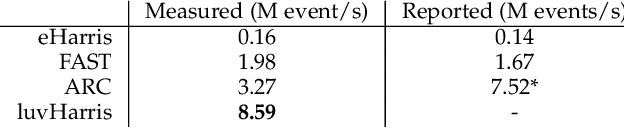
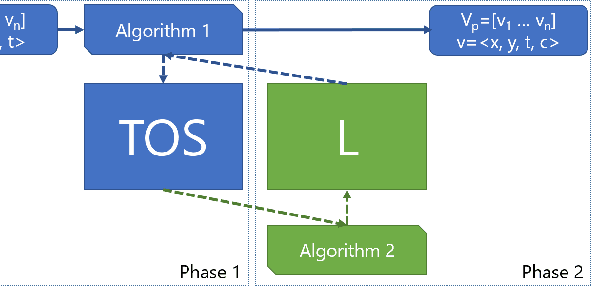

Abstract:There have been a number of corner detection methods proposed for event cameras in the last years, since event-driven computer vision has become more accessible. Current state-of-the-art have either unsatisfactory accuracy or real-time performance when considered for practical use; random motion using a live camera in an unconstrained environment. In this paper, we present yet another method to perform corner detection, dubbed look-up event-Harris (luvHarris), that employs the Harris algorithm for high accuracy but manages an improved event throughput. Our method has two major contributions, 1. a novel "threshold ordinal event-surface" that removes certain tuning parameters and is well suited for Harris operations, and 2. an implementation of the Harris algorithm such that the computational load per-event is minimised and computational heavy convolutions are performed only 'as-fast-as-possible', i.e. only as computational resources are available. The result is a practical, real-time, and robust corner detector that runs more than $2.6\times$ the speed of current state-of-the-art; a necessity when using high-resolution event-camera in real-time. We explain the considerations taken for the approach, compare the algorithm to current state-of-the-art in terms of computational performance and detection accuracy, and discuss the validity of the proposed approach for event cameras.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge