Siddharth Kumar
Two Stage Transformer Model for COVID-19 Fake News Detection and Fact Checking
Nov 26, 2020



Abstract:The rapid advancement of technology in online communication via social media platforms has led to a prolific rise in the spread of misinformation and fake news. Fake news is especially rampant in the current COVID-19 pandemic, leading to people believing in false and potentially harmful claims and stories. Detecting fake news quickly can alleviate the spread of panic, chaos and potential health hazards. We developed a two stage automated pipeline for COVID-19 fake news detection using state of the art machine learning models for natural language processing. The first model leverages a novel fact checking algorithm that retrieves the most relevant facts concerning user claims about particular COVID-19 claims. The second model verifies the level of truth in the claim by computing the textual entailment between the claim and the true facts retrieved from a manually curated COVID-19 dataset. The dataset is based on a publicly available knowledge source consisting of more than 5000 COVID-19 false claims and verified explanations, a subset of which was internally annotated and cross-validated to train and evaluate our models. We evaluate a series of models based on classical text-based features to more contextual Transformer based models and observe that a model pipeline based on BERT and ALBERT for the two stages respectively yields the best results.
Multi-level Attention network using text, audio and video for Depression Prediction
Sep 03, 2019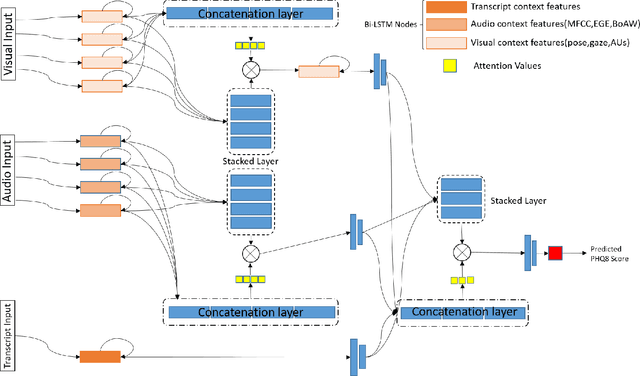
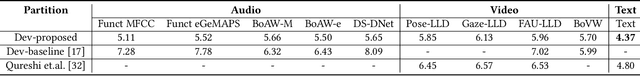

Abstract:Depression has been the leading cause of mental-health illness worldwide. Major depressive disorder (MDD), is a common mental health disorder that affects both psychologically as well as physically which could lead to loss of lives. Due to the lack of diagnostic tests and subjectivity involved in detecting depression, there is a growing interest in using behavioural cues to automate depression diagnosis and stage prediction. The absence of labelled behavioural datasets for such problems and the huge amount of variations possible in behaviour makes the problem more challenging. This paper presents a novel multi-level attention based network for multi-modal depression prediction that fuses features from audio, video and text modalities while learning the intra and inter modality relevance. The multi-level attention reinforces overall learning by selecting the most influential features within each modality for the decision making. We perform exhaustive experimentation to create different regression models for audio, video and text modalities. Several fusions models with different configurations are constructed to understand the impact of each feature and modality. We outperform the current baseline by 17.52% in terms of root mean squared error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge