Siddhartha Bhattacharyya
Few-Shot Classification and Anatomical Localization of Tissues in SPECT Imaging
Feb 10, 2025

Abstract:Accurate classification and anatomical localization are essential for effective medical diagnostics and research, which may be efficiently performed using deep learning techniques. However, availability of limited labeled data poses a significant challenge. To address this, we adapted Prototypical Networks and the Propagation-Reconstruction Network (PRNet) for few-shot classification and localization, respectively, in Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) images. For the proof of concept we used a 2D-sliced image cropped around heart. The Prototypical Network, with a pre-trained ResNet-18 backbone, classified ventricles, myocardium, and liver tissues with 96.67% training and 93.33% validation accuracy. PRNet, adapted for 2D imaging with an encoder-decoder architecture and skip connections, achieved a training loss of 1.395, accurately reconstructing patches and capturing spatial relationships. These results highlight the potential of Prototypical Networks for tissue classification with limited labeled data and PRNet for anatomical landmark localization, paving the way for improved performance in deep learning frameworks.
Runway vs. Taxiway: Challenges in Automated Line Identification and Notation Approaches
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:The increasing complexity of autonomous systems has amplified the need for accurate and reliable labeling of runway and taxiway markings to ensure operational safety. Precise detection and labeling of these markings are critical for tasks such as navigation, landing assistance, and ground control automation. Existing labeling algorithms, like the Automated Line Identification and Notation Algorithm (ALINA), have demonstrated success in identifying taxiway markings but encounter significant challenges when applied to runway markings. This limitation arises due to notable differences in line characteristics, environmental context, and interference from elements such as shadows, tire marks, and varying surface conditions. To address these challenges, we modified ALINA by adjusting color thresholds and refining region of interest (ROI) selection to better suit runway-specific contexts. While these modifications yielded limited improvements, the algorithm still struggled with consistent runway identification, often mislabeling elements such as the horizon or non-relevant background features. This highlighted the need for a more robust solution capable of adapting to diverse visual interferences. In this paper, we propose integrating a classification step using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) named AssistNet. By incorporating this classification step, the detection pipeline becomes more resilient to environmental variations and misclassifications. This work not only identifies the challenges but also outlines solutions, paving the way for improved automated labeling techniques essential for autonomous aviation systems.
Exploring Machine Learning Engineering for Object Detection and Tracking by Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV)
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:With the advancement of deep learning methods it is imperative that autonomous systems will increasingly become intelligent with the inclusion of advanced machine learning algorithms to execute a variety of autonomous operations. One such task involves the design and evaluation for a subsystem of the perception system for object detection and tracking. The challenge in the creation of software to solve the task is in discovering the need for a dataset, annotation of the dataset, selection of features, integration and refinement of existing algorithms, while evaluating performance metrics through training and testing. This research effort focuses on the development of a machine learning pipeline emphasizing the inclusion of assurance methods with increasing automation. In the process, a new dataset was created by collecting videos of moving object such as Roomba vacuum cleaner, emulating search and rescue (SAR) for indoor environment. Individual frames were extracted from the videos and labeled using a combination of manual and automated techniques. This annotated dataset was refined for accuracy by initially training it on YOLOv4. After the refinement of the dataset it was trained on a second YOLOv4 and a Mask R-CNN model, which is deployed on a Parrot Mambo drone to perform real-time object detection and tracking. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the models in accurately detecting and tracking the Roomba across multiple trials, achieving an average loss of 0.1942 and 96% accuracy.
AssistTaxi: A Comprehensive Dataset for Taxiway Analysis and Autonomous Operations
Sep 10, 2024Abstract:The availability of high-quality datasets play a crucial role in advancing research and development especially, for safety critical and autonomous systems. In this paper, we present AssistTaxi, a comprehensive novel dataset which is a collection of images for runway and taxiway analysis. The dataset comprises of more than 300,000 frames of diverse and carefully collected data, gathered from Melbourne (MLB) and Grant-Valkaria (X59) general aviation airports. The importance of AssistTaxi lies in its potential to advance autonomous operations, enabling researchers and developers to train and evaluate algorithms for efficient and safe taxiing. Researchers can utilize AssistTaxi to benchmark their algorithms, assess performance, and explore novel approaches for runway and taxiway analysis. Addition-ally, the dataset serves as a valuable resource for validating and enhancing existing algorithms, facilitating innovation in autonomous operations for aviation. We also propose an initial approach to label the dataset using a contour based detection and line extraction technique.
ALINA: Advanced Line Identification and Notation Algorithm
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Labels are the cornerstone of supervised machine learning algorithms. Most visual recognition methods are fully supervised, using bounding boxes or pixel-wise segmentations for object localization. Traditional labeling methods, such as crowd-sourcing, are prohibitive due to cost, data privacy, amount of time, and potential errors on large datasets. To address these issues, we propose a novel annotation framework, Advanced Line Identification and Notation Algorithm (ALINA), which can be used for labeling taxiway datasets that consist of different camera perspectives and variable weather attributes (sunny and cloudy). Additionally, the CIRCular threshoLd pixEl Discovery And Traversal (CIRCLEDAT) algorithm has been proposed, which is an integral step in determining the pixels corresponding to taxiway line markings. Once the pixels are identified, ALINA generates corresponding pixel coordinate annotations on the frame. Using this approach, 60,249 frames from the taxiway dataset, AssistTaxi have been labeled. To evaluate the performance, a context-based edge map (CBEM) set was generated manually based on edge features and connectivity. The detection rate after testing the annotated labels with the CBEM set was recorded as 98.45%, attesting its dependability and effectiveness.
Conceptualizing Suicidal Behavior: Utilizing Explanations of Predicted Outcomes to Analyze Longitudinal Social Media Data
Dec 30, 2023



Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has escalated mental health crises worldwide, with social isolation and economic instability contributing to a rise in suicidal behavior. Suicide can result from social factors such as shame, abuse, abandonment, and mental health conditions like depression, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, and bipolar disorders. As these conditions develop, signs of suicidal ideation may manifest in social media interactions. Analyzing social media data using artificial intelligence (AI) techniques can help identify patterns of suicidal behavior, providing invaluable insights for suicide prevention agencies, professionals, and broader community awareness initiatives. Machine learning algorithms for this purpose require large volumes of accurately labeled data. Previous research has not fully explored the potential of incorporating explanations in analyzing and labeling longitudinal social media data. In this study, we employed a model explanation method, Layer Integrated Gradients, on top of a fine-tuned state-of-the-art language model, to assign each token from Reddit users' posts an attribution score for predicting suicidal ideation. By extracting and analyzing attributions of tokens from the data, we propose a methodology for preliminary screening of social media posts for suicidal ideation without using large language models during inference.
DQNAS: Neural Architecture Search using Reinforcement Learning
Jan 17, 2023



Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks have been used in a variety of image related applications after their rise in popularity due to ImageNet competition. Convolutional Neural Networks have shown remarkable results in applications including face recognition, moving target detection and tracking, classification of food based on the calorie content and many more. Designing of Convolutional Neural Networks requires experts having a cross domain knowledge and it is laborious, which requires a lot of time for testing different values for different hyperparameter along with the consideration of different configurations of existing architectures. Neural Architecture Search is an automated way of generating Neural Network architectures which saves researchers from all the brute-force testing trouble, but with the drawback of consuming a lot of computational resources for a prolonged period. In this paper, we propose an automated Neural Architecture Search framework DQNAS, guided by the principles of Reinforcement Learning along with One-shot Training which aims to generate neural network architectures that show superior performance and have minimum scalability problem.
Qutrit-inspired Fully Self-supervised Shallow Quantum Learning Network for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Sep 14, 2020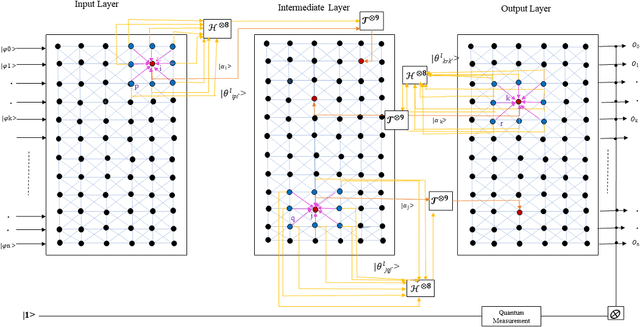

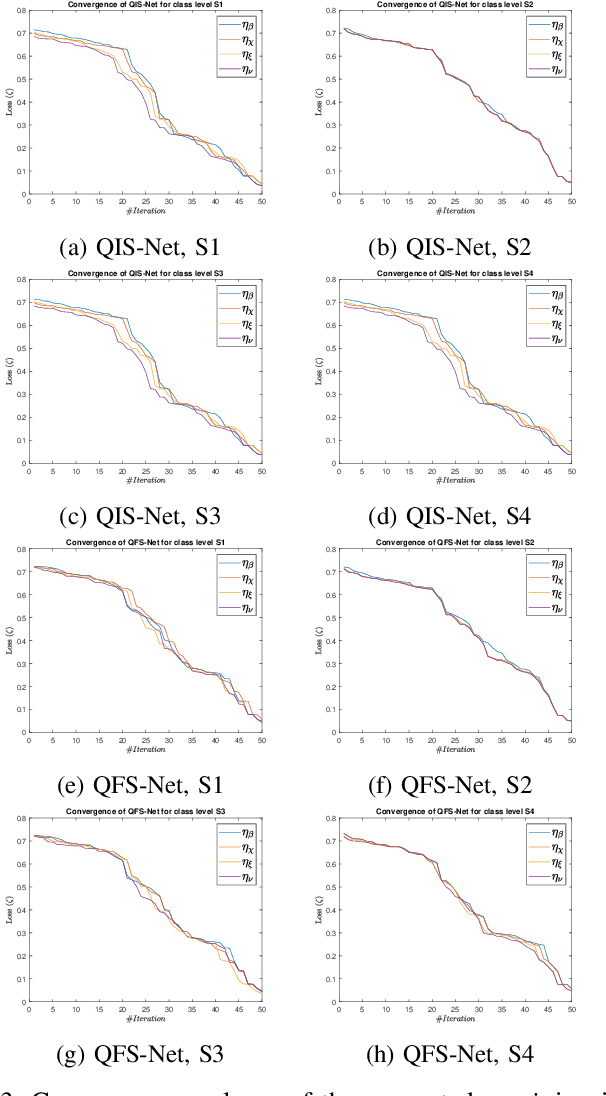

Abstract:Classical self-supervised networks suffer from convergence problems and reduced segmentation accuracy due to forceful termination. Qubits or bi-level quantum bits often describe quantum neural network models. In this article, a novel self-supervised shallow learning network model exploiting the sophisticated three-level qutrit-inspired quantum information system referred to as Quantum Fully Self-Supervised Neural Network (QFS-Net) is presented for automated segmentation of brain MR images. The QFS-Net model comprises a trinity of a layered structure of qutrits inter-connected through parametric Hadamard gates using an 8-connected second-order neighborhood-based topology. The non-linear transformation of the qutrit states allows the underlying quantum neural network model to encode the quantum states, thereby enabling a faster self-organized counter-propagation of these states between the layers without supervision. The suggested QFS-Net model is tailored and extensively validated on Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA) data set collected from Nature repository and also compared with state of the art supervised (U-Net and URes-Net architectures) and the self-supervised QIS-Net model. Results shed promising segmented outcome in detecting tumors in terms of dice similarity and accuracy with minimum human intervention and computational resources.
Comparative study of variational quantum circuit and quantum backpropagation multilayer perceptron for COVID-19 outbreak predictions
Aug 19, 2020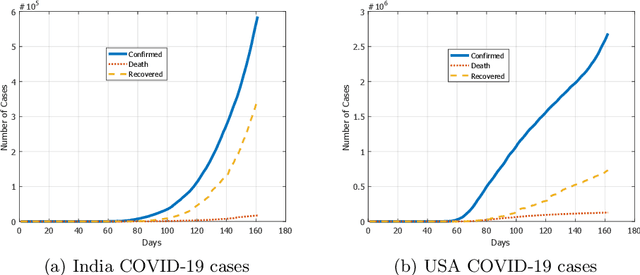

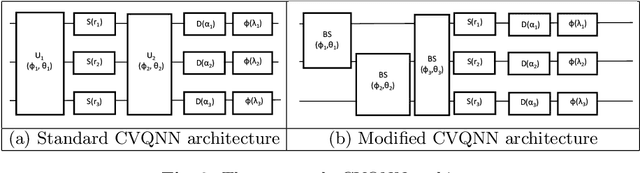
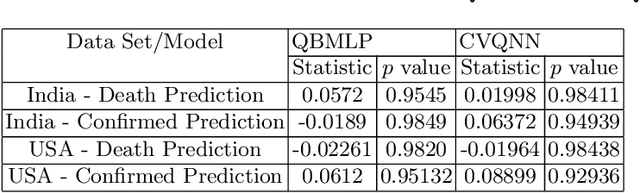
Abstract:There are numerous models of quantum neural networks that have been applied to variegated problems such as image classification, pattern recognition etc.Quantum inspired algorithms have been relevant for quite awhile. More recently, in the NISQ era, hybrid quantum classical models have shown promising results. Multi-feature regression is common problem in classical machine learning. Hence we present a comparative analysis of continuous variable quantum neural networks (Variational circuits) and quantum backpropagating multi layer perceptron (QBMLP). We have chosen the contemporary problem of predicting rise in COVID-19 cases in India and USA. We provide a statistical comparison between two models , both of which perform better than the classical artificial neural networks.
Gray Image extraction using Fuzzy Logic
Jun 20, 2012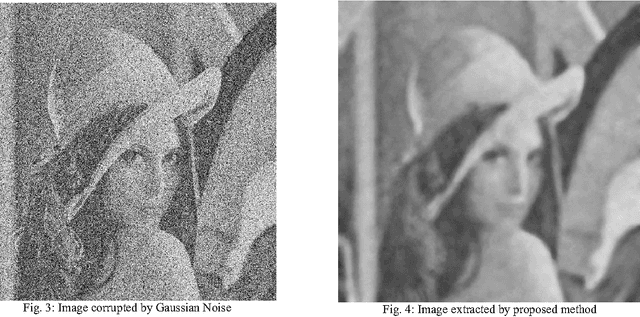
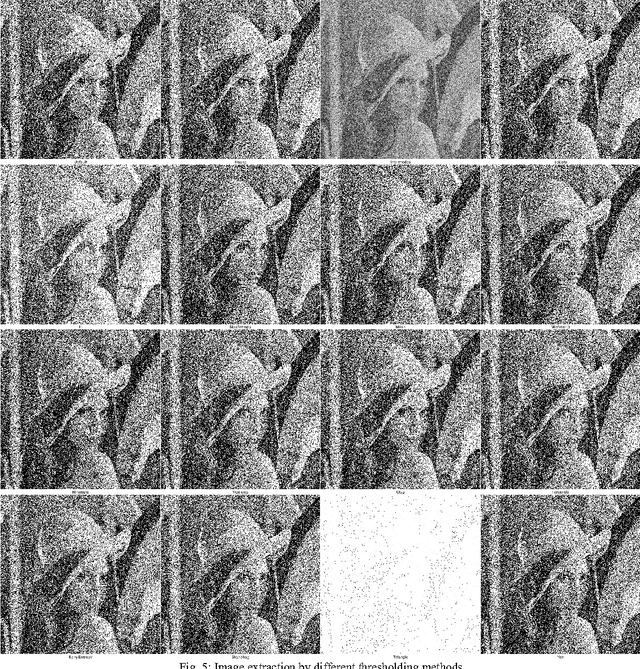

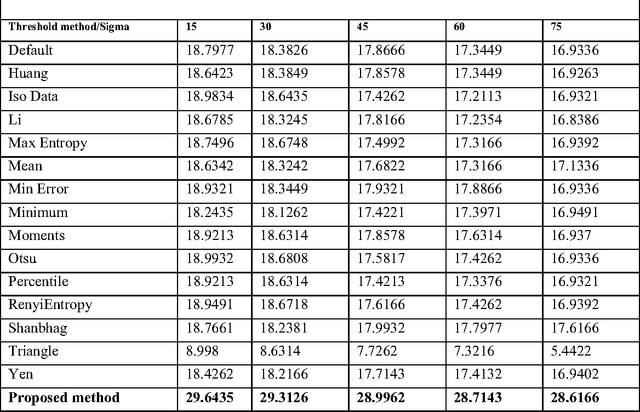
Abstract:Fuzzy systems concern fundamental methodology to represent and process uncertainty and imprecision in the linguistic information. The fuzzy systems that use fuzzy rules to represent the domain knowledge of the problem are known as Fuzzy Rule Base Systems (FRBS). On the other hand image segmentation and subsequent extraction from a noise-affected background, with the help of various soft computing methods, are relatively new and quite popular due to various reasons. These methods include various Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models (primarily supervised in nature), Genetic Algorithm (GA) based techniques, intensity histogram based methods etc. providing an extraction solution working in unsupervised mode happens to be even more interesting problem. Literature suggests that effort in this respect appears to be quite rudimentary. In the present article, we propose a fuzzy rule guided novel technique that is functional devoid of any external intervention during execution. Experimental results suggest that this approach is an efficient one in comparison to different other techniques extensively addressed in literature. In order to justify the supremacy of performance of our proposed technique in respect of its competitors, we take recourse to effective metrics like Mean Squared Error (MSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Peak Signal to Noise Ratio (PSNR).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge